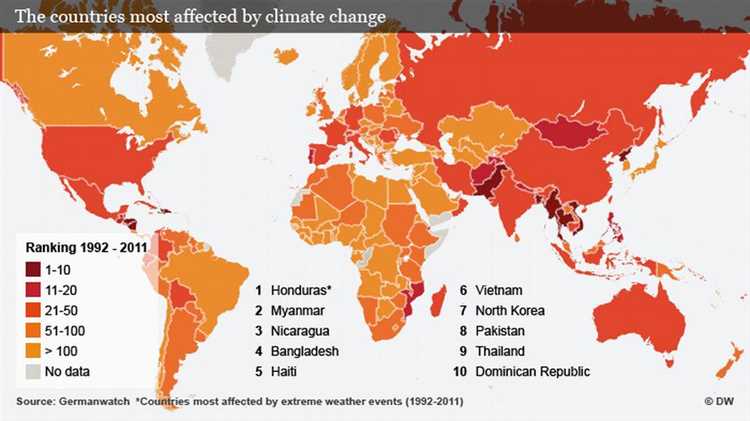
Climate change is a global issue that affects every country, but some nations are more vulnerable than others. When it comes to assessing the impact of climate change, there are certain countries that stand out due to the severity of their challenges. These countries are experiencing the most immediate and negative consequences of global warming, leading to environmental, economic, and social consequences.
One such country that is particularly affected by climate change is Bangladesh. Located in South Asia, Bangladesh is highly prone to natural disasters, such as cyclones, floods, and droughts. Rising sea levels due to global warming pose a significant threat to the low-lying country, making it highly vulnerable to coastal erosion and submergence of land. With a density of over 160 million people, Bangladesh also faces the challenge of providing adequate resources and infrastructure for its population amidst the changing climate.
Another country heavily impacted by climate change is the island nation of Maldives, located in the Indian Ocean. With an average elevation of only 1.5 meters above sea level, the Maldives faces the risk of being completely submerged if sea levels continue to rise. The nation’s economy heavily relies on tourism and fishing, which are both highly sensitive to climate change. The Maldivian government has been actively advocating for global climate action, as the fate of their country depends on it.
In conclusion, while climate change affects the entire planet, some countries are more vulnerable to its consequences than others. Bangladesh and the Maldives are just two examples of nations that are already experiencing the severe impacts of global warming. It is essential for the international community to prioritize support and assistance to these nations, as they navigate the challenges posed by climate change and work towards a more sustainable future.
- The Most Impacted Country by Climate Change
- Overview of Climate Change
- Causes of Climate Change
- Impacts of Climate Change
- Factors Contributing to Climate Change
- Evidence of Impact on Countries
- 1. Maldives
- 2. Bangladesh
- Case Study Analysis
- Q&A:
- Is climate change impacting every country equally?
- Which country is considered to be the most impacted by climate change?
- What are some factors that contribute to a country being heavily impacted by climate change?
- How does climate change impact developing countries differently from developed countries?
- Is there any global effort to assist countries impacted by climate change?
The Most Impacted Country by Climate Change
Climate change is a global issue that affects every country in the world, but some countries are more impacted than others. When it comes to the country that is most impacted by climate change, there are several factors to consider.
One country that stands out in terms of the impact of climate change is Bangladesh. Located in the delta of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, Bangladesh is highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Rising sea levels, increased flooding, and more frequent cyclones are some of the challenges that the country faces.
With a population of over 160 million people, Bangladesh is one of the most densely populated countries in the world. This population density combined with its geographical location makes it even more susceptible to the negative impacts of climate change.
One of the biggest threats that Bangladesh faces due to climate change is the risk of displacement and migration. As sea levels rise and floods become more severe, many coastal communities are at risk of being submerged. This not only leads to the loss of homes and livelihoods but also puts pressure on other parts of the country as people are forced to migrate to safer areas.
The agricultural sector, which is vital to the country’s economy, is also heavily impacted by climate change. Erratic rainfall patterns, increased salinity in the soil, and extreme weather events all contribute to decreased crop yields and food insecurity.
Despite the challenges it faces, Bangladesh has been proactive in adapting to the impacts of climate change. The country has invested in climate-resilient infrastructure, implemented early warning systems for cyclones, and introduced sustainable agricultural practices. However, with limited resources and a rapidly growing population, Bangladesh still requires support from the international community to effectively address the impacts of climate change.
In conclusion, while climate change affects every country, Bangladesh is one of the most impacted countries. Its vulnerability to rising sea levels, increased flooding, and other climate-related hazards make it a high priority in terms of climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts.
Overview of Climate Change
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature patterns, precipitation levels, wind patterns, and other aspects of weather conditions around the world. These changes are primarily caused by human activities, with the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas being the main contributor to the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The release of these gases traps heat from the sun, causing the Earth’s surface temperature to rise.
Climate change is a global issue that affects every country, but some regions are more impacted than others. Developing countries with weak infrastructure and limited resources often face severe impacts of climate change, including droughts, floods, and extreme weather events. However, even developed countries are not immune to the effects of climate change.
Causes of Climate Change
The main factors contributing to climate change include:
- Greenhouse gas emissions: The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial activities release carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to enhanced global warming.
- Deforestation: The removal of forests reduces the Earth’s capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, further contributing to the increased concentration of greenhouse gases.
- Agriculture: The agricultural sector, particularly livestock farming, is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, mainly in the form of methane.
- Industrial activities: Industrial processes release various greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels and other manufacturing processes.
Impacts of Climate Change
The impacts of climate change are wide-ranging and include:
- Rising temperatures: Higher temperatures contribute to more frequent and intense heatwaves, leading to heat-related illnesses and deaths, as well as reduced agricultural productivity.
- Extreme weather events: Climate change increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, cyclones, droughts, and floods, causing widespread destruction and loss of lives.
- Sea-level rise: As temperatures rise, glaciers and ice sheets melt, leading to an increase in sea levels. This poses a significant threat to coastal areas, causing erosion, flooding, and the loss of valuable ecosystems.
- Impact on ecosystems: Climate change disrupts ecosystems by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, which affects the distribution and behavior of plants and animals. This can lead to the extinction of species and loss of biodiversity.
Addressing climate change requires global cooperation and concerted efforts from governments, organizations, and individuals. Mitigation measures, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources, reducing carbon emissions, and implementing sustainable land management practices, are crucial in combating climate change and minimizing its impacts on societies and the environment.
Factors Contributing to Climate Change
Climate change is a complex issue that is influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for finding effective solutions and mitigating the impacts of global warming. Here are some key factors contributing to climate change:
1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The main driver of climate change is the increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, release large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat and contribute to the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming.
2. Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture, urbanization, and logging is a significant contributor to climate change. Trees absorb carbon dioxide as they grow, acting as natural carbon sinks. However, deforestation reduces the number of trees and the planet’s capacity to absorb CO2, leading to higher levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
3. Burning of Fossil Fuels: The combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, for energy production is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. These activities release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
4. Agricultural Activities: Agriculture is another significant factor contributing to climate change. The use of synthetic fertilizers, livestock production, and rice cultivation release large amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, which have a much higher global warming potential compared to carbon dioxide.
5. Industrial Processes: Industrial activities, such as manufacturing, cement production, and chemical processes, emit greenhouse gases through the burning of fossil fuels and the release of industrial byproducts. These activities contribute to the overall greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
6. Waste Management: Improper waste management, including landfilling and open burning, releases methane and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Landfills are a significant source of methane emissions, which contribute to global warming.
It is important to note that natural factors, such as volcanic eruptions and variations in the solar radiation, also contribute to climate change. However, the current trend of global warming can be attributed primarily to human activities and the excessive release of greenhouse gases.
Addressing these factors requires collective action and international cooperation. Governments, industries, and individuals need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable practices, and adopt cleaner energy sources to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Evidence of Impact on Countries
Climate change has become a global crisis, affecting countries around the world in various ways. The evidence of its impact on countries is overwhelming, with clear indicators of changing weather patterns, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events, among others. Let us explore the evidence of climate change impact on some of the most affected countries.
1. Maldives
Located in the Indian Ocean, the Maldives is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change. Rising sea levels threaten its existence, as its highest point is just a few meters above sea level. With increased flooding and erosion of beaches, the Maldives’ stunning coral reefs and vibrant marine life are at risk. The country’s economy, heavily reliant on tourism and fishing, is also under threat.
2. Bangladesh
Bangladesh, situated at the delta of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, faces multiple challenges due to climate change. It experiences frequent cyclones, floods, and storms, causing extensive damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and the lives of its people. Additionally, rising sea levels lead to saltwater intrusion, impacting agricultural productivity and freshwater availability.
These are just two examples of countries heavily impacted by climate change, but the list goes on. Other countries such as small island nations in the Pacific, like Tuvalu and Kiribati, face similar threats due to their low-lying geography. Likewise, countries with vulnerable ecosystems, such as Peru and Ecuador, experience changes in rainfall patterns affecting agricultural productivity and water resources.
It is crucial for countries and the international community to take urgent action to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change on countries. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable development, and supporting vulnerable communities, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future for all.
Case Study Analysis
Climate change affects countries all over the world, but some are more impacted than others. In this case study analysis, we will examine which country is the most impacted by climate change.
One country that is particularly vulnerable to climate change is Bangladesh. Situated in South Asia, Bangladesh faces a wide range of climate-related challenges such as increased temperatures, sea-level rise, floods, cyclones, and droughts. These impacts have severe consequences for the country’s population and economy.
One of the primary reasons why Bangladesh is highly impacted by climate change is its geographical location. The country is situated in the delta region of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, making it prone to frequent and intense flooding. As sea levels rise, the risk of coastal inundation increases, threatening densely populated areas and vital infrastructure.
The effects of climate change in Bangladesh are already visible and have been exacerbating existing vulnerabilities. For example, the country experienced devastating floods in recent years, resulting in loss of lives, displacement, and damage to crops and livestock. These extreme weather events have a significant impact on the country’s agriculture sector, which employs a large portion of the population.
Moreover, climate change also poses a threat to the availability of freshwater resources in Bangladesh. As glaciers melt and rainfall patterns change, the country faces challenges in maintaining a sufficient water supply for both agricultural and domestic use. This can lead to conflicts over water resources and further exacerbate the country’s socio-economic issues.
Despite these challenges, Bangladesh has shown resilience and is actively working towards adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change. The government has implemented various strategies, including early warning systems, climate-resilient infrastructure development, and community-based adaptation programs. International collaborations and financial support also play a crucial role in assisting Bangladesh’s efforts to combat climate change.
In conclusion, Bangladesh is one of the countries most impacted by climate change. Its geographical location, susceptibility to flooding, and dependence on agriculture make it particularly vulnerable. However, the country is taking steps to address these challenges and build resilience in the face of climate change.
Q&A:
Is climate change impacting every country equally?
No, climate change is impacting different countries to varying degrees. Some countries are more vulnerable due to factors such as their geography, economic development, and population density.
Which country is considered to be the most impacted by climate change?
It is difficult to pinpoint one country as the most impacted by climate change as the effects vary across regions. However, countries in the Global South, such as Bangladesh, the Maldives, and Haiti, are often mentioned for their vulnerability to climate change.
What are some factors that contribute to a country being heavily impacted by climate change?
Several factors can contribute to a country being heavily impacted by climate change. These include its geographical location, level of economic development, dependence on agriculture, infrastructure, and ability to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change.
How does climate change impact developing countries differently from developed countries?
Developing countries are often more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change due to factors such as limited resources, weaker infrastructure, and higher dependence on climate-sensitive sectors like agriculture. Developed countries, on the other hand, usually have more resources and technology to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
Is there any global effort to assist countries impacted by climate change?
Yes, there are various global efforts to assist countries impacted by climate change. The United Nations Green Climate Fund, for example, was established to provide financial support to developing countries to help them adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change. Additionally, international agreements like the Paris Agreement aim to mobilize resources and collaboration to address climate change impacts globally.
