In our modern world, plastic has become an integral part of our daily lives. It is used in nearly everything we buy and use, from packaging to household items. However, not all plastics are created equal when it comes to safety. With the growing concerns about the impact of plastics on our health and the environment, it is important to understand which types of plastics are considered the safest.
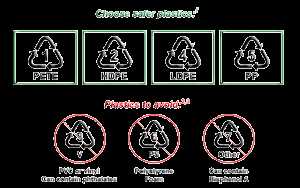
One type of plastic that is often touted as being safe is polyethylene, commonly known as PE. It is a versatile plastic that is used in a wide range of products, including food packaging, bottles, and toys. PE is considered safe because it does not contain harmful chemicals, such as BPA or phthalates, which have been linked to various health issues.
Another safe option is polypropylene, or PP. This type of plastic is commonly used in food containers, microwave-safe dishes, and medical supplies. PP is considered safe because it has a high melting point, which means it is less likely to release harmful substances when heated. It is also resistant to chemical leaching, making it a preferred choice for food storage.
On the other hand, there are types of plastics that are best to avoid when it comes to safety. For example, polystyrene, or PS, is commonly used in disposable coffee cups, food containers, and packaging materials. PS has been found to release toxic chemicals when heated, which can have harmful effects on our health. Similarly, polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is another type of plastic that is best to avoid. PVC contains additives such as phthalates, which have been associated with hormone disruption and other health problems.
In conclusion, when it comes to plastic safety, it is important to choose materials that are labeled as BPA-free and phthalate-free. Polyethylene and polypropylene are considered the safest options, while polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride should be avoided. By making informed choices, we can reduce our exposure to potentially harmful chemicals and contribute to a healthier and safer environment.
- The Safest Type of Plastic
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Other Safe Plastics
- Evaluating Plastic Safety Ratings
- Understanding Different Types of Plastics
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET or PETE)
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Examining Health Risks Associated with Plastics
- Exploring Environmental Impact of Plastics
- Production
- Usage and Disposal
- Sustainable Solutions
- Tips for Reducing Plastic Usage
- 1. Bring Your Own Bags
- 2. Use a Reusable Water Bottle
- 3. Say No to Plastic Straws
- 4. Choose Non-Plastic Alternatives
- 5. Buy in Bulk
- 6. Support Plastic-Free Businesses
- 7. Keep a Reusable Utensil Set
- 8. Recycle Properly
- Making Informed Choices for a Safer Future
- Question-answer:
- What are the different types of plastic?
- Are all types of plastic safe for use?
- Which type of plastic is considered the safest?
- Is it safe to microwave plastic containers?
The Safest Type of Plastic
When it comes to plastic, safety is a major concern. Many types of plastic can release harmful chemicals into our food and environment, so it’s important to know which types are the safest. Below, we will discuss the safest type of plastic and why it’s considered the best option.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
One of the safest types of plastic is high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This type of plastic is commonly used in food and beverage containers because it is highly resistant to chemicals and does not leach any harmful substances into the products it holds. HDPE is also easy to recycle, which makes it an environmentally friendly choice.
HDPE is known for its durability and strength, making it ideal for packaging and storage purposes. It is commonly used for milk jugs, water bottles, and detergent containers. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved HDPE for use in food packaging, further confirming its safety.
Other Safe Plastics
While HDPE is considered the safest type of plastic, there are a few other types that are also considered safe for use.
- Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene is another safe plastic that is commonly used in food containers, particularly for hot liquids. It has a high melting point, which makes it resistant to heat and chemicals.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET or PETE): PET is commonly used for single-use beverage bottles. While it is generally considered safe, it is recommended to avoid reusing PET bottles as they can degrade over time and release harmful chemicals.
It’s important to note that even though these plastics are considered safe, it’s always a good idea to check for any specific safety recommendations or guidelines for the particular product or container you are using.
In conclusion, if you’re looking for the safest type of plastic, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is the best choice. Its resistance to chemicals, durability, and recyclability make it an excellent option for food and beverage containers. However, it’s always important to make informed choices and be aware of any specific safety guidelines for the plastic products you use.
Evaluating Plastic Safety Ratings
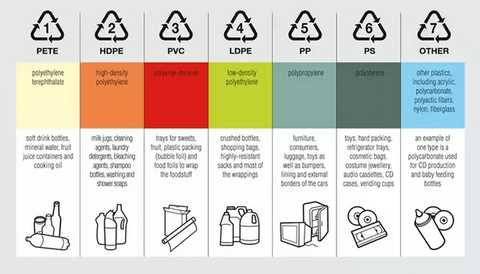
When it comes to determining which type of plastic is the safest, it is important to understand the plastic safety ratings. These ratings are often indicated by a number inside a triangle made of arrows, commonly known as the recycling symbol. However, it is important to note that these symbols do not necessarily indicate the safety of the plastic for direct human contact or consumption.
The numbers inside the recycling symbols range from 1 to 7, with each number representing a different plastic resin. Evaluating plastic safety ratings involves understanding the properties and potential risks associated with each resin:
1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): This is one of the most commonly used plastics for food and beverage containers such as water bottles and soda bottles. While it is generally considered safe for single use, it is not intended for long-term reuse as it may leach chemicals over time.
2. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): This plastic is commonly used for milk jugs, detergent bottles, and other household containers. It is considered safe and generally accepted for food and beverage storage.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC is often used for plumbing pipes, vinyl flooring, and certain packaging materials. It is not recommended for food or beverage storage as it may contain harmful additives like phthalates.
4. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): LDPE is commonly used for plastic bags, plastic wraps, and flexible packaging. It is generally considered safe for food contact.
5. PP (Polypropylene): PP is often used for food containers, including yogurt cups and takeout containers. It is generally considered safe and has a high melting point, making it suitable for microwave use.
6. PS (Polystyrene): PS is used for foam products, disposable food containers, and packaging materials. It is not recommended for food and beverage storage as it may leach styrene, a potential toxic chemical.
7. Other: The number 7 is a catch-all category for other types of plastics that do not fit into the previous six categories. This category includes polycarbonate, which is often used in baby bottles and reusable water bottles. Polycarbonate may leach bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical of concern.
When evaluating plastic safety ratings, it is important to consider factors such as intended use, duration of contact, and potential leaching of chemicals. Additionally, it is always a good idea to look for plastics that are labeled as BPA-free or food-grade to ensure safer use.
In conclusion, understanding plastic safety ratings can help consumers make more informed choices when it comes to selecting plastics for various purposes. While each plastic resin comes with its own safety considerations, it is crucial to always prioritize health and choose plastics that are designed for the specific use in question.
Understanding Different Types of Plastics

Plastics are widely used in our everyday lives, from packaging materials to household items. However, not all plastics are created equal when it comes to safety. Understanding the different types of plastics can help you make more informed choices when it comes to the products you use and the impact they have on your health and the environment.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET or PETE)
PET is commonly used in beverage bottles, food containers, and polyester fabrics. It is considered safe for single-use applications, but it can leach harmful chemicals when exposed to heat or repeated use. It is important to avoid using PET containers for hot liquids or microwaving them.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is commonly used in milk jugs, shampoo bottles, and other household products. It is considered a safe plastic for food and beverage storage, as it does not leach harmful chemicals. It is also recyclable and widely accepted by recycling programs.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE is commonly used in plastic bags, shrink wrap, and squeeze bottles. It is considered safe for food storage, but it may not be accepted by all recycling programs. LDPE is known for its flexibility and durability.
Polypropylene (PP)
PP is commonly used in medicine bottles, yogurt containers, and reusable food storage containers. It is considered safe for food and beverage storage, and it has a high melting point, making it suitable for use in the microwave.
Polystyrene (PS)
PS is commonly used in foam packaging, disposable cups, and takeout containers. It is considered safe for single-use applications, but it can leach styrene, a potential carcinogen, when exposed to heat or acidic foods. It is best to avoid using PS containers for hot liquids or microwaving them.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is commonly used in pipes, vinyl flooring, and shower curtains. It is not safe for food storage or heating, as it can leach harmful chemicals, including phthalates and lead. It is best to avoid PVC whenever possible.
Polycarbonate (PC)
PC is commonly used in water bottles, baby bottles, and food storage containers. It can leach bisphenol A (BPA), a hormone-disrupting chemical, especially when exposed to heat or acidic foods. It is best to avoid PC containers and opt for alternatives labeled “BPA-free.”
Understanding the different types of plastics can help you make safer and more sustainable choices. Remember to look for recycling symbols on plastic products and check with your local recycling program to ensure proper disposal.
Examining Health Risks Associated with Plastics
Plastics have become an integral part of our daily lives, but concerns have been raised about their potential health risks. Various types of plastics are used for different purposes, but not all of them are safe for human health.
One of the main concerns with plastics is the leaching of harmful chemicals into food and beverages. Bisphenol A (BPA), for example, is a commonly used chemical in the production of plastic containers and linings. Studies have shown that BPA can leach into the contents of these containers, especially when exposed to heat or acidic substances. BPA has been linked to hormone disruption and has been associated with various health issues such as obesity, infertility, and developmental problems in children.
Another chemical of concern is phthalates, which are commonly found in plastic products such as vinyl flooring, shower curtains, and food packaging. Phthalates have been linked to hormonal imbalances, reproductive issues, and developmental problems in children. Pregnant women and young children are particularly vulnerable to the effects of phthalate exposure.
In addition to chemical leaching, microplastics have also become a growing concern. These are small particles of plastic that are less than 5 millimeters in size. They are found in a variety of sources, including food, water, and even the air we breathe. Microplastics can enter our bodies through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. The long-term health effects of microplastic exposure are still being studied, but there is evidence to suggest that they may contribute to inflammation, oxidative stress, and damage to internal organs.
It is important to note that not all plastics are created equal when it comes to health risks. Some types of plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are generally considered to have a lower risk of leaching harmful chemicals. These types of plastics are commonly used in food containers and water bottles. However, it is always a good idea to check for labeling that indicates the plastic is BPA-free or phthalate-free to further minimize any potential risks.
In conclusion, the health risks associated with plastics cannot be ignored. While certain types of plastics are considered safer than others, it is important to be mindful of potential chemical leaching and to reduce exposure whenever possible. Choosing safer alternatives, such as glass or stainless steel containers, can help minimize the potential health risks associated with plastics.
Exploring Environmental Impact of Plastics
Plastics have become an integral part of our daily lives, but it is important to understand the environmental impact they have. From production to disposal, plastics can have a significant effect on our ecosystems and overall sustainability.
Production
The production of plastics involves the extraction of raw materials, such as fossil fuels, and the use of energy-intensive processes. This leads to the emission of greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Additionally, the production process can release harmful pollutants into the air and water, further degrading the environment.
Plastic production also requires large amounts of water, which can strain local water supplies and harm aquatic ecosystems. The extraction of fossil fuels, a key component in plastic production, often involves destructive drilling practices that disrupt natural habitats and endanger wildlife.
Usage and Disposal
Plastics are lightweight and versatile, making them attractive for various applications. However, their durability also presents a challenge when it comes to disposal. The vast majority of plastics are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years.
Improper disposal of plastics, such as littering or inadequate recycling, leads to their accumulation in landfills, waterways, and oceans. This pollution harms wildlife, as animals can get entangled in plastic debris or mistakenly ingest it. Plastics can also break down into microplastics, tiny particles that can enter the food chain and pose potential risks to human health.
Sustainable Solutions
To mitigate the environmental impact of plastics, it is crucial to prioritize sustainable solutions. This includes reducing the production and consumption of single-use plastics, promoting recycling and waste management initiatives, and encouraging the development of alternative materials.
Efforts are underway to improve the recyclability of plastics, develop biodegradable alternatives, and invest in innovative technologies. Additionally, consumer awareness and education play a vital role in reducing plastic waste and encouraging responsible consumption habits.
Government regulations and policies can also create incentives for businesses to adopt more sustainable practices and promote the development of environmentally friendly materials. By working together, we can make a positive impact and create a more sustainable future for our planet.
Tips for Reducing Plastic Usage

Plastic pollution is a major environmental concern that is impacting our planet. One of the most effective ways to combat this issue is by reducing our personal plastic usage. Here are some tips to help you reduce your plastic footprint:
1. Bring Your Own Bags
When you go shopping, bring your own reusable bags instead of relying on plastic bags provided by the store. Keep a few reusable bags in your car or bag so that you always have them on hand.
2. Use a Reusable Water Bottle
Avoid using single-use plastic water bottles by investing in a reusable water bottle. This not only helps reduce plastic waste but also saves you money in the long run.
3. Say No to Plastic Straws
Plastic straws are one of the most commonly found plastic items in the ocean. Skip the straw altogether or opt for reusable metal or bamboo straws instead.
4. Choose Non-Plastic Alternatives
When purchasing household items, look for non-plastic alternatives. For example, choose glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic ones, or invest in reusable silicone food wraps instead of disposable plastic cling wraps.
5. Buy in Bulk
Buying in bulk reduces the amount of packaging used overall. Instead of purchasing individually wrapped items, choose larger quantities and store them in reusable containers at home.
6. Support Plastic-Free Businesses
Support businesses that are committed to reducing their plastic usage. Look for stores and restaurants that use eco-friendly packaging and offer plastic-free alternatives.
7. Keep a Reusable Utensil Set
Carry a compact set of reusable utensils, such as a stainless steel fork, knife, and spoon, in your bag or car. This way, you can avoid using disposable plastic utensils when you eat out.
8. Recycle Properly
Make sure you properly recycle plastic items that cannot be avoided entirely. Familiarize yourself with your local recycling guidelines to ensure you’re recycling correctly and effectively.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce your plastic usage and contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet for future generations.
Making Informed Choices for a Safer Future
As we become more aware of the environmental impacts of plastics, it’s important to make informed choices when selecting the types of plastics we use. This not only helps protect the planet, but also ensures the safety of ourselves and future generations.
One factor to consider when choosing plastic is its safety. Certain types of plastics are known to leach harmful chemicals into food and beverages, posing potential health risks. By understanding the different plastic types, we can make more informed decisions about the products we purchase and use.
One of the safest types of plastic is high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This plastic is commonly used for milk jugs, detergent bottles, and food storage containers. HDPE is considered safe for use in direct contact with food and beverages and is not known to leach harmful chemicals.
Another safe plastic option is polypropylene (PP). This plastic is often used for reusable food containers, yogurt cups, and medicine bottles. PP is generally recognized as safe and does not leach harmful chemicals.
On the other hand, plastics such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polystyrene (PS) are known to be less safe. PVC is used in pipes, vinyl flooring, and some food packaging, but it can leach chemicals like phthalates and lead. PS, often used in Styrofoam products and disposable food containers, can potentially leach styrene, a possible carcinogen.
It’s important to note that even with safe plastics, proper use and care is necessary to minimize any potential risks. Avoid microwaving plastic containers or using them to store hot liquids, as heat can accelerate the leaching process. Opt for glass or stainless steel containers for these purposes instead.
| Plastic Type | Common Uses | Safety Rating |
|---|---|---|
| High-density polyethylene (HDPE) | Milk jugs, detergent bottles, food storage containers | Safe |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Reusable food containers, yogurt cups, medicine bottles | Safe |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | Pipes, vinyl flooring, some food packaging | Less safe |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Styrofoam products, disposable food containers | Less safe |
In conclusion, when it comes to plastic, making informed choices is crucial for a safer future. By choosing plastics like HDPE and PP, we can minimize the potential risks of harmful chemical leaching. It’s also important to follow proper use and care guidelines to further ensure safety. Together, we can create a more sustainable and safe world for ourselves and future generations.
Question-answer:
What are the different types of plastic?
There are several types of plastics, including polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
Are all types of plastic safe for use?
No, not all types of plastic are safe for use. Some types of plastic, such as PVC and polystyrene, can release harmful chemicals when heated or come into contact with certain substances.
Which type of plastic is considered the safest?
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is generally considered to be the safest type of plastic. It is commonly used for water bottles and food packaging. PET does not contain harmful chemicals and is considered to have a low risk of leaching.
Is it safe to microwave plastic containers?
It is generally not recommended to microwave plastic containers, as they can release harmful chemicals when heated. However, some plastic containers are labeled as microwave-safe, meaning they are designed to withstand high temperatures without releasing harmful substances.