Plastic waste has become a major global concern, as its impact on the environment and human health continues to worsen. One of the key questions that arises is: who generates the highest amount of plastic waste in the world?
Various studies and reports have highlighted that the answer to this question lies in a combination of factors such as population, consumption patterns, and waste management practices.
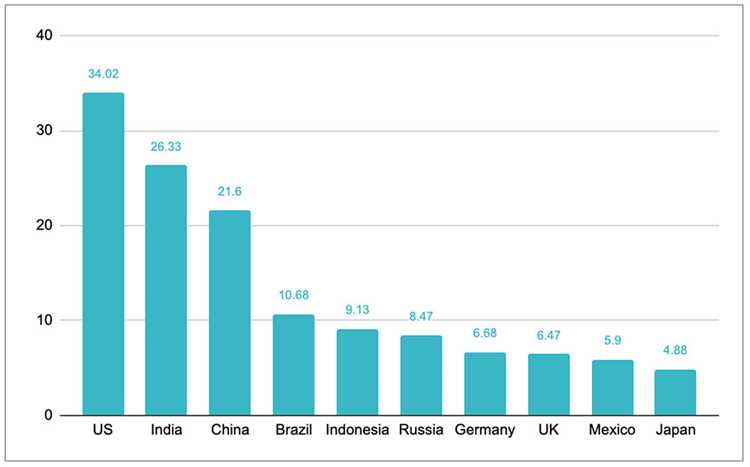
When it comes to the highest generator of plastic waste worldwide, one country stands out: the United States. With its large population and high consumption rates, the US produces a staggering amount of plastic waste each year. In fact, it is estimated that the US generates around 80 million tons of plastic waste annually, accounting for nearly a third of the global total.
However, it is important to note that plastic waste generation is not solely determined by population size and consumption patterns. Waste management practices and infrastructure also play a significant role. Countries with effective recycling facilities and waste management systems can reduce their plastic waste effectively, even with high consumption rates.
Therefore, while the United States may be the highest generator of plastic waste worldwide, addressing this global issue requires a collective effort from all countries to adopt sustainable practices, improve waste management systems, and promote the use of recyclable materials.
- The global plastic waste crisis
- Environmental impacts
- Top plastic waste generators
- 1. China
- 2. United States
- 3. Indonesia
- China: The largest producer of plastic waste
- Causes of China’s high plastic waste production:
- Consequences of China’s plastic waste production:
- United States: A major contributor to the problem
- Impact on the environment
- Efforts and solutions
- India: A rapidly growing plastic waste problem
- European Union: Taking steps towards waste reduction
- Indonesia: Battling with plastic pollution
- Q&A:
- Which country produces the most plastic waste?
- Is plastic waste production increasing worldwide?
- What are the consequences of plastic waste?
- How can we reduce plastic waste?
- Are there any countries that are successfully managing their plastic waste?
The global plastic waste crisis
Plastic waste has become a pressing global crisis, with severe implications for the environment, marine life, and human health. The production and consumption of plastic have skyrocketed in recent years, leading to an overwhelming amount of waste that is often not properly managed or recycled.
Plastic waste poses a significant threat to our oceans and marine ecosystems. It is estimated that around 8 million metric tons of plastic enter the oceans each year, leading to devastating consequences for marine life. Marine animals often mistake plastic debris for food, resulting in ingestion and entanglement, which can be fatal.
Furthermore, plastic waste does not just disappear when it enters the oceans. It breaks down into smaller pieces called microplastics, which are now pervasive in our waterways, soil, and even in the air we breathe. Microplastics pose a significant risk to human health, as they can accumulate in our bodies and potentially cause various health issues.
The global plastic waste crisis requires urgent attention and action. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainable alternatives. Efforts should be made to improve waste management infrastructure, implement stricter regulations on single-use plastics, and promote recycling initiatives.
Education and awareness are also crucial in tackling the plastic waste crisis. People need to understand the impact of their actions and make more conscious choices when it comes to plastic consumption. By reducing our reliance on single-use plastics, embracing reusable alternatives, and supporting companies that prioritize sustainability, we can collectively make a significant difference.
In conclusion, the global plastic waste crisis is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach. It is not enough to simply rely on recycling alone. We need to address the root causes of plastic waste generation and work towards a more sustainable future. By taking action now, we can mitigate the devastating consequences of plastic pollution and protect our planet for future generations.
Environmental impacts
Plastic waste has significant environmental impacts on ecosystems and the planet as a whole. Here are some of the key environmental impacts of plastic waste:
| Environmental Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Marine pollution | Plastic waste often ends up in the oceans, leading to marine pollution. Marine animals can mistake plastic for food and ingest it, causing health problems and even death. Plastic waste also degrades slowly, releasing harmful chemicals into the water, which can harm marine life and disrupt ecosystems. |
| Land pollution | Plastic waste that is not properly disposed of can end up in landfills, where it takes hundreds of years to decompose. This leads to the accumulation of plastic waste in the environment, polluting soil and water sources. Plastic waste can also leach harmful chemicals into the soil, affecting plant and animal life. |
| Air pollution | The production and incineration of plastic waste can release toxic gases and pollutants into the air. This air pollution contributes to global warming and climate change, as well as respiratory and other health problems for humans and animals. |
| Wildlife disruption | Plastic waste can disrupt wildlife habitats and ecosystems. It can entangle animals, leading to injury or death. It can also contaminate food sources, affecting the health and reproduction of wildlife populations. Disruption of the natural balance of ecosystems can have far-reaching consequences for the biodiversity and stability of the environment. |
| Microplastic contamination | Plastic waste breaks down into smaller particles called microplastics, which can be easily ingested by marine life, animals, and humans. These microplastics can enter the food chain, potentially causing harm to organisms and human health. Microplastic contamination has been found in various ecosystems, including freshwater and marine environments. |
These environmental impacts highlight the urgent need to reduce plastic waste, improve recycling and waste management practices, and promote sustainable alternatives to plastic.
Top plastic waste generators
The issue of plastic waste pollution is a global concern, and several countries have been identified as the top plastic waste generators worldwide. These countries contribute significantly to the total amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills and oceans.
1. China
China is the largest producer of plastic waste globally, contributing a significant portion to the global plastic waste problem. With its rapidly growing population and industrial development, the country produces a massive amount of plastic waste each year. In recent years, China has made efforts to reduce its plastic waste production and increase recycling efforts.
2. United States
The United States is one of the major contributors to the global plastic waste crisis. The high consumption levels, extensive packaging, and limited recycling infrastructure contribute to the country’s significant plastic waste generation. Many initiatives have been introduced in the United States to tackle the issue, including bans on single-use plastics and promoting recycling.
3. Indonesia
Indonesia is a country with a large population and an emerging economy, which leads to a substantial amount of plastic waste generation. Despite efforts to address the issue, such as implementing waste management programs and regulations, the country still struggles with proper waste disposal and recycling infrastructure.
Other countries such as Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines also contribute significantly to global plastic waste generation. The cumulative actions taken by these countries and the international community are crucial in addressing the issue of plastic waste pollution and working towards a more sustainable future.
China: The largest producer of plastic waste
When it comes to plastic waste, China is currently the highest producer in the world. The country’s rapid industrialization and population growth have led to an exponential increase in plastic consumption and subsequent waste generation.
With a population of over 1.4 billion people, China’s plastic waste output is staggering. It is estimated that the country produces more than 60 million tonnes of plastic waste annually. This accounts for one-fourth of the global plastic waste production.
Causes of China’s high plastic waste production:
- Population growth: China’s large population contributes significantly to the high plastic waste generation. As the population continues to grow, so does plastic consumption.
- Industrialization: China’s rapid industrial development has resulted in increased production of plastic products. Industries such as packaging, electronics, and construction heavily rely on plastic materials, which leads to higher plastic waste generation.
- Urbanization: The process of urbanization in China has led to a higher demand for plastic products. As more people move to cities, there is an increased need for plastic packaging, disposable items, and construction materials.
Consequences of China’s plastic waste production:
- Environmental pollution: China’s high plastic waste production has resulted in significant environmental pollution. Improper disposal and lack of proper recycling infrastructure have led to plastic waste accumulation in landfills, oceans, and waterways.
- Health hazards: Plastic waste can pose serious health risks to both humans and wildlife. The toxic chemicals present in plastic can leach into the environment, contaminating water sources and affecting ecosystems.
- Resource depletion: The production of plastic requires the extraction and consumption of fossil fuels. China’s high plastic waste production contributes to the depletion of finite resources and increases greenhouse gas emissions.
In conclusion, China’s rapid population growth, industrialization, and urbanization have made it the largest producer of plastic waste globally. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach, including stricter regulations, improved waste management systems, and promoting sustainable alternatives to plastic.
United States: A major contributor to the problem
The United States is one of the largest contributors to the global plastic waste problem. With a population of over 331 million people and a high standard of living, the country generates a massive amount of plastic waste every year. This waste comes from various sources, including household consumption, industrial production, and packaging materials.
One of the main reasons behind the United States’ high plastic waste generation is its extensive use of single-use plastics. Items such as plastic bags, bottles, and straws are widely used and disposed of after just one use. This culture of convenience, coupled with a lack of effective recycling and waste management infrastructure, has led to a significant accumulation of plastic waste in the country.
Impact on the environment

The excessive plastic waste generated by the United States has severe environmental consequences. Plastics do not easily decompose and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This leads to the pollution of land, water bodies, and ecosystems, harming wildlife and marine life in particular.
The production of plastics also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The extraction of fossil fuels and the manufacturing process required to produce plastic products result in the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change.
Efforts and solutions
Recognizing the urgency of the plastic waste problem, the United States has taken some steps to address the issue. Several states have implemented plastic bag bans or fees to reduce their consumption. Additionally, there have been efforts to improve recycling infrastructure and promote the use of alternative materials.
However, more needs to be done to effectively tackle the plastic waste crisis. This includes implementing nationwide policies and regulations to reduce plastic consumption, encouraging manufacturers to use more sustainable materials, and investing in innovative recycling technologies.
A collaborative approach involving government, businesses, and individuals is essential to effectively address the plastic waste problem in the United States and mitigate its impact on the environment.
India: A rapidly growing plastic waste problem

India, with its large population and rapidly growing economy, is facing an increasingly alarming plastic waste problem. The country is one of the world’s largest generators of plastic waste, and its infrastructure to manage and dispose of this waste is struggling to keep up with the demand.
Many factors contribute to India’s plastic waste problem. The country has a growing middle class that is increasingly adopting a western consumer lifestyle, leading to increased consumption of single-use plastic items. Additionally, the lack of efficient waste management systems and inadequate recycling facilities exacerbate the problem.
The improper disposal of plastic waste poses significant environmental and health risks. Plastic waste often ends up in waterways and oceans, causing pollution and harming marine life. Burning plastic waste releases harmful gases and toxic chemicals into the air, contributing to air pollution and respiratory problems.
The Indian government has recognized the urgency of the plastic waste problem and has taken steps to address it. In 2016, India introduced a nationwide ban on the manufacture and sale of plastic bags below a certain thickness. The government has also launched initiatives to promote recycling and encourage the use of eco-friendly alternatives to plastic.
However, addressing India’s plastic waste problem requires a multi-faceted approach. It is essential to invest in better waste management infrastructure, including recycling facilities and waste-to-energy plants. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs can also play a crucial role in promoting responsible plastic use and disposal habits.
The challenges posed by India’s rapidly growing plastic waste problem are significant, but with concerted efforts and collaborative solutions, the country can work towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
European Union: Taking steps towards waste reduction
The European Union (EU) has taken significant steps towards reducing plastic waste in recent years. Through a combination of legislation, awareness campaigns, and support for innovative technologies, the EU is working towards a more sustainable future.
One of the major initiatives undertaken by the EU is the Single-Use Plastics Directive. This legislation, which came into effect in July 2019, aims to reduce the impact of certain single-use plastic products on the environment. It includes bans on items like plastic cutlery, straws, and stirrers, as well as requirements for plastic bottle caps to remain attached to the bottles they are sold with. By targeting these items, which are often found in large quantities in landfills and oceans, the EU hopes to significantly reduce plastic waste.
In addition to legislation, the EU has also launched various awareness campaigns to educate the public about the consequences of plastic waste and the importance of waste reduction. These campaigns aim to change consumer behavior by promoting alternatives to single-use plastics and encouraging the use of reusable products.
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Plastic Bag Charge | The EU has encouraged member states to introduce charges for single-use plastic bags, leading to a significant reduction in their consumption. |
| Extended Producer Responsibility | The EU has implemented regulations that hold producers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including proper waste management and recycling. |
| Plastic Packaging Waste Targets | The EU has set specific targets for member states to reduce plastic packaging waste and increase recycling rates. |
Furthermore, the EU is actively supporting the development and implementation of innovative technologies to tackle plastic waste. This includes investing in research and development of new materials, recycling technologies, and sustainable packaging solutions. The EU also provides funding programs and grants to support initiatives that aim to reduce plastic waste and promote circular economy principles.
Overall, the European Union is committed to taking significant steps towards waste reduction and a more sustainable future. By implementing legislation, raising awareness, and supporting innovative technologies, the EU is making progress in reducing plastic waste and encouraging responsible consumption and production practices.
Indonesia: Battling with plastic pollution
Indonesia, a country located in Southeast Asia, faces a severe challenge when it comes to plastic pollution. With a population of over 270 million people and a rapidly growing economy, the use of plastic has skyrocketed in the past few decades.
The Indonesian government has recognized the urgency of the plastic pollution problem and has implemented various measures to tackle it. One of the key initiatives is the National Action Plan on Marine Plastic Debris, which aims to reduce marine plastic debris by 70% by 2025.
In addition to government efforts, several organizations and communities in Indonesia have taken up the fight against plastic pollution. One such example is the Bali-based organization Bye Bye Plastic Bags, founded by two young sisters who are determined to clean up the beaches and oceans of Indonesia.
Despite these efforts, Indonesia faces significant challenges in combating plastic pollution. The lack of proper waste management infrastructure, combined with a growing middle class that increasingly consumes plastic products, has led to a massive amount of plastic waste being generated.
A major contributor to Indonesia’s plastic waste problem is the use of single-use plastics, such as plastic bags and straws. These items are widely used in the country, and their disposal often ends up in rivers and oceans, causing harm to marine life and ecosystems.
Efforts are being made to address this issue, including the implementation of a ban on single-use plastics in certain cities. However, the effectiveness of these bans is limited without proper enforcement and alternative solutions for consumers.
Education and awareness are also crucial in tackling plastic pollution in Indonesia. Many Indonesians are not aware of the environmental impact of plastic waste or the alternatives to single-use plastics. By promoting sustainable practices and providing information on recycling and waste management, Indonesia can make significant strides in reducing plastic pollution.
| Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Lack of proper waste management infrastructure | Investment in waste management infrastructure and recycling facilities |
| Growing middle class consumption of plastic products | Promotion of sustainable alternatives and reduction in plastic consumption |
| Use of single-use plastics | Implementation and enforcement of bans on single-use plastics, promotion of reusable alternatives |
| Lack of awareness and education | Educational campaigns, consumer awareness programs, and school curriculum integration |
Indonesia has a long road ahead in battling plastic pollution, but with continued efforts from the government, organizations, and individuals, positive change is attainable. By addressing the challenges and working together, Indonesia can protect its environment and contribute to the global fight against plastic pollution.
Q&A:
Which country produces the most plastic waste?
According to recent studies, the country that produces the most plastic waste is China. It generates over 30% of the world’s total plastic waste.
Is plastic waste production increasing worldwide?
Yes, unfortunately, plastic waste production is increasing worldwide. It has been estimated that the global production of plastic waste has increased by more than 400% over the past 30 years.
What are the consequences of plastic waste?
Plastic waste has numerous negative consequences on the environment and human health. It pollutes our oceans, harms marine life, contributes to climate change, and poses a risk to human health through the contamination of food and water sources.
How can we reduce plastic waste?
There are several ways we can reduce plastic waste. We can start by using reusable bags, water bottles, and food containers instead of single-use plastic ones. Recycling and composting are also important. Additionally, governments and businesses can implement policies and initiatives to reduce plastic waste on a larger scale.
Are there any countries that are successfully managing their plastic waste?
Yes, there are some countries that are successfully managing their plastic waste. For example, Germany has one of the highest recycling rates in the world and has implemented various policies to reduce plastic waste. Other countries like Sweden and Switzerland are also known for their effective waste management systems.