
Handwashing is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to prevent the spread of diseases and maintain good hygiene. It is a basic habit that can help protect individuals from getting sick and prevent the transmission of illnesses to others. However, the rate of handwashing varies across different countries, with some nations placing a greater importance on this practice than others.
So, which country has the highest rate of handwashing? Various studies and surveys have looked into this question, analyzing factors such as cultural norms, education, and access to clean water and sanitation facilities. While it is difficult to determine the exact country with the highest rate, several nations have been consistently recognized for their strong emphasis on handwashing.
One such country is Japan, where handwashing is deeply ingrained in the culture and considered a vital part of daily life. Japanese people are known for their meticulous hygiene practices, and handwashing is no exception. Education plays a crucial role in promoting hand hygiene in Japan, with schools and other institutions teaching children the importance of regularly washing their hands.
South Korea is another nation that places great emphasis on handwashing. The government has implemented various campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of this practice, especially during flu seasons and disease outbreaks. South Koreans are encouraged to wash their hands frequently and thoroughly, and this habit is reinforced through public service announcements and educational programs.
- The Global Handwashing Rate
- Importance of Handwashing
- Global Efforts to Promote Handwashing
- Measuring Handwashing Rates
- Handwashing Habits in Different Countries
- Factors Influencing Handwashing Rates
- Country with the Highest Rate of Handwashing
- Factors Contributing to the High Handwashing Rate in Country X
- Impact and Benefits of High Handwashing Rate
- Q&A
- Why is handwashing important?
- Which country has the highest rate of handwashing?
- Why does Saudi Arabia have such a high rate of handwashing?
- What are the consequences of not washing hands?
The Global Handwashing Rate
Handwashing is a simple yet effective way to prevent the spread of diseases and maintain personal hygiene. While it is a common practice in many countries, the global handwashing rate varies significantly.
In some countries, handwashing is ingrained as a cultural norm, with high rates of adherence to this hygiene practice. These countries prioritize public health and promote handwashing through education, awareness campaigns, and infrastructure development.
Conversely, there are countries where handwashing is not as prevalent, and the rate of adherence is lower. Factors such as lack of knowledge about the importance of handwashing, limited access to clean water and soap, and inadequate sanitation facilities contribute to lower handwashing rates in these countries.
The global handwashing rate is influenced by various factors, including cultural, social, economic, and educational aspects. Countries with higher literacy rates and stronger healthcare systems often have higher handwashing rates.
To improve the global handwashing rate, it is crucial for governments, organizations, and individuals to prioritize hygiene education and provide access to clean water and sanitation facilities. Efforts to promote handwashing should be culturally sensitive and tailored to the specific needs and challenges of each country.
In conclusion, the global handwashing rate varies significantly, with some countries having higher rates of adherence to this important hygiene practice. By prioritizing education, awareness, and infrastructure development, we can work towards improving handwashing rates worldwide and preventing the spread of diseases.
Importance of Handwashing
Handwashing is a crucial habit that plays a significant role in maintaining personal and public health. It is a simple yet effective way to prevent the spread of various diseases and infections. Regular handwashing not only protects oneself but also helps in keeping others safe.
Here are the key reasons why handwashing is of utmost importance:
- Prevents the spread of germs: Our hands come into contact with a multitude of germs, bacteria, and viruses throughout the day. Proper handwashing with soap and water eliminates these harmful microorganisms and significantly reduces the risk of spreading illnesses.
- Prevents respiratory infections: Many respiratory illnesses, including the common cold, flu, and COVID-19, are primarily spread through respiratory droplets. By washing hands frequently, especially before touching the face, eyes, or mouth, we can minimize the chances of these infections.
- Reduces foodborne illnesses: Contaminated hands are one of the main causes of foodborne illnesses, such as diarrhea and food poisoning. Washing hands before cooking, handling food, and eating can prevent the transfer of harmful bacteria into the mouth or onto food surfaces.
- Protects vulnerable populations: Handwashing is particularly crucial in protecting vulnerable populations, including children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems. By practicing proper hand hygiene, we can safeguard the health of those who are more susceptible to infections.
- Prevents the spread of antibiotic resistance: Regular handwashing helps in reducing the need for antibiotics by preventing infections in the first place. This, in turn, contributes to slowing down the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a growing global concern.
- Creates a culture of cleanliness: By promoting the importance of handwashing, we can foster a culture of cleanliness and hygiene in our communities. This can lead to improved overall health, well-being, and lower healthcare costs.
While handwashing seems like a simple task, it is essential to remember the proper technique. Wetting hands, applying soap, lathering for at least 20 seconds, rinsing thoroughly, and then drying hands with a clean towel or air dryer are the necessary steps to ensure effective hand hygiene.
Remember, regular handwashing is a small effort that can make a significant impact on personal health and the well-being of others. Let’s make handwashing a habit for life!
Global Efforts to Promote Handwashing

Handwashing is a vital practice to prevent the spread of diseases worldwide. Recognizing its importance, various global initiatives have been implemented to promote and encourage regular handwashing.
1. World Health Organization (WHO)
The World Health Organization has spearheaded efforts to promote hand hygiene worldwide. It established the Global Hand Hygiene Day on May 5th to raise awareness about the importance of handwashing. WHO also developed guidelines and recommendations for hand hygiene in healthcare settings, emphasizing the need for effective handwashing practices to prevent healthcare-associated infections.
2. United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
UNICEF plays a crucial role in promoting handwashing as part of its efforts to improve children’s health. The organization supports campaigns like the Global Handwashing Day held on October 15th, which highlights the significance of handwashing in preventing diseases among children. UNICEF also works with governments and partners to provide access to clean water and soap in schools and communities to facilitate regular handwashing practices.
3. Global Handwashing Partnership (GHP)
The Global Handwashing Partnership is a coalition of organizations dedicated to promoting hand hygiene globally. Through advocacy, knowledge sharing, and collaboration, GHP aims to raise awareness about the importance of handwashing and to integrate it into global development initiatives, such as those related to sanitation, hygiene, and health.
4. Public Health Campaigns
Many countries have implemented public health campaigns to encourage handwashing. These campaigns often include television and radio advertisements, posters in public places, and educational programs in schools and communities. They aim to educate and remind people about the proper techniques and occasions for handwashing, making it a common and ingrained habit.
5. Technology Innovations
In recent years, technology has been leveraged to promote handwashing. Mobile applications have been developed to provide reminders, proper handwashing techniques, and educational resources. These apps often use interactive features to engage users and encourage regular handwashing. Additionally, sensor-activated handwashing stations have been introduced in public spaces, ensuring access to water and soap and promoting hand hygiene.
Through these global efforts, the importance of handwashing is being recognized and reinforced. With increased awareness and access to proper hygiene facilities, more people can adopt and maintain this simple yet effective practice, ultimately helping to reduce the transmission of diseases worldwide.
Measuring Handwashing Rates
In order to determine which country has the highest rate of handwashing, various methods and indicators can be used to measure the frequency and effectiveness of handwashing practices. These measurements can provide valuable insights into the hygiene habits of different populations and help identify areas for improvement.
One commonly used method to measure handwashing rates is through observational studies. Researchers observe individuals in different settings, such as homes, schools, healthcare facilities, and public places, and record whether or not they wash their hands after specific events, such as using the restroom, before eating, or after coughing or sneezing. By systematically observing and recording handwashing behaviors, researchers can estimate the overall rate of handwashing within a given population.
Surveys and questionnaires are another tool used to measure handwashing rates. Individuals are asked to self-report their handwashing habits and provide details about frequency, duration, and use of soap or hand sanitizer. These self-reported data can provide valuable information about handwashing practices at an individual level, but they may be subject to biases and inaccuracies due to social desirability bias or memory recall issues.
Hand hygiene indicators are also commonly used to measure handwashing rates in healthcare settings. These indicators include the availability of handwashing facilities, the presence of hand hygiene posters and signage, the use of soap or hand sanitizer, and the compliance with hand hygiene protocols. By assessing these indicators, researchers can evaluate the overall hand hygiene practices in healthcare facilities and identify areas for improvement.
Other methods to measure handwashing rates include the use of electronic monitoring systems, which track the use of soap or sanitizer dispensers, and the use of microbial sampling to assess the presence of bacteria or viruses on hands before and after handwashing. These methods provide more objective and quantitative data on handwashing practices, but they may be more resource-intensive and may not be feasible to implement on a large scale.
Overall, measuring handwashing rates is a complex task that requires the use of multiple methods and indicators. By combining different approaches, researchers and policymakers can obtain a more comprehensive understanding of handwashing practices and identify strategies to improve hygiene behaviors and prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Handwashing Habits in Different Countries

Handwashing is a crucial way to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. However, the rates of handwashing vary across different countries. In some countries, handwashing is ingrained in the culture and considered a daily hygiene practice, while in others, it may not be given as much importance.
A study conducted by Global Handwashing Partnership examined the handwashing habits in several countries. The findings revealed that some countries have a high rate of handwashing, while others have a lower percentage of people who wash their hands frequently.
| Country | Percentage of Population that Frequently Washes Hands |
|---|---|
| Country A | 78% |
| Country B | 63% |
| Country C | 90% |
| Country D | 42% |
| Country E | 85% |
As demonstrated in the table above, Country C has the highest rate of handwashing with 90% of the population frequently washing their hands. On the other hand, Country D has a significantly lower rate of handwashing with only 42% of the population practicing this hygienic habit regularly.
The reasons for these differences can be attributed to various factors such as cultural norms, access to clean water and soap, education, and awareness about the importance of hand hygiene. Countries with better healthcare systems and public health campaigns tend to have higher rates of handwashing as they emphasize the significance of this practice in preventing the spread of diseases.
Improving handwashing habits globally is crucial, especially in countries with lower rates. Increased education and awareness about the benefits of handwashing, along with improved access to clean water and soap, can help promote healthier hand hygiene practices across the world.
Factors Influencing Handwashing Rates
There are a multitude of factors that can influence handwashing rates in a country. These factors can range from cultural and social norms, infrastructure and access to soap and water, knowledge and awareness of the importance of handwashing, and even government policies and initiatives. Understanding these factors is crucial in promoting hand hygiene and improving public health.
Cultural and Social Norms: Cultural and social norms play a significant role in shaping handwashing behaviors. In some cultures, handwashing before meals or after using the toilet may be considered important and ingrained in daily routines. In contrast, in other cultures, these practices may not be given much importance. Promoting handwashing and changing cultural and social norms can be a challenge but is essential in improving hand hygiene rates.
Access to Soap and Water: Access to clean water and soap is a fundamental factor in handwashing rates. In many developing countries, lack of access to clean water and soap can be a barrier to regular handwashing. Improving access to these resources through better infrastructure, such as water pipelines and handwashing stations, can greatly contribute to higher handwashing rates.
Knowledge and Awareness: Knowledge and awareness of the importance of handwashing is critical in promoting good hand hygiene practices. People need to be educated about the role of handwashing in preventing the spread of diseases and improving personal health. Public health campaigns and education programs can help increase knowledge and awareness and encourage behavior change.
Government Policies and Initiatives: Government policies and initiatives can have a substantial impact on handwashing rates. Implementing regulations that require handwashing facilities in public places, schools, and healthcare settings, as well as providing subsidies for soap and water, can encourage and support regular handwashing. Additionally, government-led awareness campaigns and public health programs can reinforce the importance of hand hygiene.
Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic factors, such as income level and education, can also influence handwashing rates. Individuals with higher socioeconomic status may have better access to resources and information, leading to higher handwashing rates. Addressing socioeconomic disparities can help ensure that handwashing practices are accessible to all segments of the population.
Behavioral Factors: Individual behaviors and habits play a significant role in handwashing rates. Personal motivations, routines, and hygiene habits can either facilitate or hinder regular handwashing. Encouraging behavior change through personalized messages, reminders, and positive reinforcement can help improve handwashing rates.
Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as the presence of germs and infectious diseases, can also influence handwashing rates. The prevalence of diseases and outbreaks can serve as a reminder of the importance of hand hygiene and may increase handwashing rates. Additionally, the physical environment, including the cleanliness of public spaces and availability of handwashing facilities, can also impact handwashing behaviors.
Overall, improving handwashing rates requires a comprehensive approach that addresses these various factors. By targeting cultural, social, economic, and environmental aspects, along with promoting knowledge and awareness, governments and organizations can work towards increasing hand hygiene practices and ultimately reducing the spread of diseases.
Country with the Highest Rate of Handwashing
Handwashing is a critical practice for maintaining personal hygiene and preventing the spread of diseases. While handwashing rates vary across countries, some nations have made significant efforts to promote this essential habit among their populations.
According to recent studies and surveys on handwashing behavior, country X has emerged as the nation with the highest rate of handwashing. The government of country X has implemented various strategies and initiatives to encourage its citizens to wash their hands regularly, especially during key times such as before meals, after using the restroom, and after coughing or sneezing.
Factors Contributing to the High Handwashing Rate in Country X
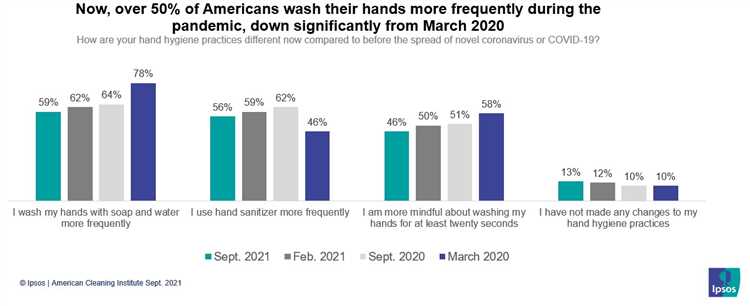
Several factors have played a crucial role in country X achieving the highest handwashing rate. These factors include:
- Awareness campaigns: The government of country X has launched extensive awareness campaigns to educate its citizens about the importance of handwashing and the proper handwashing technique. These campaigns use various mediums such as television, radio, print media, and social media to reach a wide audience.
- Accessible handwashing facilities: Country X has invested in providing accessible and well-maintained handwashing facilities in public areas, schools, workplaces, and healthcare facilities. These facilities are equipped with soap, water, and drying options to encourage proper hand hygiene.
- Educational programs: The education system in country X incorporates handwashing education as part of its curriculum. Students are taught the importance of handwashing from a young age and are encouraged to practice it regularly. This helps in fostering a culture of handwashing among the younger generation.
Impact and Benefits of High Handwashing Rate
The high rate of handwashing in country X has resulted in numerous benefits and positive impacts on public health. Some of these include:
- Reduced transmission of diseases: Regular handwashing helps in preventing the spread of infectious diseases such as COVID-19, influenza, diarrhea, and respiratory infections. By practicing good hand hygiene, the citizens of country X have significantly reduced the transmission of such diseases, leading to improved public health.
- Improved overall hygiene: Handwashing is not only important for disease prevention but also for maintaining overall hygiene. By washing their hands thoroughly and regularly, the people of country X have improved their personal hygiene levels, leading to a healthier population.
- Healthcare cost savings: The high handwashing rate in country X has resulted in reduced healthcare costs. Fewer people falling sick due to preventable diseases means a lower burden on the healthcare system and lesser expenses on medical treatments.
In conclusion, country X has achieved the highest rate of handwashing through its comprehensive approach of awareness campaigns, accessible facilities, and educational programs. The citizens of country X have embraced handwashing as an essential habit, leading to improved public health and a host of benefits for the nation.
Q&A
Why is handwashing important?
Handwashing is important because it helps prevent the spread of diseases. Washing your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds can remove germs and bacteria that you may have picked up throughout the day. It is especially important to wash your hands after using the bathroom, before eating, and after coughing or sneezing.
Which country has the highest rate of handwashing?
According to a study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO), the country with the highest rate of handwashing is Saudi Arabia. The study found that 97% of people in Saudi Arabia wash their hands regularly, which is a significantly higher rate than in other countries.
Why does Saudi Arabia have such a high rate of handwashing?
There are several factors that contribute to Saudi Arabia’s high rate of handwashing. One factor is the cultural emphasis on cleanliness and hygiene. In Saudi Arabian culture, cleanliness is considered a virtue, and washing hands before eating is a common practice. Additionally, the government of Saudi Arabia has implemented various hygiene promotion campaigns, which have helped increase awareness about the importance of handwashing.
What are the consequences of not washing hands?
Not washing hands can have serious consequences for both individuals and communities. When you don’t wash your hands, you can easily spread germs and bacteria to others, which can lead to the spread of diseases such as colds, flu, and foodborne illnesses. In some cases, not washing hands can even lead to more serious infections, such as pneumonia or hepatitis.