Microplastics are tiny plastic particles measuring less than 5 mm in size. These pollutants have been widely detected in various environmental compartments, including our drinking water. As the awareness about the potential harmful effects of microplastics on human health and the environment grows, scientists and researchers are actively exploring different methods to remove these contaminants from water sources.
One such method that has gained attention recently is boiling water. Boiling water is a simple and affordable technique that has been used for centuries to purify water and kill harmful microorganisms. But can boiling water effectively remove microplastics as well?
Several studies have investigated the effectiveness of boiling water in removing microplastics, and the results are promising. Researchers have found that boiling water can indeed help in reducing the concentration of microplastics. When water is boiled, it reaches its boiling point, causing the microplastic particles to heat up and potentially break apart. This can result in the physical removal of microplastics from the water, making it cleaner and safer to consume.
- Reducing Microplastic Pollution: Boiling Water as an Effective Solution
- Understanding the Microplastic Problem
- Boiling Water: The Simple Remedy
- The Science Behind Boiling Water
- The Effectiveness of Boiling Water in Removing Microplastics
- The Science Behind Boiling Water
- Heat is the Key
- The Boiling Process
- Limitations of Boiling Water
- Key Considerations for Boiling Water Treatment
- 1. Duration of Boiling
- 2. Water Source
- Spreading Awareness and Encouraging Action
- Q&A:
- Is boiling water an effective method to remove microplastics?
- Are there any other methods besides boiling water to remove microplastics?
- Can boiling water remove all types of microplastics?
- What is the recommended boiling time to remove microplastics?
- Can boiling water remove all microplastics from food?
Reducing Microplastic Pollution: Boiling Water as an Effective Solution

Microplastic pollution is a growing concern worldwide, as these tiny particles pose a significant threat to the environment and human health. Microplastics can be found in various sources, including synthetic fibers, plastic bags, and microbeads in personal care products. These microplastics are small enough to be ingested by marine organisms and can easily enter the food chain, ultimately affecting humans.
To address this issue, various methods have been proposed to remove microplastics from water sources. One such method is boiling water, which has shown promising results in removing microplastics effectively.
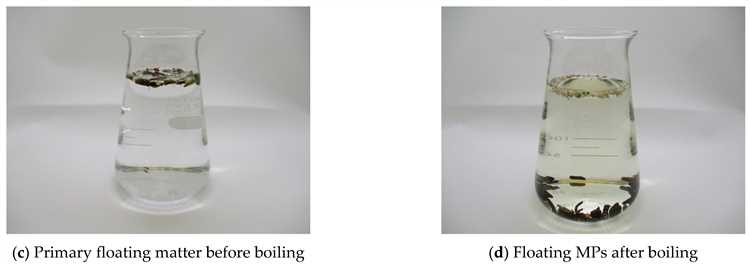
Boiling water is a simple and cost-effective technique that can be easily implemented at home or in industrial settings. When water is boiled, the microplastics present in the water tend to float to the surface, making it easier to separate them from the water. This process is known as surface skimming.
However, it is important to note that boiling water alone may not completely remove all microplastics. Some microplastics may still remain suspended in the water or settle back down after boiling. Therefore, additional filtration techniques such as using activated carbon filters or reverse osmosis systems may be necessary to achieve a more thorough removal of microplastics.
Boiling water also has the advantage of being a chemical-free method, as no additional chemicals or additives are required. This makes it a safer and more environmentally friendly solution compared to other methods that may involve the use of potentially harmful chemicals.
Furthermore, boiling water can be easily adopted by individuals as a preventive measure to reduce microplastic pollution. By boiling water before consumption, individuals can help minimize their exposure to microplastics and protect their health.
In conclusion, boiling water is an effective solution for reducing microplastic pollution. Though it may not completely eliminate all microplastics, it provides a simple and accessible method for removing a significant portion of these harmful particles. As individuals and industries continue to address the issue of microplastic pollution, boiling water can be a valuable tool in the fight to protect the environment and human well-being.
Understanding the Microplastic Problem

Microplastics are small plastic particles that are less than 5 millimeters in size. They are commonly found in the environment, including in water bodies such as oceans, rivers, and lakes. These particles are a result of the breakdown of larger plastic items or can be intentionally manufactured at a microscopic scale.
One of the major sources of microplastics is the improper disposal of plastic waste. When plastic items such as bottles, bags, or packaging materials are not properly managed and end up in the environment, they can break down over time into smaller particles. These microplastics can also be released into the environment during the manufacturing and use of plastic products.
The presence of microplastics in water bodies has raised concerns due to their potential impacts on the environment and human health. Microplastics can be ingested by aquatic organisms, such as fish and shellfish, which can then make their way up the food chain. Studies have shown that microplastics can cause physical harm to marine life, leading to reduced reproductive success, altered behavior, and even death.
In addition to their impact on aquatic ecosystems, microplastics can also pose a risk to human health. It has been found that microplastics can accumulate in the human body through the ingestion of contaminated food and water. Although the long-term effects of microplastics on human health are not yet fully understood, there is growing concern about the potential for these particles to release harmful chemicals and toxins into the body.
Efforts are being made to address the microplastic problem and reduce its impact on the environment. This includes initiatives to reduce plastic waste, improve waste management practices, and develop more sustainable alternatives to plastic materials. Understanding the sources, distribution, and potential risks associated with microplastics is essential in developing effective strategies to tackle this global issue.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| Microplastics are small plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size. |
| Improper disposal of plastic waste is a major source of microplastics. |
| Microplastics can harm aquatic organisms and potentially impact human health. |
| Efforts are being made to address the microplastic problem and reduce its impact. |
Boiling Water: The Simple Remedy
Microplastics have become a growing concern in recent years due to their potential impact on human health and the environment. These tiny plastic particles, often measuring less than 5 millimeters, can be found in various sources, including the water we drink.
One simple method that has been suggested to remove microplastics from water is boiling. Boiling water has long been used as a method of purification, killing off harmful bacteria and parasites. But can it effectively remove microplastics?
The Science Behind Boiling Water
When water is boiled, it undergoes a physical change from a liquid to a gas. This process, known as vaporization, destroys microorganisms by breaking their cell walls. However, boiling water does not remove dissolved or suspended particles such as microplastics, which are too small to be affected by the change in state.
The Effectiveness of Boiling Water in Removing Microplastics
While boiling water alone may not remove microplastics, it can still play a role in reducing their presence. Boiling water can be combined with filtration methods to increase its effectiveness in removing microplastics. For example, using a fine mesh filter after boiling can help to physically trap and remove the tiny particles from the water.
It’s important to note that boiling water is not a foolproof method for completely eliminating microplastics. Some microplastics may still remain in the water even after boiling and filtering. Additionally, boiling water may have other limitations, such as the potential release of volatile compounds from plastic containers or pipes.
Further research is needed to determine the extent to which boiling water can remove microplastics and the potential risks associated with boiling and filtering water. In the meantime, it is advised to use alternative methods of filtration, such as activated carbon filters or reverse osmosis systems, which have been shown to be more effective in removing microplastics.
The Science Behind Boiling Water
Boiling water has long been considered a reliable and effective method for purifying drinking water. But what is the science behind this process? How does boiling water actually remove microplastics?
Heat is the Key
When water is heated to its boiling point, the temperature causes the water molecules to gain energy and become more active. This increased energy disrupts the bonds holding microplastics together, causing them to break down and separate from the water.
Microplastics are small pieces of plastic debris that are less than 5 millimeters in length. They can come from a variety of sources, including microbeads in cosmetics, fibers from synthetic clothing, and disintegration of larger plastic items. These tiny particles are not visible to the naked eye and can easily go undetected in water sources.
The Boiling Process
When water is boiled, the increased temperature causes the water molecules to move faster and collide with one another. This collision transfers energy, causing the bonds of the microplastics to weaken and eventually break. As a result, the microplastics separate from the water and are left behind as sediment or residues.
Once the water has reached its boiling point and the microplastics have been separated, the water can be cooled down and filtered if desired. This additional filtration step can further remove any remaining particles or impurities, ensuring the water is as clean as possible.
Limitations of Boiling Water
While boiling water is effective in removing microplastics, it does have its limitations. Boiling alone may not be sufficient to remove all types of microplastics, especially those that are smaller in size. Additionally, boiling does not remove other contaminants such as heavy metals or chemicals that may be present in the water.
Therefore, it is important to consider using a combination of methods, such as boiling and filtration, to ensure the water is free from various types of impurities. Regular testing of water sources is also recommended to ensure the ongoing safety and quality of the water.
- Heat disrupts the bonds holding microplastics together
- Movement of water molecules during boiling weakens and breaks these bonds
- Boiling may not remove all types of microplastics or other contaminants
Key Considerations for Boiling Water Treatment

Boiling water is a popular method for purifying drinking water and has been used by many individuals to effectively remove various contaminants, including microplastics. However, there are several key considerations that individuals should take into account when using boiling water as a treatment method for removing microplastics:
1. Duration of Boiling
It is important to ensure that water is boiled for an adequate duration to effectively remove microplastics. While boiling water for at least one minute is generally recommended to kill pathogens, it may take longer to effectively eliminate microplastics. Research suggests that boiling water for at least 10 minutes may provide better results in removing microplastics.
2. Water Source
The source of water being boiled is another crucial consideration. If the water being treated contains a high concentration of microplastics, such as water from plastic-contaminated sources, the effectiveness of boiling alone may be limited. In such cases, using additional filtration methods, such as activated carbon filters, before boiling can enhance the removal of microplastics.
3. Temperature Control
Controlling the temperature of the boiling water is essential to ensure effective removal of microplastics. Water should reach a rolling boil, where large bubbles break at the surface continuously, before starting the timer to ensure the desired temperature is achieved. Maintaining the water at a rolling boil throughout the treatment duration is also important to maximize the removal of microplastics.
In conclusion, boiling water can be an effective method for removing microplastics. However, careful consideration should be given to the duration of boiling, the source of water, and temperature control to maximize its effectiveness. Combining boiling with additional filtration methods can further improve the removal of microplastics from drinking water, ensuring a safer and cleaner water supply.
Spreading Awareness and Encouraging Action
As the concern over microplastic pollution continues to grow, it is crucial to spread awareness about the issue and encourage action from individuals and communities.
Education plays a vital role in raising awareness about the harmful effects of microplastics on our environment and health. Through various channels such as social media campaigns, educational videos, and informational articles, individuals can learn about the sources, risks, and potential solutions to this problem.
Engaging influential individuals and organizations can also significantly impact the level of awareness and action taken. Celebrities, scientists, environmental activists, and NGOs can leverage their platforms and expertise to raise public consciousness about microplastic pollution. Collaborations between these influential entities can help amplify the message and inspire positive change.
Government and policy engagement are crucial in addressing the issue at a broader scale. By creating and enforcing regulations, governments can limit the production and usage of single-use plastics, encourage proper waste management, and support the development of sustainable alternatives. Individuals can contribute to this effort by actively participating in public consultations, signing petitions, and supporting political candidates who prioritize environmental issues.
Individual actions also make a significant difference. By making conscious choices in our daily lives, such as reducing plastic consumption, properly disposing of waste, and supporting businesses and brands that prioritize sustainability, we can collectively reduce the amount of microplastics entering our ecosystems. Small actions can have a ripple effect, inspiring others to follow suit.
Collaboration and research are essential for finding effective solutions to the microplastic pollution problem. By partnering with universities, research institutions, and other stakeholders, we can develop innovative technologies and methods for removing microplastics from water sources. Such collaborations can also help create standardized testing and filtration processes to ensure the effectiveness of various microplastic removal techniques.
With a combination of awareness, engagement, individual actions, and collaborative efforts, we can work towards reducing the presence of microplastics in our water sources and safeguarding the health of our environment for future generations.
Q&A:
Is boiling water an effective method to remove microplastics?
Yes, boiling water can effectively remove microplastics from water. When water is boiled, it reaches a high temperature that can cause the microplastics to dislodge and float to the surface, making them easier to remove.
Are there any other methods besides boiling water to remove microplastics?
Yes, there are several other methods to remove microplastics from water. These include filtration systems, activated carbon filters, and reverse osmosis systems. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the method that suits your needs.
Can boiling water remove all types of microplastics?
No, boiling water cannot remove all types of microplastics. Some microplastics may be resistant to high temperatures and may not dislodge or float to the surface during the boiling process. It’s important to use additional methods, such as filtration systems, to ensure the removal of all types of microplastics.
What is the recommended boiling time to remove microplastics?
There is no specific recommended boiling time to remove microplastics. However, boiling water for at least 5 minutes is generally considered effective in killing or removing most microorganisms and pollutants, including microplastics. It’s important to let the water cool down before using or consuming it.
Can boiling water remove all microplastics from food?
No, boiling water alone cannot remove all microplastics from food. While boiling water may help dislodge or remove some microplastics, there may still be other microscopic particles or contaminants present. It’s important to practice good food hygiene, such as washing fruits and vegetables thoroughly, to minimize the ingestion of microplastics.