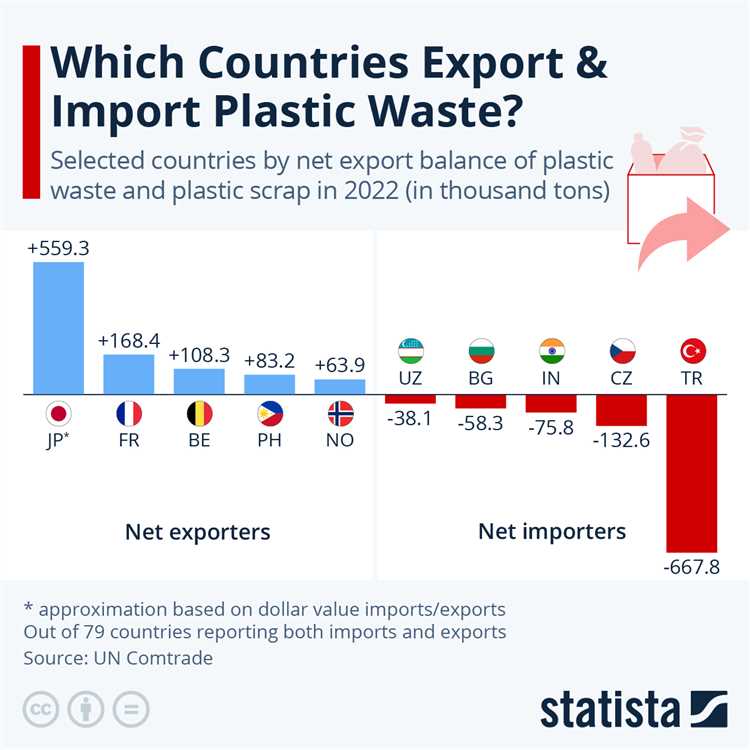
When it comes to garbage, most people would assume that it’s something to get rid of. However, there is one country in the world that sees value in other people’s rubbish. This country is none other than China, which has become a major importer of waste from around the globe.
But why would a country want to buy garbage? The answer lies in China’s rapid industrialization and the increasing demand for raw materials. As the world’s largest manufacturer, China needs a constant supply of resources to sustain its production. By importing garbage, China can extract valuable materials from it, such as metals, plastics, and paper, which can be used in its manufacturing processes.
Not only does this practice help China meet its resource needs, but it also provides an economic opportunity for other countries. Exporting garbage allows them to reduce their own waste management costs and generate revenue from selling it to China. However, there are concerns about the environmental impact of this trade, as some countries might send contaminated or hazardous waste.
- Demand for Waste: Countries that Buy Garbage
- Economic Benefits: Why Countries Pursue Waste Import
- 1. Resource Scarcity
- 2. Recycling and Waste Management Infrastructure
- Recycling Efficiency: How Imported Waste is Managed
- Waste Sorting and Classification
- Processing and Treatment Facilities
- Quality Control and Environmental Standards
- Financial Incentives and Economic Benefits
- Environmental Concerns: Challenges of Waste Import
- Case Studies: Successful Waste Importing Nations
- Future Prospects: Growing Market for Waste
- Q&A,
- Which country buys garbage?
- Why does Sweden buy garbage?
- How does Sweden use the garbage they buy?
- What are the benefits of Sweden buying garbage?
Demand for Waste: Countries that Buy Garbage
In recent years, the global waste crisis has become increasingly concerning, with landfills overflowing and oceans being polluted. However, some countries have found innovative solutions to this problem by turning garbage into a valuable resource. These countries have recognized the potential in recycling and have started buying garbage from other nations to meet their own recycling demands.
One country that has emerged as a major player in the global garbage trade is Sweden. Known for its advanced waste management systems, Sweden imports millions of tons of waste every year to fuel its waste-to-energy plants. These plants convert the waste into heat and electricity, providing sustainable energy solutions for the country. Sweden’s success in converting waste into valuable resources has made it an attractive option for countries looking to offload their garbage.
Another country that has shown a strong demand for waste is Norway. Like Sweden, Norway has invested heavily in waste-to-energy technologies and imports waste from other countries to sustain its energy production. The country has made significant progress in reducing its reliance on fossil fuels by using waste as an alternative energy source.
Meanwhile, Germany has also made strides in the waste industry. The country has implemented robust recycling and waste management systems, enabling it to recycle a significant portion of its own waste. However, Germany still imports waste from other countries, particularly plastic waste, which is in high demand due to the country’s advanced plastic recycling facilities.
The Netherlands is another country that buys garbage to meet its recycling needs. With limited space for landfills, the Netherlands has focused on recycling and waste-to-energy as sustainable waste management solutions. The country imports waste from neighboring countries to ensure a steady supply for its recycling and renewable energy industries.
These countries that buy garbage have not only found a way to tackle their own waste problems but also contribute to global sustainability efforts. By turning garbage into a valuable resource, they are reducing the need for resource extraction and preventing further environmental damage.
As the demand for waste continues to grow, more countries are likely to join the global garbage trade. This trend highlights the importance of finding innovative and sustainable solutions to the waste crisis, as well as the potential for waste to become a valuable commodity in the future.
Economic Benefits: Why Countries Pursue Waste Import
Importing waste may seem counterintuitive, but many countries have found economic benefits in pursuing this practice. Here are some reasons why countries choose to import waste:
1. Resource Scarcity
Some countries face a scarcity of resources, including raw materials and energy sources. By importing waste, they can recover valuable materials and energy from the discarded items. This reduces their dependence on importing raw materials and helps them meet their domestic demand for resources.
2. Recycling and Waste Management Infrastructure
Many countries that import waste have well-established recycling and waste management infrastructure. They have the facilities and expertise to sort, process, and recycle the waste efficiently. Importing waste allows them to keep their recycling plants running at their full capacity and utilize their infrastructure effectively.
Moreover, waste import provides a more sustainable option for countries that lack adequate recycling facilities. Instead of sending their waste to landfills or incinerators, they can export it to countries with advanced recycling capabilities.
3. Job Creation and Economic Growth
The waste import industry can create employment opportunities and contribute to economic growth. The infrastructure required for waste sorting, processing, and recycling creates jobs in the recycling sector and related industries. It also generates revenue through waste import taxes and fees.
Additionally, waste import can attract investment and stimulate the growth of local businesses. Companies involved in waste management, recycling technology, and renewable energy may establish their operations in countries that import waste, contributing to a thriving green economy.
In conclusion, while importing waste may raise environmental concerns, it can bring significant economic advantages to the importing countries. By embracing waste importation and investing in recycling infrastructure, these countries can capitalize on the value of discarded materials and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Recycling Efficiency: How Imported Waste is Managed

The importation of waste for recycling purposes has become a common practice in many countries around the world. This approach helps countries manage their own waste and also contributes to the recycling efforts globally. However, the management of imported waste requires a high level of efficiency and infrastructure to ensure proper handling, sorting, and processing.
Waste Sorting and Classification
When imported waste arrives in a country, it goes through a sorting and classification process. This involves separating different types of waste materials such as plastics, paper, metals, and glass. Advanced machinery and manual labor are often utilized to carefully sort and categorize the waste, ensuring that each material is processed correctly.
Processing and Treatment Facilities
Once waste materials have been sorted, they are sent to processing and treatment facilities. These facilities can vary depending on the type of waste being handled. For example, plastics may go through a shredding and melting process, while paper and cardboard are often pulped and reformed into new products. Metal waste might be melted down and used for new production, and glass can be crushed and used in the manufacturing of new bottles or other glass products.
Quality Control and Environmental Standards

Throughout the entire process, strict quality control measures and adherence to environmental standards are crucial to ensure that the recycling process is efficient and environmentally friendly. Regular inspections and tests are conducted to monitor the quality of the recycled materials and to identify any potential issues or contaminants. These standards help maintain the integrity and sustainability of the recycling process.
Financial Incentives and Economic Benefits
Importing waste for recycling can also bring financial incentives and economic benefits to certain countries. Some countries offer subsidies or tax breaks to businesses involved in the recycling industry, encouraging investment and job creation. Additionally, the sale of recycled materials can generate revenue, especially when there is a high demand for these materials in the global market. These economic benefits further motivate countries to efficiently manage and recycle imported waste.
In conclusion, the management of imported waste for recycling requires a well-established infrastructure, efficient sorting and processing facilities, strict adherence to environmental standards, and the potential for economic benefits. By effectively managing and recycling imported waste, countries can contribute to the global efforts of sustainability and waste reduction.
Environmental Concerns: Challenges of Waste Import
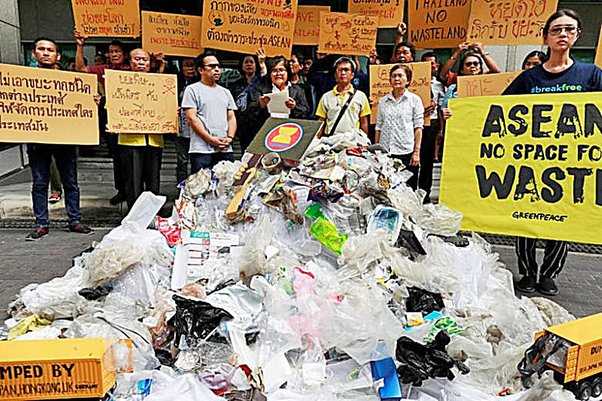

As the world continues to grapple with the growing issue of waste management, the practice of waste import has emerged as a controversial topic. Waste import refers to the practice of one country importing waste materials, such as plastic, paper, and electronic waste, from another country for recycling or disposal purposes.
While waste import may seem like a practical solution to manage waste in countries with limited resources or inadequate recycling facilities, it comes with its fair share of environmental challenges.
- Pollution and Contamination: One of the main concerns associated with waste import is the potential for pollution and contamination. Imported waste materials may contain hazardous substances or pollutants that can seep into the soil, contaminate water sources, or release toxic fumes into the air.
- Inadequate Waste Management: Importing waste can put a strain on the receiving country’s waste management infrastructure. The sudden influx of waste may overwhelm existing recycling or disposal facilities, leading to inefficiencies and increased environmental risks.
- Illegal Dumping: Some unscrupulous waste importers may resort to illegal dumping as a means to dispose of the imported waste, especially if the cost of proper recycling or disposal is deemed too high. This can result in the creation of makeshift dumpsites and further exacerbate environmental pollution.
- Loss of Resources: Importing waste from other countries means that valuable resources, such as plastics or metals, are being exported instead of being utilized within the country. This can result in a loss of potential economic and environmental benefits through recycling or reusing these resources.
- Transportation Emissions: The transportation of waste materials over long distances contributes to carbon emissions and air pollution. The carbon footprint associated with waste import, including the use of fossil fuels for transportation, should be taken into account when evaluating the overall environmental impact.
Overall, while waste import can provide temporary relief for countries struggling with waste management, it is crucial to address the environmental concerns and challenges that arise from this practice. Implementing stricter regulations, investing in domestic waste management infrastructure, and promoting sustainable waste reduction practices can all contribute to a more environmentally conscious approach to dealing with waste.
Case Studies: Successful Waste Importing Nations
1. Japan
- Japan has been a successful waste importing nation for many years. They have implemented efficient recycling and waste management systems that turn imported waste into valuable resources.
- By importing waste materials such as plastic, paper, and metal, Japan has been able to meet its high demand for raw materials while reducing the burden on landfills.
- The country has invested in advanced technology to sort and process waste, enabling them to extract valuable materials and minimize environmental impacts.
2. Germany
- Germany is another successful example of a waste importing nation. The country has implemented strict recycling laws and infrastructure that allows them to import waste materials and convert them into energy.
- Through their waste-to-energy programs, Germany has significantly reduced their reliance on fossil fuels and landfilling.
- They have also developed a comprehensive system for sorting and processing waste, ensuring that imported waste is properly managed and recycled.
3. Netherlands
- The Netherlands is known for its advanced waste management systems, making it a successful waste importing nation. They have implemented innovative recycling technologies and policies that allow the country to import waste and convert it into valuable resources.
- The Netherlands has prioritized waste reduction and resource recovery, ensuring that imported waste is properly sorted and processed to extract maximum value.
- They have also invested in research and development to continuously improve their waste management practices and find new ways to utilize imported waste.
Future Prospects: Growing Market for Waste
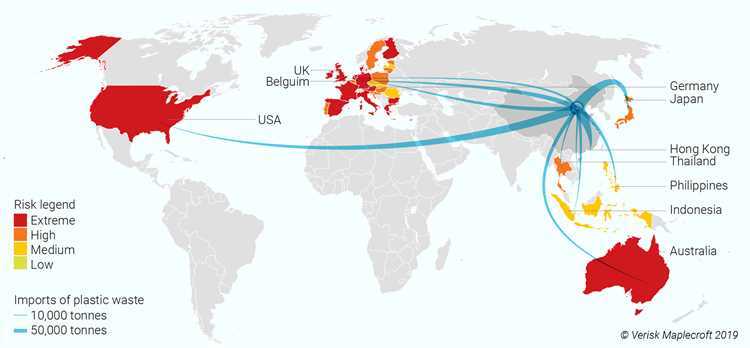
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the global demand for recycling and waste management solutions. As governments and businesses become increasingly aware of the environmental impact of waste, they are actively seeking ways to reduce their ecological footprint.
This growing awareness has created a promising market for waste management services and technologies. Recycling companies are exploring innovative ways to process and reuse various types of waste, turning them into valuable resources. This includes turning plastic waste into new products, converting organic waste into renewable energy, and recovering valuable materials from electronic waste.
The demand for recycled materials is also on the rise as consumers become more conscious of their consumption habits. Many companies are now striving to incorporate recycled content into their products to appeal to environmentally-minded consumers. This creates a lucrative market for waste materials, driving the need for efficient waste management and recycling infrastructures.
Furthermore, governments around the world are implementing stricter regulations on waste management and disposal. This provides opportunities for waste management companies to offer compliant solutions and services. Additionally, governments are also investing in waste-to-energy technologies and other environmentally friendly waste management initiatives.
The overall outlook for the waste management market is positive, with continued growth expected in the coming years. The urgent need to address environmental concerns and the growing demand for sustainability make waste management a vital sector for future development.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of waste management, it is clear that the market for waste solutions will continue to expand. This creates opportunities for innovation and investment in technologies that can help reduce waste, protect the environment, and create a more sustainable future.
Q&A,
Which country buys garbage?
Sweden buys garbage to use it as fuel for their waste-to-energy plants.
Why does Sweden buy garbage?
Sweden buys garbage because they have invested heavily in waste-to-energy plants, which rely on burning garbage as fuel to generate electricity and heat.
How does Sweden use the garbage they buy?
Sweden uses the garbage they buy as fuel for their waste-to-energy plants. The garbage is burned, and the heat generated is used to produce electricity and heat for homes and businesses.
What are the benefits of Sweden buying garbage?
The benefits of Sweden buying garbage include reducing landfill waste, generating electricity and heat from waste, and reducing reliance on fossil fuels for energy production.