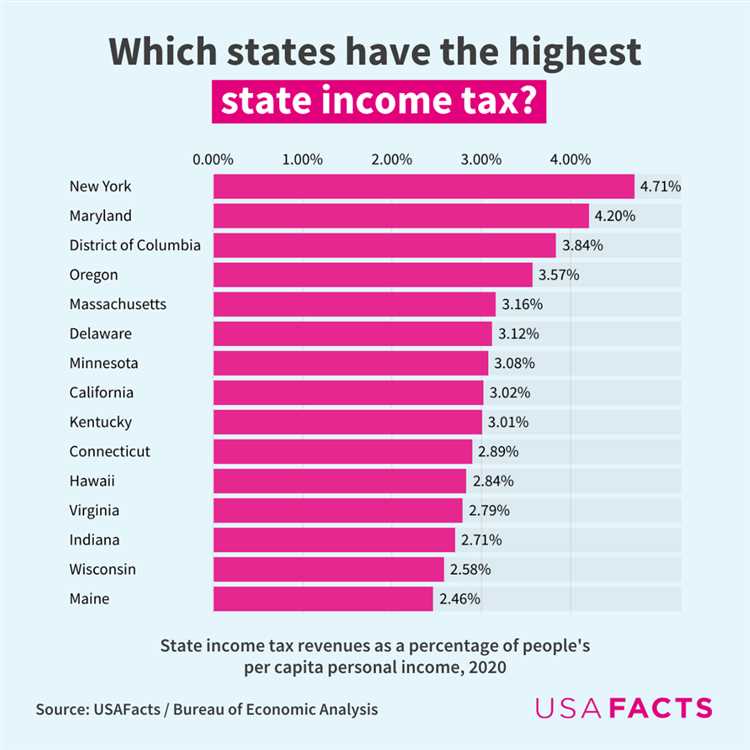
When it comes to taxes, some states stand out for their high tax rates and substantial revenue collected. These top-taxing states are known for their robust tax systems that help fund various public services and infrastructure projects. In this article, we will take a closer look at the most tax-rich state in the US and explore the factors that contribute to its high tax burden.
The most tax-rich state in the US is known for its progressive tax structure and extensive range of taxes. With a strong emphasis on income and property taxes, this state ensures that its residents contribute a significant portion of their earnings towards state funding. Additionally, the state imposes sales taxes on various goods and services, further bolstering its revenue streams.
One of the key reasons behind the high tax burden in this state is the need to maintain and develop its extensive infrastructure. From roads and bridges to public transportation systems, the state invests heavily in improving its infrastructure to support economic growth and ensure the well-being of its residents. These ambitious infrastructure projects require substantial funding, which is primarily obtained through taxation.
Furthermore, this tax-rich state is often praised for its robust social programs and public services. The revenue generated from taxes contributes to funding essential services such as education, healthcare, and social welfare programs. The state prioritizes the well-being of its residents and strives to provide high-quality services to all its citizens, which necessitates a higher tax burden.
- Overview of State Taxes in the US
- Income Tax:
- Sales Tax:
- Property Tax:
- The State with the Highest Overall Tax Burden
- Analysis of Income Taxes in the Top-Taxing States
- A Closer Look at Sales and Property Taxes
- Comparing Business Taxes in the Top-Taxing States
- Discussion on the Impact of High State Taxes
- Q&A,
- Which state in the US has the highest taxation?
- What are the factors that make a state tax-rich?
- How does California compare to other states in terms of taxation?
- What are some of the effects of high taxation in a state?
- Are there any states in the US with low taxation?
Overview of State Taxes in the US
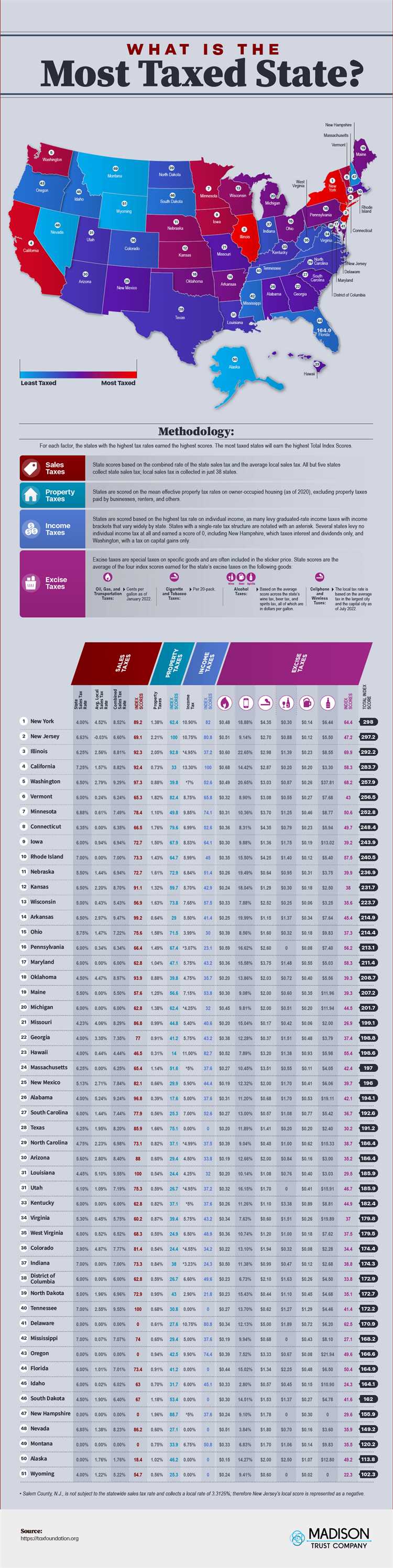
State taxes play a crucial role in the financial well-being of each state in the US. These taxes serve as a significant source of revenue for states to fund public services and infrastructure. Understanding the different types of state taxes is essential for both individuals and businesses operating within the country.
Income Tax:
Income tax is a tax imposed on individuals and businesses based on their taxable income. Each state has the authority to set its own income tax rates and brackets. Some states have a progressive tax system, where the tax rates increase as income levels rise, while others have a flat tax rate for all income levels.
Sales Tax:
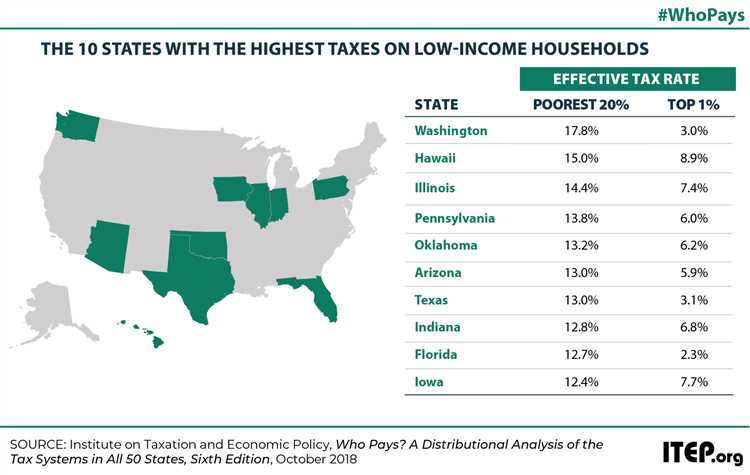
Sales tax is a tax levied on the sale of goods and services. Similar to income tax, states have the power to set their own sales tax rates. The rates can vary significantly from state to state and may also include local sales tax imposed by cities or counties.
Property Tax:
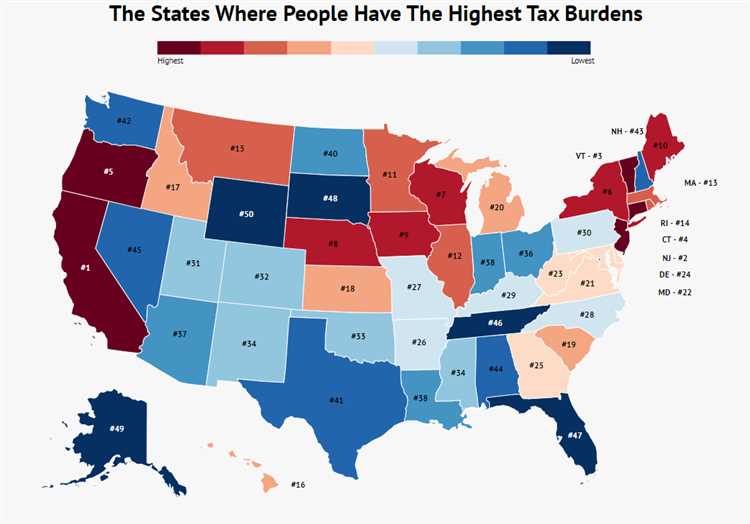
Property tax is a tax levied on real estate properties, including land and buildings. The amount of property tax owed is based on the assessed value of the property. Each state has its own method of assessing property values and determining tax rates, which can vary widely.
In addition to these major taxes, states may also impose other taxes such as estate tax, inheritance tax, fuel tax, and excise tax on specific goods or services. Some states have additional taxes and fees, such as vehicle registration fees or tolls, to fund transportation infrastructure.
It is important to note that not all states have the same tax structure, and the tax burden can vary greatly from state to state. Some states have higher overall tax rates but may offer certain deductions or exemptions that can lower the individual’s tax liability. Understanding the tax structure of a state is crucial when making financial decisions, such as where to locate a business or where to live.
In conclusion, state taxes are a vital component of a state’s revenue and play a significant role in financing public services and infrastructure. Knowing the different types of state taxes and their variations across states is essential for individuals and businesses to navigate the complex tax landscape in the US.
The State with the Highest Overall Tax Burden
When it comes to taxes, some states have a heavier burden on their residents than others. One state that stands out with the highest overall tax burden is California. Known for its high cost of living and progressive tax structure, California consistently ranks at the top when it comes to total taxes paid by its residents.
California has a progressive income tax system, which means that higher earners are subject to higher tax rates. The state also has one of the highest sales tax rates in the country, which adds to the overall tax burden for its residents. Additionally, property taxes in California can be quite high, especially in areas with high housing costs.
Furthermore, California imposes various additional taxes and fees, such as fuel taxes, vehicle registration fees, and business taxes. These additional taxes contribute to the high overall tax burden experienced by the residents of the state.
Despite the high tax burden, California also offers various services and benefits to its residents, including quality education, healthcare, and infrastructure. These services require funding, which comes in part from the taxes paid by its residents.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| Income Tax | Up to 13.3% |
| Sales Tax | 7.25% (statewide average) |
| Property Tax | 1% of assessed value (plus additional local rates) |
| Fuel Tax | $0.417 per gallon |
| Vehicle Registration Fee | Varies based on vehicle value and other factors |
It’s important to note that the tax burden can vary for individuals based on factors such as income level, deductions, and credits. While California may have the highest overall tax burden, it’s also home to some of the highest income earners in the country. Ultimately, the decision to reside in a high-tax state like California is a personal one, weighing the benefits of the state against the financial implications of higher taxes.
Analysis of Income Taxes in the Top-Taxing States
When it comes to income taxes, some states in the US impose higher rates than others. In this analysis, we will dive into the details of the income tax structures in the top-taxing states. Understanding how these states tax individual income can provide valuable insights into the overall tax burden and financial landscape of these regions.
1. California:
- California has one of the highest income tax rates in the country, with a progressive tax structure that ranges from 1% to 13.3%.
- Individuals earning more than a certain threshold are subject to the top marginal rate of 13.3%.
- California also has a high standard deduction and provides various tax credits and incentives for certain industries and individuals.
2. New York:
- New York also imposes a progressive income tax structure, with rates ranging from 4% to 8.82%.
- The highest tax bracket applies to individuals earning over a certain threshold.
- In addition to income taxes, New York City levies additional local taxes on residents.
3. Hawaii:
- Hawaii has a relatively high income tax rate that ranges from 1.4% to 11%.
- The state uses a progressive tax structure, with higher rates for those with higher incomes.
- Hawaii also has a state general excise tax, which is similar to a sales tax and is applied to most transactions.
4. Oregon:
- Oregon has a unique income tax structure with rates ranging from 4.75% to 9.9%.
- The state imposes a higher tax rate on individuals with higher incomes.
- Oregon also has no sales tax, which can slightly offset the higher income tax rates.
5. Minnesota:
- Minnesota has a progressive income tax structure with rates ranging from 5.35% to 9.85%.
- The state has multiple income tax brackets, with the highest rate applying to individuals earning the most.
- Minnesota also has a sales tax, making it important to consider the overall tax burden when evaluating the state’s tax policy.
These are just a few examples of the top-taxing states and their income tax structures. It’s important to note that individual situations can vary depending on deductions, credits, and other factors. Understanding these tax structures can help individuals and businesses plan their finances and make informed decisions.
A Closer Look at Sales and Property Taxes
When it comes to paying taxes, income tax is often the first thing that comes to mind. However, there are two other major types of taxes that individuals and businesses must also consider: sales tax and property tax.
Sales tax is a tax imposed on the sale of goods and services. It is typically a percentage of the purchase price and is paid by the consumer at the time of purchase. Different states have different sales tax rates, and some states even allow cities and counties to impose additional local sales taxes. This means that the total amount of sales tax paid can vary depending on where you live or shop. Sales tax revenue is an important source of funding for state and local governments, helping to finance services and infrastructure.
Property tax, on the other hand, is a tax imposed on real estate, such as land and buildings. It is generally based on the assessed value of the property and is paid by the property owner. Property tax rates can vary significantly between states and even within counties, and the revenue generated from property taxes is a major source of funding for local governments. It helps pay for schools, roads, police and fire departments, and other essential services.
Both sales tax and property tax play a crucial role in the overall tax system of each state. While income tax might grab most of the attention, it is important to recognize the impact of sales and property taxes on individuals and businesses. Understanding these taxes can help individuals make informed decisions about their purchases and property ownership, and businesses can factor these taxes into their pricing and financial planning.
In conclusion, sales tax and property tax are significant components of the tax system in the United States. They provide a vital source of revenue for state and local governments, and understanding their implications is essential for individuals and businesses alike.
Comparing Business Taxes in the Top-Taxing States
When it comes to the top-taxing states in the US, business owners are always keeping an eye on how much they have to pay in taxes. Let’s take a closer look at how the business tax environments differ between these states.
State A: In State A, businesses face a high corporate tax rate of 10%, which is one of the highest in the country. Additionally, there is a personal income tax that business owners must pay on their profits. However, State A offers some tax incentives to attract businesses, such as tax credits for research and development activities.
State B: Businesses in State B also face a high corporate tax rate of 9%, but there is no personal income tax on business profits. Instead, business owners in State B are subject to a flat tax rate on their personal income. State B has a reputation for having a relatively business-friendly environment, with few additional taxes or regulations.
State C: In State C, the corporate tax rate is moderate at 7%, and there is no personal income tax on business profits. However, business owners are required to pay a high sales tax on goods and services. State C also offers tax incentives for businesses, such as property tax abatements for new investments.
State D: State D has a high corporate tax rate of 8%, but it allows businesses to deduct federal taxes from their taxable income. This deduction helps to offset the burden of the state tax. Additionally, State D has a low personal income tax rate on business profits, making it a more attractive option for business owners.
While these are just a few examples, it’s clear that business taxes in the top-taxing states can vary significantly. Business owners need to carefully consider the tax implications when choosing where to establish or expand their operations.
In conclusion, the top-taxing states have different approaches to business taxes. Some prioritize corporate taxes, while others focus on personal income taxes or sales taxes. Understanding these differences can help business owners make informed decisions and optimize their tax strategies.
Discussion on the Impact of High State Taxes
High state taxes can have both positive and negative effects on a state’s economy and its residents. This section will discuss some of the potential impacts of high state taxes.
One of the primary concerns with high state taxes is the potential negative impact on economic growth. When individuals and businesses are subject to higher tax rates, they may have less money to invest, hire employees, or expand their operations. This can hinder economic growth and make a state less attractive to businesses and individuals looking to relocate or start new ventures.
Additionally, high state taxes can place a burden on taxpayers, especially those with lower incomes. This can reduce their disposable income and make it more difficult for them to meet their basic needs or save for the future. It can also discourage consumption, as individuals may choose to save their money rather than spend it due to the high tax burden. This can lead to a slowdown in economic activity and reduced consumer demand.
On the other hand, high state taxes can also provide funding for important public services and infrastructure. States with higher tax rates may be able to invest more in education, healthcare, transportation, and other essential services that can improve the quality of life for their residents. This can attract businesses and individuals who value these services and are willing to pay higher taxes for them.
Furthermore, high state taxes can contribute to a more progressive tax system, where individuals with higher incomes pay a larger share of their income in taxes. This can help reduce income inequality and provide more funding for social programs that support the most vulnerable members of society.
It’s important to note that the impact of high state taxes can vary depending on a variety of factors, including the overall tax burden, the competitiveness of neighboring states, the specific tax policies in place, and the overall economic climate. Different states may experience different effects based on their unique circumstances.
In conclusion, high state taxes can have both positive and negative impacts on a state’s economy and its residents. While they can potentially hinder economic growth and place a burden on taxpayers, they can also provide funding for important public services and contribute to a more progressive tax system. The impact of high state taxes will depend on a range of factors and should be evaluated in the context of a state’s specific circumstances.
Q&A,
Which state in the US has the highest taxation?
The most tax-rich state in the US is California.
What are the factors that make a state tax-rich?
There are several factors that contribute to a state being tax-rich. These can include high income tax rates, high sales tax rates, and high property tax rates.
How does California compare to other states in terms of taxation?
California has the highest top marginal income tax rate in the country, as well as high sales tax rates and property tax rates. Overall, it is considered one of the most tax-rich states in the US.
What are some of the effects of high taxation in a state?
High taxation can have both positive and negative effects. On the positive side, it can provide funding for important public services such as education and healthcare. On the negative side, it can put a burden on businesses and individuals, potentially leading to a loss of economic growth and residents relocating to states with lower taxation.
Are there any states in the US with low taxation?
Yes, there are several states in the US with low taxation. For example, states like Florida, Nevada, and Texas have no income tax, while states like Alaska and Wyoming have no state sales tax. These states are often seen as more tax-friendly for businesses and individuals.