Zero waste is an environmental concept that aims to eliminate the production of waste and promote the efficient use of resources. While achieving zero waste may seem like an ambitious goal for many countries, some nations around the world have made significant progress towards this objective.
One country that has made remarkable strides in achieving zero waste is Norway. With a strong focus on recycling, the country has implemented comprehensive waste management systems and set strict recycling targets. Through these efforts, Norway has managed to recycle more than 97% of its plastic bottles and consistently ranks among the top countries in terms of recycling rates.
Another country leading the way in zero waste is Slovenia. The small European nation has implemented a range of innovative strategies, including waste separation at source and extensive composting programs. As a result, Slovenia has managed to divert more than 80% of its waste from landfills and has become an inspiration for other countries in their zero waste journey.
In Asia, Japan has emerged as a pioneer in waste management and recycling practices. The country has implemented a comprehensive waste separation and recycling program, involving strict regulations and high-tech recycling facilities. Thanks to these efforts, Japan has managed to achieve a recycling rate of over 80%, making it one of the most environmentally conscious countries in the world.
These are just a few examples of countries that have made significant progress towards achieving zero waste. Their experiences serve as inspiration and demonstrate that with a combination of innovative strategies, strong government commitment, and active participation from citizens, a zero waste future is possible.
- The Countries That Have Successfully Achieved Zero Waste
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- Innovators in Waste Management
- Sustainable Practices in the Nordic Countries
- 1. Waste management infrastructure
- 2. Circular economy
- Singapore’s Leading Approach to Waste Reduction
- 1. Public Awareness and Education
- 2. Advanced Recycling Systems
- 3. Circular Economy Initiatives
- Japan’s Effective Waste Management Strategies
- 1. Source Separation
- 2. Waste-to-Energy Incineration
- Successful Waste Reduction Initiatives in Germany
- Advancements in Zero Waste Efforts in South Korea
- Waste Management and Recycling Infrastructure
- Public Awareness and Education
- Question and answer:
- Which countries have achieved zero waste?
- How did Sweden achieve zero waste?
- What are the benefits of achieving zero waste?
- Are there any challenges to achieving zero waste?
- What can individuals do to support zero waste initiatives?
- Which countries have achieved zero waste?
The Countries That Have Successfully Achieved Zero Waste

Zero waste is a concept that aims to reduce and ultimately eliminate the amount of waste that is sent to landfills or incinerators. Several countries around the world have made significant progress in achieving zero waste, implementing innovative strategies and policies to minimize waste generation and maximize recycling and reuse.
Slovenia
Slovenia is often regarded as a leader in waste management and has made remarkable progress towards achieving zero waste. The country has implemented a comprehensive waste management system, which includes separate collection of recyclable materials and organic waste. Slovenia has also invested in waste-to-energy facilities and composting plants, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
Sweden
Sweden is known for its efficient waste management system, which has enabled the country to achieve a near-zero waste lifestyle. Through a combination of source segregation, recycling facilities, and waste-to-energy incineration plants, less than 1% of Sweden’s household waste ends up in landfills. The country also heavily invests in recycling infrastructure and promotes the circular economy.
Other countries that have made notable progress towards zero waste include:
- Germany: Germany has implemented strict waste regulations and recycling programs, leading to high recycling rates and low landfill usage.
- Japan: Japan has implemented advanced waste management practices, encouraging citizens to sort and recycle their waste effectively.
- New Zealand: New Zealand has set a goal to become a zero waste nation by 2020 and has implemented various waste reduction initiatives.
- Scotland: Scotland has set a target of achieving zero waste by 2025 and has implemented measures such as waste prevention programs and recycling infrastructure improvements.
These countries serve as examples and inspiration for others looking to achieve zero waste. Their strategies and policies showcase the importance of a holistic approach to waste management, including waste reduction, recycling, and sustainable resource use.
Innovators in Waste Management
Several countries around the world have made significant progress in waste management and have become innovators in the field. These countries have implemented unique strategies and technologies to achieve zero waste or minimize waste to a great extent.
| Country | Innovations |
|---|---|
| Sweden |
|
| Japan |
|
| Austria |
|
These countries serve as examples for others to follow in their journey towards achieving zero waste. By implementing innovative waste management strategies and technologies, they have managed to minimize waste generation and maximize resource recovery.
Sustainable Practices in the Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries, consisting of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, have been at the forefront of implementing sustainable practices and striving towards zero waste. These countries have a rich history of environmental consciousness and have implemented various initiatives and policies to reduce, recycle, and manage waste effectively.
1. Waste management infrastructure
The Nordic countries have implemented a comprehensive waste management infrastructure that focuses on waste prevention, recycling, and energy recovery. They have developed advanced sorting and recycling systems, ensuring that a significant portion of waste is diverted from landfills. In addition, incineration plants are widely used to recover energy from non-recyclable waste.
2. Circular economy
The Nordic countries have adopted a circular economy approach, emphasizing the reuse, repair, and recycling of products. They have implemented extended producer responsibility programs, requiring manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire life cycle of their products. This includes designing products for durability, recyclability, and ease of repair, as well as establishing systems for product take-back and recycling. By embracing the circular economy model, these countries aim to reduce the use of virgin resources and minimize waste generation.
Denmark has implemented a successful waste-to-energy program, where a large portion of the waste is incinerated to generate electricity and heat.
Finland has made significant progress in waste management by implementing sophisticated waste sorting systems and promoting recycling and composting. The country has also introduced a deposit system for beverage containers, encouraging people to recycle.
Iceland has focused on reducing waste generation by implementing measures such as recycling and composting programs, as well as promoting sustainable consumption and production practices.
Norway has placed a strong emphasis on waste prevention and has implemented strict regulations on waste disposal. The country has also achieved high recycling rates through efficient collection and sorting systems.
Sweden has one of the most advanced waste management systems in the world. The country has successfully implemented measures to reduce waste and has achieved a high level of recycling. Sweden also imports waste from other countries to generate energy through incineration.
In conclusion, the Nordic countries have set a remarkable example in sustainable waste management. Through their comprehensive waste management infrastructure, circular economy approach, and emphasis on waste prevention, recycling, and energy recovery, these countries have achieved significant progress towards zero waste.
Singapore’s Leading Approach to Waste Reduction
Singapore is widely recognized as a global leader in waste reduction. The country has implemented innovative strategies and policies to minimize waste and promote sustainable practices. Through a combination of public awareness campaigns, advanced recycling systems, and circular economy initiatives, Singapore has made significant progress in achieving its goal of becoming a zero-waste nation.
1. Public Awareness and Education
A key pillar of Singapore’s waste reduction strategy is raising public awareness and promoting behavioral change. The government has launched several education campaigns to inform citizens about the importance of waste reduction, recycling, and responsible consumption. These campaigns emphasize the environmental impact of waste and provide practical tips on reducing waste in daily life.
2. Advanced Recycling Systems
Singapore has implemented state-of-the-art recycling systems to maximize resource recovery. The country has a comprehensive recycling infrastructure that includes facilities for recycling various materials, such as paper, plastic, and glass. Advanced technologies, including automated sorting systems and waste-to-energy plants, ensure efficient waste management and minimize landfill waste.
The government also promotes the practice of source separation, where households and businesses separate their recyclable waste from general waste. This allows for easier recycling and reduces contamination of recyclable materials.
3. Circular Economy Initiatives

Singapore is actively promoting the shift towards a circular economy, which aims to minimize waste generation and maximize the use of resources. The government collaborates with industries to develop innovative solutions, such as the adoption of eco-design principles, the development of recycling technologies, and the implementation of product stewardship programs.
Furthermore, Singapore encourages the use of recycled materials and supports industries in developing sustainable manufacturing practices. This enables the country to reduce its reliance on virgin resources and decrease its environmental footprint.
In conclusion, Singapore’s leading approach to waste reduction encompasses public awareness campaigns, advanced recycling systems, and circular economy initiatives. The country’s efforts and achievements in waste reduction serve as an inspiration for other nations striving to achieve zero waste.
Japan’s Effective Waste Management Strategies
Japan is widely recognized as a global leader in waste management, implementing a number of effective strategies to achieve zero waste. Through a combination of government policies, technological advancements, and public participation, Japan has been able to significantly reduce the amount of waste generated and increase recycling rates.
1. Source Separation
One key strategy employed by Japan is source separation, which involves sorting waste into different categories at the point of disposal. This allows for more effective recycling and reduces the amount of waste that goes to landfill. The government has implemented clear guidelines and provided educational materials to ensure that citizens understand the importance of separating waste.
2. Waste-to-Energy Incineration
Japan has also invested heavily in waste-to-energy incineration plants, which use advanced technology to combust waste and generate electricity. This not only helps to reduce the volume of waste that needs to be landfilled but also provides a sustainable source of energy for the country. Strict regulations are in place to ensure these facilities meet stringent environmental standards.
Furthermore, Japan has established a strong recycling culture, with citizens actively participating in recycling programs and initiatives. The government has implemented a comprehensive recycling system that covers a wide range of materials, including paper, plastic, glass, and metals. This system includes collection and sorting facilities, as well as programs to promote recycling awareness.
In conclusion, Japan’s effective waste management strategies, such as source separation, waste-to-energy incineration, and a strong recycling culture, have played a significant role in the country’s success in achieving zero waste. The government’s commitment to environmental sustainability, combined with technological advancements and public participation, has made Japan a model for other countries to follow.
Successful Waste Reduction Initiatives in Germany
Germany is widely recognized as a leader in waste management and has implemented several successful initiatives to reduce waste and promote recycling. These initiatives have significantly contributed to the country’s progress towards achieving zero waste.
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Mandatory Recycling | Germany has implemented strict policies mandating recycling and waste separation. Residents are required to separate their waste into different categories such as paper, plastics, glass, and bio-waste. This initiative has greatly increased the recycling rates in the country and reduced the amount of waste sent to landfills. |
| Extended Producer Responsibility | Under this initiative, manufacturers are responsible for the entire life cycle of their products, including their disposal. This encourages manufacturers to produce goods with fewer resources and facilitates the recycling and proper disposal of waste generated from their products. It has helped to reduce waste and promote a more sustainable approach to product design and manufacturing. |
| Bottle Deposit System | Germany has implemented a successful bottle deposit system, known as Pfand. Consumers pay a small deposit when purchasing beverages in plastic or glass bottles, and they can get the deposit back by returning the empty bottles to designated collection points. This has significantly increased bottle recycling rates and reduced littering. |
| Resource and Energy Recovery | Germany has developed advanced technologies for waste management, including waste-to-energy plants. These facilities convert non-recyclable waste into energy through processes such as incineration. This initiative helps to reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills while generating renewable energy. |
| Education and Awareness Campaigns | Germany places great emphasis on educating and raising awareness among its citizens about waste reduction and recycling. The government organizes various campaigns and programs to promote sustainable waste management practices. These initiatives have helped to instill a culture of environmental responsibility among the population. |
Overall, Germany’s waste reduction initiatives have been highly successful, leading to significant progress in achieving zero waste. The country’s commitment to sustainable waste management and recycling serves as an inspiration for other nations striving to reduce waste and protect the environment.
Advancements in Zero Waste Efforts in South Korea
South Korea has made significant advancements in its efforts to achieve zero waste. The country has implemented a series of policies and initiatives aimed at reducing waste generation, promoting recycling, and promoting sustainable lifestyles.
Waste Management and Recycling Infrastructure
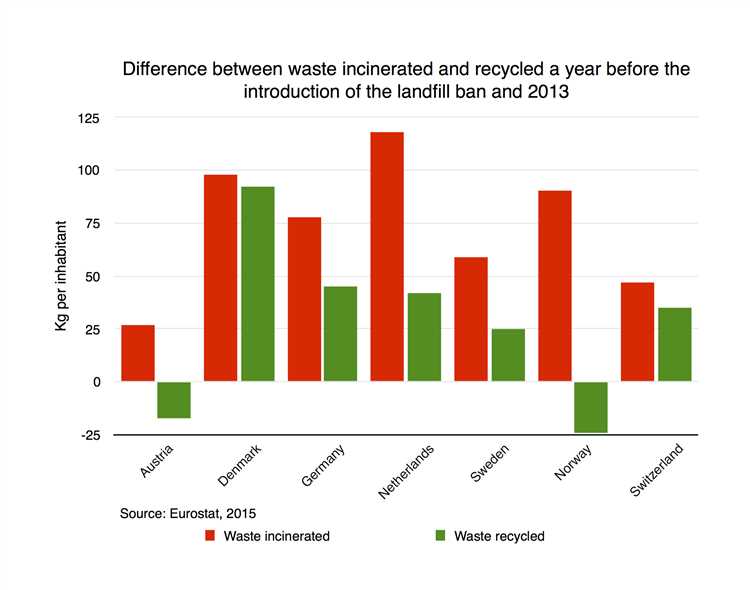
South Korea has developed a robust waste management and recycling infrastructure that has played a crucial role in its zero waste efforts. The country has established a comprehensive network of waste collection systems, including separate bins for different types of waste such as recyclables, food waste, and general waste. This segmented waste collection system has made recycling and waste separation more convenient for the citizens.
Public Awareness and Education

Public awareness and education programs have been vital in promoting zero waste practices in South Korea. The government has launched numerous campaigns to educate the public about the importance of waste reduction and recycling. Schools, community centers, and media outlets have also been involved in spreading awareness about waste management practices and encouraging individuals to adopt sustainable lifestyles.
Technological Innovations
South Korea has embraced technological advancements to enhance its zero waste efforts. The country has invested in state-of-the-art waste treatment facilities and has implemented innovative technologies such as waste-to-energy plants and advanced recycling processes. These technological advancements have not only helped the country reduce waste but also generate clean energy and valuable resources from waste materials.
Partnerships and Collaborations
South Korea has actively collaborated with international organizations, businesses, and local communities to promote zero waste practices. The government has established partnerships with waste management companies, recycling industries, and environmental organizations to develop innovative solutions and share best practices. This collaborative approach has enabled South Korea to learn from others’ experiences and accelerate its progress towards achieving zero waste.
In conclusion, South Korea’s zero waste efforts have been marked by significant advancements in waste management and recycling infrastructure, public awareness and education, technological innovations, and partnerships. These efforts have positioned South Korea as a leader in waste management and have paved the way for a more sustainable future.
Question and answer:
Which countries have achieved zero waste?
Several countries have made significant progress towards achieving zero waste. Some examples include Sweden, which is on track to becoming a zero waste society by 2020, and Slovenia, which has been praised for its successful waste management practices. Many other countries, including New Zealand, Japan, and Germany, have also made efforts to reduce waste and increase recycling rates.
How did Sweden achieve zero waste?
Sweden has achieved zero waste through a combination of policies and programs. The country has implemented strict recycling and waste separation requirements, and has invested in waste-to-energy technologies. Additionally, Sweden has placed a strong emphasis on reducing consumption and promoting a circular economy, where resources are reused and recycled instead of being discarded.
What are the benefits of achieving zero waste?
Achieving zero waste has several benefits. It helps to reduce pollution and conserve natural resources, as less waste is sent to landfills or incinerated. Zero waste also creates economic opportunities, as waste can be seen as a valuable resource that can be recycled or used for energy generation. Additionally, zero waste initiatives often encourage communities to adopt more sustainable practices and promote environmental awareness.
Are there any challenges to achieving zero waste?
Achieving zero waste can be challenging for several reasons. One of the main challenges is changing people’s attitudes and behaviors towards waste. It requires a shift towards a more sustainable mindset, where people prioritize recycling and reducing consumption. Additionally, it can be difficult to implement the necessary infrastructure and systems for waste management, such as recycling facilities and waste-to-energy plants. Financial constraints and lack of public support can also be obstacles to achieving zero waste.
What can individuals do to support zero waste initiatives?
There are several things individuals can do to support zero waste initiatives. One of the most important steps is reducing consumption and using reusable products whenever possible. This can include bringing reusable bags and water bottles, as well as buying products with minimal packaging. Recycling and composting are also key actions that individuals can take to reduce waste. Additionally, supporting local initiatives and advocating for stricter waste management policies can help drive change at a larger scale.
Which countries have achieved zero waste?
At this time, no country has achieved zero waste on a national scale. However, several cities and regions around the world have made significant progress towards zero waste goals.