Plastic waste has become a global crisis in recent years, with devastating consequences for the environment and human health. As more and more plastic is produced and consumed worldwide, it is important to understand which countries are the biggest culprits when it comes to plastic waste.
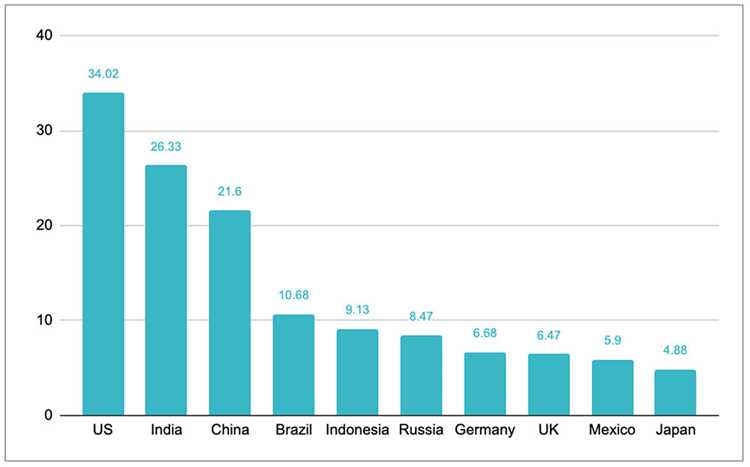
According to a recent report by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), the United States is the country that produces the most plastic waste in the world. With its high population and consumption rates, the US generates a staggering amount of plastic waste every day. This waste often ends up in landfills or, even worse, in the ocean, where it poses a serious threat to marine life.
However, the US is not the only country contributing to the plastic waste crisis. China, which has the largest population in the world, is also a major player. Despite recent efforts to reduce plastic consumption and improve waste management practices, China still generates a significant amount of plastic waste. Other countries, such as India, Indonesia, and Brazil, also rank high on the list of plastic waste producers.
It is important to note that plastic waste is not just a problem for developing countries. In fact, some of the wealthiest nations, such as Japan and Germany, also generate substantial amounts of plastic waste. This highlights the need for global action and cooperation to address the plastic waste crisis and find sustainable solutions for the future.
- Plastic Waste: A Global Problem
- The Impact of Plastic Waste on the Environment
- 1. Pollution
- 2. Marine Life
- 3. Ecosystem Disruption
- 4. Microplastics
- Measuring Plastic Waste: Which Approach is Most Accurate?
- Analysing Plastic Waste Generation by Country
- The Top Plastic Waste Generating Countries
- The Impact on the Environment
- Which Country Produces the Most Plastic Waste?
- The Consequences of Plastic Waste Mismanagement
- Addressing the Plastic Waste Crisis: Global Initiatives and Solutions
- The Role of International Agreements
- Legislation and Regulations
- Innovation and Technology
- Q&A:
- Which country is the biggest producer of plastic waste?
- What are the reasons behind the high plastic waste production in these countries?
- How does this plastic waste affect the environment?
- What measures are being taken to reduce plastic waste?
Plastic Waste: A Global Problem
Plastic waste has become a significant global problem, affecting countries across the world. It poses a threat to the environment, wildlife, and human health. The excessive use of single-use plastics and poor waste management practices have led to a massive accumulation of plastic waste in landfills, oceans, and other natural habitats.
Plastic waste is particularly problematic due to its durability and slow decomposition rate. It can take hundreds of years for plastic to break down, leading to long-lasting pollution that harms ecosystems and biodiversity. Additionally, plastic waste in the oceans poses a direct threat to marine life, with animals often mistaking plastic for food or becoming entangled in plastic debris.
The production and consumption of plastic have skyrocketed in recent decades, with an estimated 359 million metric tons of plastic produced worldwide in 2018 alone. This rapid increase has outpaced recycling and waste management efforts, resulting in a large portion of plastic waste being discarded improperly.
While plastic waste is a global problem, some countries are more responsible for its generation than others. Factors such as population size, lifestyle, industrial activities, and waste management infrastructure play a significant role in determining a country’s plastic waste output. Multiple studies have identified countries such as China, the United States, and Indonesia as major contributors to global plastic waste.
The impact of plastic waste goes beyond environmental concerns. It has economic implications as well, with the cleanup and management of plastic waste costing governments and industries billions of dollars each year. Moreover, plastic waste can contaminate food and water sources, leading to potential health risks for humans.
To address the plastic waste crisis, countries and international organizations are working together to implement measures such as plastic waste reduction targets, bans on single-use plastics, and improved recycling and waste management systems. It is crucial for individuals, governments, and industries to take collective action and adopt more sustainable practices to combat the global problem of plastic waste.
The Impact of Plastic Waste on the Environment
Plastic waste has emerged as one of the most significant environmental challenges faced by our planet. The impact of this waste on the environment is immense and has far-reaching consequences for both humans and wildlife. Here are some key areas where plastic waste has a negative impact:
1. Pollution
Plastic waste pollutes our land, oceans, and air. Improper disposal of plastic items such as bottles, bags, and packaging leads to the accumulation of plastic in our environment. This not only affects the aesthetic beauty of our surroundings but also poses a serious threat to the health of humans and animals.
2. Marine Life
Plastic waste in the oceans poses a grave threat to marine life. Marine animals often mistake plastic debris for food, which can lead to fatal consequences. Additionally, plastic waste can entangle marine creatures, causing injuries, suffocation, and death.
3. Ecosystem Disruption
The accumulation of plastic waste disrupts ecosystems and harms biodiversity. Plastic pollution affects the balance of ecosystems, as organisms may struggle to survive in a contaminated environment. This disruption ultimately impacts the stability and health of ecosystems around the world.
4. Microplastics
Plastic waste breaks down into tiny particles over time, forming microplastics. These microplastics can be found in soil, water, and even the air we breathe. They have the potential to enter the food chain, impacting both human and animal health. The long-term effects of microplastic ingestion are still being researched but are a cause for concern.
In conclusion, the impact of plastic waste on the environment is widespread and alarming. It is crucial for individuals, communities, and governments to take decisive action to reduce plastic waste and find sustainable alternatives. By addressing this issue collectively, we can mitigate the environmental damage caused by plastic waste and protect the future well-being of our planet.
Measuring Plastic Waste: Which Approach is Most Accurate?
When it comes to measuring plastic waste, finding the most accurate approach can be a challenging task. Given the vast amount of plastic waste generated globally, having reliable data is crucial for understanding the extent of the problem and developing effective solutions. However, different measuring methods can lead to varying results, making it difficult to determine which approach is the most accurate.
One common approach to measuring plastic waste is through waste audits. Waste audits involve sorting and categorizing plastic waste to determine the composition and quantity of different types of plastic. This approach provides valuable insights into the types of plastic being discarded and helps identify areas for improvement in waste management practices. However, waste audits may not capture all plastic waste, as they rely on samples and may not accurately reflect the true extent of plastic waste generation.
Another approach is through the analysis of plastic waste in landfills. Landfills are a common destination for plastic waste that is not properly managed or recycled. By studying the plastic waste in landfills, researchers can estimate the amount of plastic that is being discarded. However, this approach has certain limitations as well, as not all plastic waste ends up in landfills, and the data may not be representative of the entire plastic waste stream.
Surveys and questionnaires are also used to measure plastic waste. These methods involve collecting data from individuals and households about their plastic usage and disposal habits. While surveys provide valuable insights into individual behavior, they rely on self-reporting, which can be subjective and prone to bias. Moreover, surveys may not capture the plastic waste generated by other sectors such as industries and commercial establishments.
Remote sensing and satellite imagery are emerging technologies that have the potential to provide a more comprehensive view of plastic waste. These methods involve using satellite imagery to identify and quantify areas with high plastic waste concentration, such as plastic-covered landfills or polluted bodies of water. While remote sensing can provide valuable data on the spatial distribution of plastic waste, it may not accurately measure the total volume of plastic waste generated.
Ultimately, the most accurate approach to measuring plastic waste may lie in combining multiple methods. By using a combination of waste audits, landfill analysis, surveys, and remote sensing, researchers can obtain a more holistic understanding of the plastic waste problem. This multi-dimensional approach can help in developing targeted strategies and policies to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable practices.
While it may be challenging to determine the most accurate approach, ongoing research and advancements in technology are improving our ability to measure plastic waste. By continuing to refine and validate these measurement methods, we can obtain more accurate data and make informed decisions to address the plastic waste crisis.
Analysing Plastic Waste Generation by Country
Plastic waste generation is a major environmental issue that affects countries around the world. The amount of plastic waste generated by a country can have significant implications on its environment, economy, and public health. In this analysis, we will examine the plastic waste generation by different countries and highlight the top contributors to this global problem.
The Top Plastic Waste Generating Countries
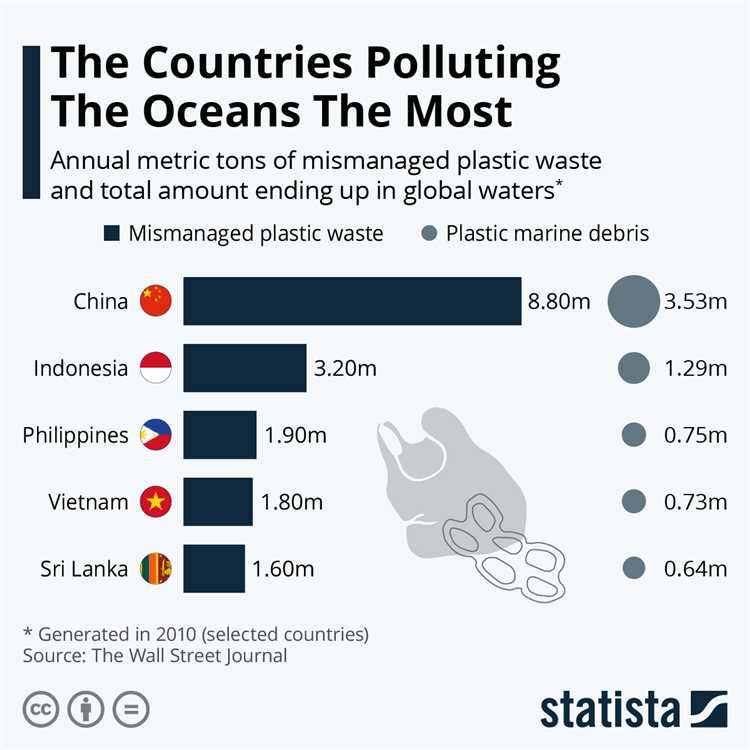
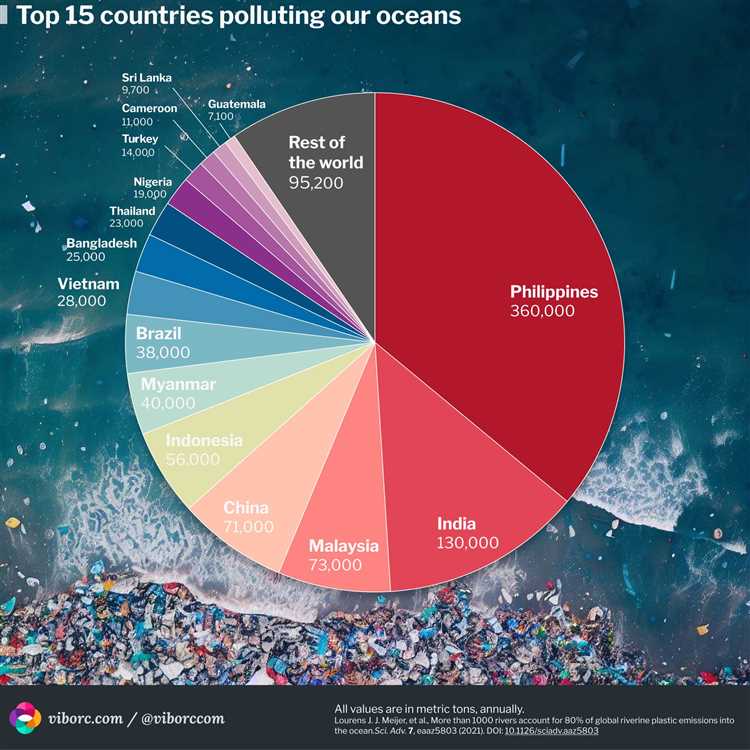
According to recent data, some of the top plastic waste generating countries are China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam. These countries are located in regions with high population densities and have rapidly growing economies, which contribute to increased plastic consumption and waste generation.
China, with its large population and expansive manufacturing industry, has been the biggest contributor to global plastic waste generation for many years. However, efforts are being made to reduce plastic waste in the country through policies and initiatives promoting recycling and banning certain single-use plastic items.
The Impact on the Environment
The excessive plastic waste generated by these countries has a severe impact on the environment. Plastic waste often finds its way into rivers and oceans, polluting water bodies and harming marine life. Landfills filled with plastic waste contribute to soil contamination and leach harmful chemicals into the surrounding environment.
Furthermore, the disposal of plastic waste often involves burning, which releases toxic emissions into the air and contributes to air pollution. This pollution not only affects the immediate surroundings but can also travel long distances, causing health issues for communities living far from the waste disposal sites.
Conclusion
The analysis of plastic waste generation by country highlights the need for global collaboration to address this pressing issue. Efforts should be made to reduce plastic consumption, promote recycling, and develop sustainable alternatives to single-use plastics. By working together, countries can mitigate the negative impacts of plastic waste on the environment and create a cleaner and healthier future.
Which Country Produces the Most Plastic Waste?
Plastic waste has become a major global environmental issue, with the production and disposal of plastics contributing to pollution, climate change, and harm to marine life. While many countries are working towards reducing their plastic waste, there are still a few leading contributors to the global plastic waste problem.
According to a study conducted by the Break Free From Plastic movement, the top 5 countries that produce the most plastic waste are:
- China: With its large population and industrial growth, China is responsible for the highest amount of plastic waste production in the world. The country consumes a significant amount of plastic products, contributing to its high plastic waste output.
- United States: As one of the most developed countries, the United States produces a substantial amount of plastic waste. The country’s consumption habits and reliance on disposable plastic products contribute to its high plastic waste generation.
- India: With a growing population and rapid urbanization, India has witnessed a significant increase in plastic waste production. Inadequate waste management systems and the lack of awareness about sustainable practices further exacerbate the problem.
- Indonesia: Indonesia is known for its stunning natural landscapes, but it is also one of the world’s largest contributors to plastic waste. The country’s booming tourism industry and the improper disposal of plastic waste contribute to its high plastic waste production.
- Philippines: Similar to Indonesia, the Philippines’ beautiful beaches and natural attractions are marred by its significant plastic waste problem. The country generates a considerable amount of plastic waste due to inadequate waste management infrastructure and the lack of awareness about plastic pollution.
These countries play a significant role in global plastic waste production, but it’s important to remember that plastic waste is a global issue that requires collective efforts to address. Efforts are being made globally to reduce plastic waste, such as implementing plastic bans, promoting recycling, and advocating for sustainable alternatives to plastic products. It is crucial for countries worldwide to work together and prioritize sustainable solutions to tackle the plastic waste problem and protect our environment.
The Consequences of Plastic Waste Mismanagement
Plastic waste mismanagement has become a global crisis that poses severe consequences for the environment, wildlife, and human health. When plastic waste is not properly managed, it ends up polluting our land, rivers, and oceans, causing significant harm to ecosystems and biodiversity.
One of the major consequences of plastic waste mismanagement is marine pollution. Plastic waste that enters the oceans poses a serious threat to marine life. Marine animals like turtles, whales, and seabirds often mistake plastic debris for food and ingest it, leading to suffocation, internal injuries, and death. Moreover, plastics in the oceans break down into smaller pieces known as microplastics, which can be ingested by smaller marine organisms and enter the food chain, ultimately affecting human health.
Plastic waste mismanagement also contributes to climate change. The production and incineration of plastics result in the release of greenhouse gases, further exacerbating global warming. Additionally, the disposal of plastic waste through open burning releases toxic pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and respiratory problems for humans.
Furthermore, the improper management of plastic waste leads to plastic litter, which is not only unsightly but also clogs drains and waterways, causing flooding and damage to infrastructure. Plastic waste also hinders waste management systems, as its long lifespan and low recycling rates make it difficult to efficiently manage and dispose of.
To address the consequences of plastic waste mismanagement, it is crucial for countries to implement effective waste management strategies, including reduction, recycling, and proper disposal. Adopting sustainable alternatives to single-use plastics and investing in education and awareness campaigns can also help reduce plastic waste and its detrimental impacts on the environment and human health.
Addressing the Plastic Waste Crisis: Global Initiatives and Solutions
The issue of plastic waste has reached critical levels worldwide, prompting global initiatives and solutions to combat the crisis. With plastic pollution threatening ecosystems, endangering marine life, and contributing to climate change, it has become imperative for countries and organizations to take action.
The Role of International Agreements
Recognizing the severity of the plastic waste crisis, numerous international agreements have been established to address the issue. The Basel Convention, for instance, seeks to control the transboundary movement of plastic waste and promote its environmentally sound management. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has also launched the Clean Seas campaign, which aims to reduce marine pollution, including plastic waste, through global cooperation and individual action.
Legislation and Regulations
Many countries have implemented legislation and regulations to reduce plastic waste. Some have imposed bans or restrictions on single-use plastics, such as plastic bags, straws, and styrofoam products. Others have introduced extended producer responsibility schemes, making manufacturers and retailers responsible for the collection and proper disposal of their plastic products. These measures aim to reduce plastic consumption, encourage recycling, and promote the use of alternative materials.
A prime example of successful legislation is the European Union’s Single-Use Plastics Directive, which bans certain single-use plastic products and sets targets for plastic waste reduction and recycling. This directive serves as a model for other countries seeking to tackle plastic waste and transition to a more sustainable economy.
Innovation and Technology
Innovation and technology play a crucial role in addressing the plastic waste crisis. Researchers and inventors around the world are working on alternative materials to replace plastic and developing new recycling technologies. Biodegradable plastics, compostable packaging, and innovative recycling processes are just a few examples of the breakthrough solutions being explored.
Furthermore, initiatives like the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s New Plastics Economy aim to transform the way plastics are designed, used, and reused, promoting a circular economy where waste is minimized and materials are kept in use for as long as possible.
Conclusion:
The plastic waste crisis requires a multi-faceted approach, involving international cooperation, legislation and regulations, and innovation. By implementing and supporting global initiatives and solutions, countries and organizations can make significant progress in tackling this urgent issue. Through collective action and individual responsibility, it is possible to address the plastic waste crisis and create a more sustainable future for our planet.
Q&A:
Which country is the biggest producer of plastic waste?
The biggest producer of plastic waste is China, followed by Indonesia and the Philippines.
What are the reasons behind the high plastic waste production in these countries?
There are several reasons behind the high plastic waste production in these countries. One reason is the large population, which leads to higher consumption and consequently higher waste generation. Another reason is the lack of proper waste management systems and infrastructure.
How does this plastic waste affect the environment?
Plastic waste has a detrimental effect on the environment. It pollutes land, water bodies, and oceans. It also harms wildlife, as animals often mistake plastic for food and can get entangled in it.
What measures are being taken to reduce plastic waste?
Many countries are taking measures to reduce plastic waste. These include implementing plastic bag bans, promoting recycling and waste management practices, and encouraging the use of environmentally friendly alternatives to plastic.