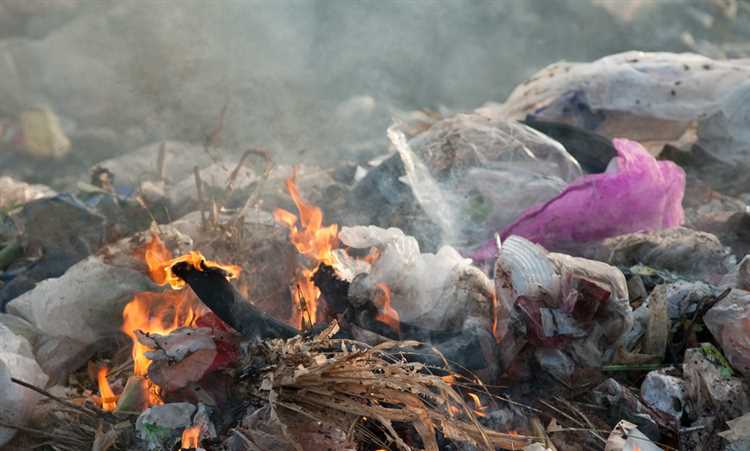

Plastic pollution is a global environmental crisis that requires urgent attention. As the world is producing more and more plastic waste every year, finding sustainable solutions to deal with this issue has become paramount. While some may argue that burning plastic could be a viable solution, it is important to understand that this method is far from sustainable and only exacerbates the problem.
First and foremost, burning plastic releases harmful toxins into the atmosphere. When plastic is burned, it generates toxic gases and particulate matter that contribute to air pollution. These pollutants not only harm the environment but also pose serious health risks to humans and wildlife. Inhaling these toxic fumes can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and even certain types of cancer.
Furthermore, burning plastic contributes to climate change. Plastic is made from fossil fuels, and when it is burned, it releases carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming. With the increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the earth’s temperature is rising, leading to devastating consequences such as extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and loss of biodiversity.
Lastly, burning plastic is a wasteful method of disposal. Instead of using the valuable resources contained in plastic, we are simply getting rid of them in a way that harms the environment. Plastic is a versatile material that can be recycled and reused, reducing the need for virgin materials and saving energy. By burning plastic, we are squandering this opportunity to create a circular economy and promote sustainable practices.
It is vital that we shift our focus towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions to tackle the plastic pollution crisis. Recycling, reducing plastic consumption, and promoting the use of biodegradable alternatives are just a few examples of the steps we can take. Burning plastic might seem like a quick fix, but it is clear that it is not a sustainable solution. It is time for us to rethink our approach and find innovative ways to address this pressing issue.
- The Environmental Impact of Burning Plastic Waste
- 1. Air Pollution
- 2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Harmful Emissions
- Air Pollution and Respiratory Health Risks
- Impact on Children
- Effects on Outdoor and Indoor Air Quality
- Contamination of Soil and Water
- Threats to Wildlife and Marine Life
- 1. Habitat Destruction
- 2. Ingestion and Entanglement
- Long-Term Effects on Climate Change
- Alternatives to Burning Plastic Waste
- Q&A
- Why is burning plastic not a sustainable solution?
- What are the environmental consequences of burning plastic?
- Is there a sustainable alternative to burning plastic?
- What are the long-term effects of burning plastic?
- Can burning plastic be considered a temporary solution?
- Is burning plastic a sustainable solution?
The Environmental Impact of Burning Plastic Waste

Burning plastic waste may seem like a convenient solution for getting rid of this often non-biodegradable material. However, the environmental impact of this practice is far from sustainable. Let’s explore some of the major reasons why burning plastic is harmful to our planet.
1. Air Pollution
When plastic is burned, it releases a variety of toxic pollutants into the air. This includes substances such as dioxins, furans, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). These pollutants are known to have severe health effects on both humans and animals. Inhalation of these toxic fumes can lead to respiratory problems, reproductive issues, and even cancer.
2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Plastic is primarily made from fossil fuels, such as oil and natural gas. When plastic is burned, it releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases contribute to global warming and climate change, exacerbating the already alarming environmental crisis we face.
| Environmental Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Contamination | Ash from burning plastic can contaminate soil, making it unfit for agriculture and harming ecosystems. |
| Water Pollution | Toxic chemicals released during burning can seep into water sources, polluting rivers, lakes, and oceans. |
| Wildlife Harm | Plastic waste burning can harm wildlife through air pollution, ingestion of toxic substances, and habitat destruction. |
It is evident that burning plastic waste is not a sustainable solution. To safeguard our planet and future generations, we must explore alternative methods of waste management that prioritize recycling, reducing plastic consumption, and promoting a circular economy.
Harmful Emissions
When plastic is burned, it produces harmful emissions that are extremely detrimental to both human health and the environment. The combustion of plastic releases toxic chemicals such as dioxins, furans, and heavy metals into the air.
Dioxins and furans are highly toxic and can cause a range of health problems including cancer, reproductive and developmental disorders, immune system damage, and hormonal imbalances. These chemicals are known to persist in the environment and can accumulate in the food chain, posing a risk to both animals and humans.
In addition to dioxins and furans, burning plastic also releases heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury. These metals can contaminate soil and water, damaging ecosystems and posing a threat to both wildlife and human health.
The burning of plastic also contributes to air pollution. The emissions released during the combustion process contain harmful particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and greenhouse gases. These pollutants can contribute to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and climate change.
It is important to note that even when plastic is burned in controlled incinerators, which are designed to minimize emissions, harmful chemicals and pollutants can still be released into the air. The only way to truly eliminate the harmful emissions associated with burning plastic is to reduce plastic consumption and implement sustainable recycling and waste management practices.
Conclusion: Burning plastic is not a sustainable solution due to the harmful emissions it produces. The health risks it poses to humans and the environment, as well as its contribution to air pollution and climate change, make it an unsustainable and detrimental practice. It is crucial to shift towards more sustainable alternatives and practices to mitigate the negative impacts of plastic waste.
Air Pollution and Respiratory Health Risks
Air pollution caused by burning plastic is a major contributor to respiratory health risks. When plastic is burned, it releases toxic chemicals and pollutants into the air, such as dioxins, furans, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants can be inhaled and have detrimental effects on the respiratory system.
Exposure to air pollution from burning plastic can lead to a variety of respiratory health issues. Respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath can occur, especially in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Long-term exposure to these pollutants can also increase the risk of developing respiratory infections, bronchitis, and even lung cancer.
Impact on Children

Children are particularly vulnerable to the respiratory health risks associated with air pollution from burning plastic. Their lungs are still developing, and they tend to breathe in more air relative to their body weight compared to adults. This means that they can inhale a higher concentration of pollutants, increasing their susceptibility to respiratory issues.
Exposure to air pollution in early childhood has been linked to long-term respiratory problems. It can impair lung development, leading to reduced lung function and an increased risk of developing respiratory illnesses later in life. Additionally, children exposed to air pollution may experience more frequent respiratory infections and have a higher likelihood of developing asthma.
Effects on Outdoor and Indoor Air Quality
Burning plastic not only contributes to outdoor air pollution but can also impact indoor air quality. When plastic is burned indoors, such as in trash incinerators or poorly ventilated areas, it releases pollutants that can accumulate and linger in the air. This can result in indoor air pollution, which can have similar adverse effects on respiratory health as outdoor air pollution.
Indoor air pollution from burning plastic can be especially concerning as people spend a significant amount of time indoors, particularly in their homes. It is important to ensure proper ventilation and avoid burning plastic or other materials indoors to minimize exposure to harmful pollutants.
In conclusion, air pollution caused by burning plastic poses significant respiratory health risks. The release of toxic chemicals and pollutants can lead to various respiratory issues, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children. It is crucial to find sustainable alternatives to burning plastic to protect our respiratory health and the environment.
Contamination of Soil and Water
Burning plastic is a harmful practice that can lead to significant contamination of soil and water. When plastic is incinerated, it releases toxic chemicals and pollutants into the environment, posing serious threats to both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
The combustion process of plastic produces various pollutants, including dioxins, furans, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). These substances are persistent organic pollutants that can accumulate in the environment and have detrimental effects on human health and wildlife. Dioxins, for example, are highly toxic and can cause reproductive and developmental problems, as well as damage the immune system.
When the toxic emissions from burning plastic settle on the ground, they can contaminate the soil. This contamination can have long-lasting effects on the fertility and health of the soil, making it unsuitable for agriculture and plant growth. The chemicals released from burning plastic can disrupt soil microbial communities and inhibit essential biological processes, leading to a loss of biodiversity and overall ecosystem degradation.
In addition to soil contamination, the toxic pollutants released during plastic incineration can also contaminate water sources. If the ash and airborne particles containing toxic chemicals are not properly managed and disposed of, they can find their way into nearby rivers, lakes, and groundwater. This contamination can have severe consequences for aquatic ecosystems, affecting the health and survival of fish, plants, and other aquatic organisms. It can also contaminate drinking water sources, endangering human health.
Controlling the pollution caused by burning plastic is essential for the preservation of soil and water quality. Implementing sustainable waste management practices, such as recycling and reducing the use of single-use plastics, can significantly reduce the amount of plastic waste that ends up in incinerators. By adopting a circular economy approach and promoting the use of alternative materials, we can minimize the negative impacts of plastic pollution on the environment and create a more sustainable future.
| Effects of Burning Plastic on Soil and Water |
|---|
| Contaminates soil with toxic chemicals |
| Disrupts soil microbial communities |
| Inhibits essential biological processes |
| Reduces soil fertility and health |
| Endangers aquatic ecosystems |
| Threatens human health and wildlife |
Threats to Wildlife and Marine Life
Burning plastic is not a sustainable solution for waste management, as it poses significant threats to wildlife and marine life.
1. Habitat Destruction
When plastic is burned, it releases toxic chemicals into the environment, contributing to habitat destruction. Wildlife and marine life depend on their natural habitats for survival, and the destruction of these habitats can have dire consequences for their populations. Plastic waste burning can lead to the degradation and contamination of ecosystems, making it difficult for animals and plants to thrive.
2. Ingestion and Entanglement
Plastic waste, when not properly disposed of or burned, ends up in natural environments such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. Marine animals and birds often mistake plastic waste for food, ingesting it and suffering from digestive system blockages and internal injuries. Additionally, plastic waste can entangle wildlife, causing them physical harm and even death. Burning plastic increases the likelihood of plastic debris ending up in bodies of water, exacerbating these threats to wildlife and marine life.
It is important to note that burning plastic not only affects larger marine animals and birds but also poses a threat to microscopic organisms that form the basis of the marine food chain. The toxic chemicals released during burning can accumulate in these organisms, leading to the bioaccumulation of pollutants throughout the food chain. This bioaccumulation can have far-reaching impacts on the overall health and viability of marine ecosystems.
In conclusion, burning plastic as a waste management solution not only contributes to air pollution and climate change but also poses significant threats to wildlife and marine life. The harmful effects on habitats, ingestion and entanglement risks, and the potential for toxin accumulation in the food chain all underline the importance of finding sustainable and environmentally-friendly alternatives.
Long-Term Effects on Climate Change

Burning plastic is a major contributor to climate change, with long-term effects that cannot be ignored. When plastic is burned, it releases harmful greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. These gases contribute to the greenhouse effect and trap heat, leading to global warming.
Global warming, in turn, has numerous negative consequences for our planet. Rising temperatures lead to the melting of ice caps and glaciers, causing sea levels to rise. This results in coastal flooding and erosion, endangering human settlements and wildlife habitats.
In addition to rising sea levels, global warming also disrupts weather patterns. It leads to more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, and storms, which have devastating effects on agriculture, water resources, and ecosystems. The increased occurrence of extreme weather events puts vulnerable populations at higher risk and exacerbates food and water shortages.
Furthermore, burning plastic contributes to air pollution, which has a detrimental impact on human health. The release of toxic pollutants and particulate matter from burning plastic can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. The long-term exposure to air pollution has been associated with reduced lung function, premature death, and lower life expectancy.
It is crucial to find sustainable alternatives to burning plastic and combat climate change to ensure a livable future for future generations. This includes reducing plastic consumption, promoting recycling and waste management practices, and investing in renewable energy sources. By taking these steps, we can mitigate the long-term effects of climate change and create a more sustainable and healthy environment for all.
Alternatives to Burning Plastic Waste
The problem of plastic waste has become a global crisis, but burning it is not a sustainable solution. Fortunately, there are alternatives that can effectively manage and reduce plastic waste without harming the environment.
1. Recycling: One of the most effective alternatives to burning plastic waste is recycling. By separating different types of plastic, they can be processed and reused in the manufacturing of new products. This reduces the need for new plastic production and helps to conserve resources.
2. Composting: Another option is to compost certain types of biodegradable plastics. These plastics can be broken down by microorganisms into organic matter, which can then be used to improve soil quality. Composting not only reduces plastic waste but also helps to promote sustainable agriculture.
3. Waste-to-Energy Plants: Instead of burning plastics in an uncontrolled and polluting way, waste-to-energy plants can be used. These facilities use advanced technologies to convert plastic waste into energy, such as electricity or heat. This reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and provides a sustainable energy source.
4. Circular Economy: Implementing a circular economy approach is crucial for managing plastic waste sustainably. This involves designing products with recycling and reuse in mind, as well as establishing effective collection and sorting systems. By closing the loop, plastic waste can be minimized and resources can be conserved.
5. Plastic Alternatives: Finally, exploring and promoting alternatives to plastic can greatly reduce the need for waste management. Biodegradable materials, such as plant-based plastics, can be used as substitutes for single-use plastic items. Encouraging the use of reusable products, such as cloth bags and stainless steel water bottles, also helps to decrease plastic waste.
In conclusion, it is clear that there are viable alternatives to burning plastic waste. By implementing recycling, composting, waste-to-energy plants, circular economy practices, and promoting plastic alternatives, we can effectively manage plastic waste and work towards a more sustainable future.
Q&A
Why is burning plastic not a sustainable solution?
Burning plastic releases toxic chemicals into the air and contributes to air pollution. It also emits greenhouse gases, which contribute to climate change. Moreover, burning plastic does not solve the problem of plastic waste, as it only converts it into another form of pollution.
What are the environmental consequences of burning plastic?
Burning plastic has several environmental consequences. Firstly, it releases harmful chemicals into the air, such as dioxins and furans, which are toxic and can cause respiratory problems. Secondly, it contributes to air pollution and smog formation. Finally, the greenhouse gas emissions from burning plastic contribute to climate change.
Is there a sustainable alternative to burning plastic?
Yes, there are several sustainable alternatives to burning plastic. One of them is recycling, which involves transforming plastic waste into new products. Another alternative is reducing the consumption of plastic by using eco-friendly alternatives like cloth bags or metal bottles. Additionally, investing in research and development of biodegradable plastics can also be a sustainable solution.
What are the long-term effects of burning plastic?
The long-term effects of burning plastic can be devastating. The toxic chemicals released during the burning process can contaminate soil and water sources, harming ecosystems and wildlife. The greenhouse gases emitted can contribute to long-term climate change, affecting weather patterns and increasing the frequency of natural disasters. It is important to find sustainable solutions to plastic waste in order to avoid these long-term effects.
Can burning plastic be considered a temporary solution?
Burning plastic cannot be considered a temporary solution. While it may reduce the visible amount of plastic waste, it creates other forms of pollution and contributes to long-term environmental damage. Moreover, burning plastic does not address the root cause of the problem: our overconsumption of single-use plastics. It is essential to find sustainable alternatives that focus on minimizing waste production and promoting a circular economy.
Is burning plastic a sustainable solution?
No, burning plastic is not a sustainable solution. While it may reduce the volume of plastic waste, it releases harmful pollutants into the air and contributes to climate change.