Plastic pollution has become a global crisis, with tons of plastic waste ending up in our oceans every year. If we want to tackle this issue effectively, it’s crucial to identify the countries that contribute the most to plastic pollution. One country that stands out on this list is China.
China is the world’s most populous country, with a population of over 1.4 billion people. As a result of rapid economic growth and industrialization, China has experienced a significant increase in plastic production and consumption. Unfortunately, the country lacks adequate waste management infrastructure, leading to large amounts of plastic waste being improperly disposed of.
The consequences of China’s plastic pollution are devastating. Not only does it harm marine life, but it also affects the health of the Chinese population. The pollution seeps into the soil and water, contaminating the food chain and posing a serious threat to public health.
Recognizing the severity of the problem, the Chinese government has recently implemented measures to address plastic pollution. These include bans on single-use plastics, increased recycling efforts, and awareness campaigns. While these initiatives are a step in the right direction, there is still a long way to go in tackling the plastic pollution crisis in China and around the world.
- Which Country is the Worst Offender for Plastic Pollution?
- Impact of Plastic Pollution
- Ecosystem Disruption
- Human Health Risks
- Ocean Plastic Pollution
- Solutions to Ocean Plastic Pollution
- The Way Forward
- The Top Plastic Polluting Country
- In conclusion
- Factors Contributing to Plastic Pollution
- Efforts to Combat Plastic Pollution
- Question-answer:
- Which country is the top contributor to plastic pollution?
- Why is China the leading country in plastic pollution?
- What are the consequences of plastic pollution in China?
- What measures has China taken to address plastic pollution?
Which Country is the Worst Offender for Plastic Pollution?
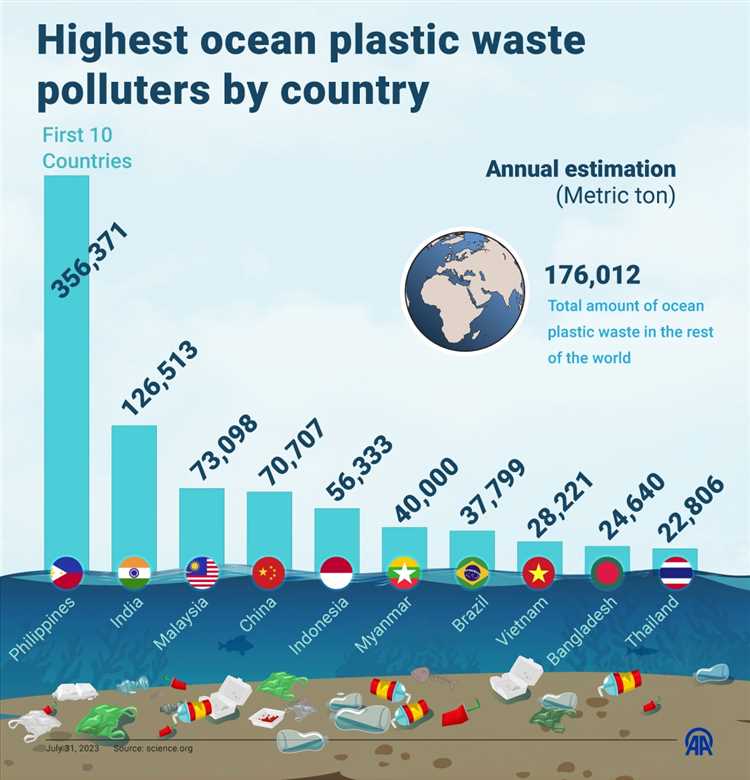
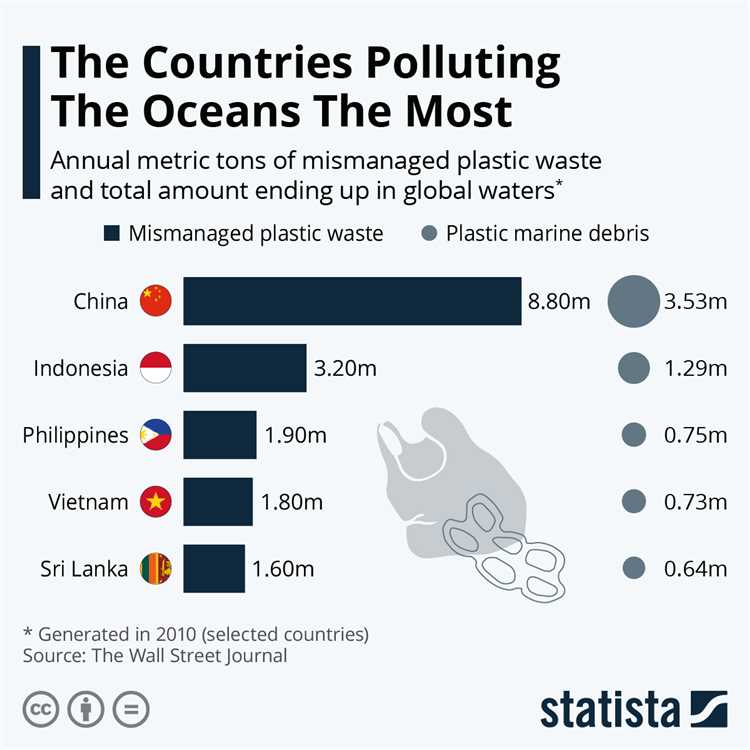
China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of plastic, producing over 60 million metric tons of plastic waste each year. Much of this plastic waste ends up in rivers and eventually makes its way into the ocean. In fact, a study found that around 2.75 million metric tons of plastic waste from China enters the ocean annually.
One of the main contributors to China’s plastic pollution problem is its inefficient waste management system. Many cities in China lack proper waste management infrastructure, leading to high levels of plastic pollution. Additionally, China has been a major importer of plastic waste from other countries, further exacerbating the problem.
The Chinese government has recognized the need to address plastic pollution and has taken steps to reduce plastic waste. In 2020, China implemented a ban on single-use plastic bags in major cities, and in 2022, the ban will be expanded to cover all cities and towns. Additionally, China has set a goal to achieve a recycling rate of 35% for plastic waste by 2025.
While China may currently be the worst offender for plastic pollution, it is important to note that plastic pollution is a global issue that requires collective efforts to solve. All countries need to work together to reduce plastic consumption, improve waste management systems, and promote sustainable alternatives to plastic.
| Country | Plastic Waste Generation (metric tons per year) |
|---|---|
| China | Over 60 million |
| United States | Over 38 million |
| India | Over 25 million |
| Indonesia | Over 10 million |
| Brazil | Over 7 million |
Impact of Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution has emerged as a global environmental crisis, with significant impact on the planet, people, and wildlife. The excessive use and poor management of plastic materials have led to detrimental effects across various aspects of life.
Ecosystem Disruption
Plastic waste contaminates ecosystems, including bodies of water and land areas, causing disruption to natural habitats and negatively affecting biodiversity. The presence of plastic debris in oceans, rivers, and forests can harm marine life, animals, and plants, and can even lead to the extinction of certain species.
Human Health Risks
Plastics contain harmful chemicals and additives, such as Bisphenol-A (BPA) and phthalates, which can leach into the environment and contaminate water supplies and food sources. These chemicals have been linked to various health issues, including hormonal imbalances, reproductive problems, and certain types of cancer.
Furthermore, microplastics, tiny particles of plastic, have been found in the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the food we consume. The ingestion or inhalation of microplastics can have long-term health consequences, as these particles can accumulate in organs and tissues.
Additionally, the improper disposal of plastic waste contributes to the spread of diseases, as it serves as a breeding ground for mosquitoes and other disease-carrying vectors.
Economic Burden
The economic impact of plastic pollution is significant, as it requires substantial resources to mitigate and clean up the waste. Environmental damage caused by plastic pollution affects industries such as tourism, fishing, and agriculture, leading to financial losses and decreased revenue.
In conclusion, plastic pollution has far-reaching consequences on the environment, human health, and the economy. Mitigating plastic pollution requires collective efforts to reduce plastic consumption, improve waste management systems, and promote sustainable alternatives. Only through these measures can we minimize the impact of plastic pollution and create a healthier and more sustainable future.
Ocean Plastic Pollution
Ocean plastic pollution has become a significant environmental issue worldwide. The accumulation of plastic waste in the oceans poses a serious threat to marine life and ecosystems.
Plastic pollution in the ocean is primarily caused by inadequate waste management and the improper disposal of plastic products. These plastics drift with ocean currents and accumulate in vast areas known as “garbage patches.”
The most well-known and alarming garbage patch is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, located between Hawaii and California. It is estimated to contain millions of metric tons of plastic debris.
Plastic pollution has detrimental effects on marine animals such as seabirds, turtles, and fish. They can mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement, which often results in injury or death.
The top contributor to ocean plastic pollution is considered to be China, followed by Indonesia, the Philippines, and Vietnam. These countries have extensive coastlines and large populations that generate significant plastic waste.
Solutions to Ocean Plastic Pollution
Efforts are being made to address and mitigate ocean plastic pollution. Some key initiatives include:
- Improving waste management systems to reduce plastic leakage into the ocean.
- Implementing policies and regulations to ban single-use plastics.
- Encouraging recycling and the use of sustainable alternatives to plastic.
- Supporting beach and ocean cleanup activities.
- Increasing public awareness and education about the impact of plastic pollution.
The Way Forward
Effective collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals is essential to combat ocean plastic pollution. By taking collective action and making sustainable choices, we can protect our oceans and preserve marine life for future generations.
The Top Plastic Polluting Country
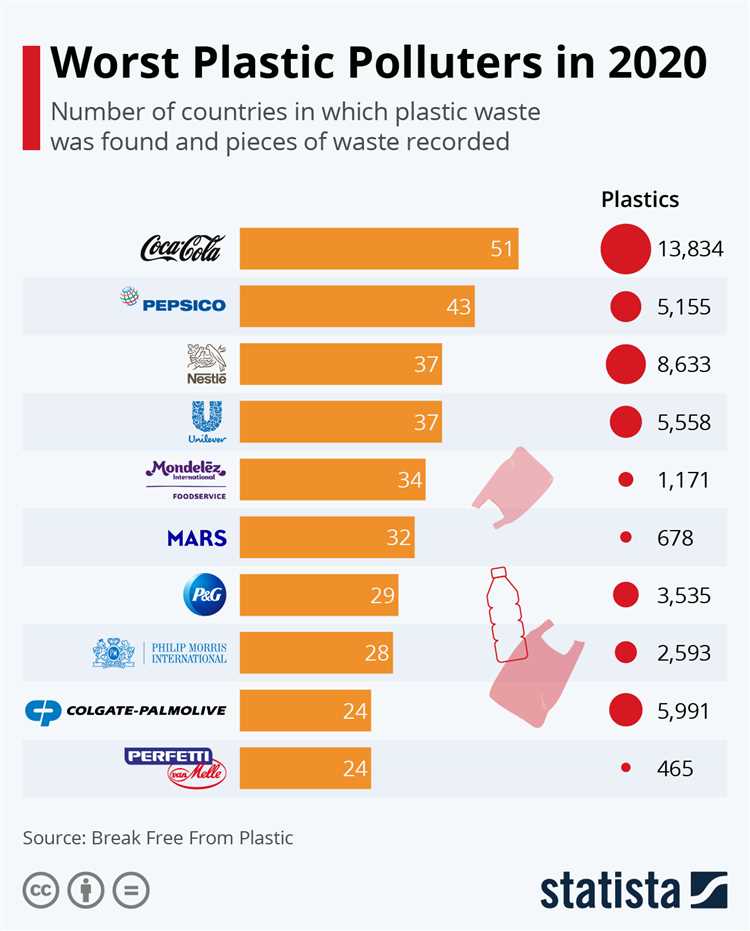
Plastic pollution has become a global crisis, with countries worldwide struggling to manage the overwhelming amount of plastic waste generated. However, one country stands out as the top plastic polluting country: China.
China’s rapid industrialization and economic growth over the past few decades have come at a cost to the environment. The country is the largest producer and consumer of plastic in the world, accounting for nearly 30% of global plastic waste.
The main contributors to China’s plastic pollution problem are its booming population, urbanization, and manufacturing industry. With a population of over 1.4 billion people, China generates an enormous amount of plastic waste every day. As the country continues to urbanize, more plastic products are being consumed and discarded.
China’s manufacturing industry, which produces a wide range of plastic products for domestic and global markets, also plays a significant role in its plastic pollution crisis. Many manufacturing processes in China rely heavily on single-use plastics, leading to a massive accumulation of plastic waste.
Despite efforts to address the issue, plastic waste management in China remains a challenge. Many cities lack proper waste collection and recycling infrastructure, leading to plastic waste ending up in landfills or being illegally dumped. Additionally, China exports a considerable amount of plastic waste to other countries, further exacerbating the global plastic pollution problem.
Awareness of the plastic pollution issue in China is growing, and the government has taken steps to reduce plastic consumption and improve waste management. In recent years, China has implemented bans on single-use plastics in certain regions and has invested in recycling facilities and technologies. However, more needs to be done to tackle the extensive plastic pollution problem in the country.
In conclusion
China has emerged as the top plastic polluting country due to its booming population, urbanization, and manufacturing industry. While efforts are being made to address the issue, the scale of the problem requires significant action to reduce plastic consumption and improve waste management. Only through collective global efforts can we hope to effectively combat the plastic pollution crisis and protect our environment for future generations.
Factors Contributing to Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution is a global problem that affects our oceans, rivers, and land. There are several factors that contribute to the widespread contamination of plastic waste:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Single-use plastics | The prevalence of single-use plastics, such as plastic bags, bottles, and packaging, contributes to plastic pollution. These items are often used once and then discarded, ending up in landfills or bodies of water. |
| Lack of recycling | The inadequate recycling infrastructure in many countries leads to a significant amount of plastic waste being improperly disposed of. Without proper recycling facilities, plastic waste often ends up being incinerated or dumped in open spaces. |
| Plastic production | The continuous production of plastic, particularly non-biodegradable plastics, contributes to the accumulation of plastic waste. This is due to the high demand for plastic products in various industries and the slow decomposition rate of plastic materials. |
| Inefficient waste management | Lack of proper waste management practices, including littering and illegal dumping, allows plastic waste to enter waterways and ecosystems. Inadequate waste management infrastructure and education contribute to the problem of plastic pollution. |
| Global consumption patterns | The increase in global consumption, especially in developing countries, has resulted in a higher production and disposal of plastic products. As more people adopt a consumer-driven lifestyle, the demand for plastic goods continues to rise. |
Addressing plastic pollution requires a multi-faceted approach, including reducing the production and consumption of plastic, improving recycling infrastructure, and promoting sustainable waste management practices. By understanding the factors that contribute to plastic pollution, we can work towards creating a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Efforts to Combat Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution has become a global crisis, and many countries are taking steps to combat it.
One country that has been leading the way in efforts to reduce plastic pollution is Rwanda. In 2008, Rwanda became one of the first countries in the world to ban plastic bags. The government implemented strict regulations and enforced heavy penalties for the production, sale, and use of plastic bags. This move has significantly reduced plastic waste in the country.
Another country that has made significant progress in tackling plastic pollution is Sweden. Sweden has been successfully implementing a waste-to-energy program, where non-recyclable waste, including plastic, is burned to produce electricity and heat. This approach has not only helped in reducing the amount of plastic waste in landfills but has also contributed to the country’s renewable energy goals.
In Kenya, a ban on plastic bags was introduced in 2017. The government imposed strict penalties for the manufacture, sale, and use of plastic bags, including fines and even imprisonment. This ban has led to a significant reduction in plastic pollution in the country and has encouraged the use of alternative packaging materials.
Canada has also taken steps to combat plastic pollution. The government has implemented a nationwide ban on single-use plastics, including items like plastic straws and bags. In addition, Canada has invested in infrastructure to improve recycling and promote the use of recyclable and biodegradable alternatives to plastic.
These are just a few examples of countries that are taking action to combat plastic pollution. It is crucial for governments, businesses, and individuals around the world to work together to find sustainable solutions and reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste.
Question-answer:
Which country is the top contributor to plastic pollution?
The top contributor to plastic pollution is China.
Why is China the leading country in plastic pollution?
China is the leading country in plastic pollution because it has a high population and a rapidly growing economy, which leads to increased consumption and production of plastic.
What are the consequences of plastic pollution in China?
The consequences of plastic pollution in China include damage to ecosystems, marine life, and human health. Plastic waste clogs waterways, pollutes the air, and contributes to global warming.
What measures has China taken to address plastic pollution?
China has taken several measures to address plastic pollution, including banning the import of certain types of plastic waste, implementing recycling programs, and promoting the use of eco-friendly alternatives to single-use plastics.