
In the modern world, where environmental issues are becoming increasingly pressing, recycling has emerged as a vital solution to reduce waste and preserve natural resources. However, while many countries have made concerted efforts to implement recycling programs, there are still several nations that lag behind in this crucial practice.
One such country is… Despite being known for its advanced technology and innovation, its recycling rates remain alarmingly low. The lack of infrastructure, coupled with a general lack of awareness and environmental education, contribute to the dismal state of recycling in this nation.
Another country… This lack of recycling not only leads to an enormous amount of waste, but also exacerbates pollution and the depletion of valuable resources within this country.
These are just a couple of examples of the countries that have yet to prioritize recycling. It is imperative for governments, organizations, and individuals to work together to address this issue and strive for a more sustainable future for our planet.
- The List of Non-Recycling Countries
- 1. Burundi
- 2. Eritrea
- 3. Libya
- 4. Papua New Guinea
- 5. Sierra Leone
- Reasons for Not Recycling
- Lack of Infrastructure
- Low awareness and Education
- Environmental Implications of Not Recycling
- Economic Impact of Not Recycling
- 1. Wasted Resources
- 2. Increased Waste Management Costs
- 3. Missed Economic Opportunities
- 4. Environmental Cleanup Costs
- Efforts to Improve Recycling Rates in Non-Recycling Countries
- Educational Campaigns and Awareness Programs
- Investment in Recycling Infrastructure
- Success Stories of Countries That Transitioned to Recycling
- Germany: A Pioneer in Recycling
- Sweden: Achieving Zero Waste Goals
- Question-answer:
- Which countries do not have recycling programs?
- Why don’t some countries recycle?
- What are the consequences of not recycling?
- How can countries without recycling programs manage their waste?
- What can individuals do in countries without recycling programs?
- What countries have the lowest recycling rates?
- Are there any countries that do not have recycling programs at all?
The List of Non-Recycling Countries
While recycling has become a global initiative in recent years, not all countries have embraced this sustainable practice. Here is a list of countries that do not have a well-established recycling system:
1. Burundi
Burundi is a landlocked country in East Africa that faces numerous environmental challenges, including a lack of recycling infrastructure. Waste management is a pressing issue in Burundi, and recycling is not yet widely practiced.
2. Eritrea
Eritrea, a country in the Horn of Africa, also struggles with inadequate waste management practices. Recycling is not a common practice in Eritrea, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion.
3. Libya
Libya, located in North Africa, faces similar challenges in waste management. The country lacks proper recycling facilities and infrastructure, leading to significant waste accumulation and environmental degradation.
4. Papua New Guinea

Papua New Guinea, a country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, has a limited recycling system. Waste management is a significant issue, particularly in urban areas, where recycling is not widely practiced or accessible.
5. Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, an African country on the west coast of the continent, also struggles with an underdeveloped recycling system. Waste management is a challenge, and recycling remains uncommon due to limited resources and infrastructure.
These countries are examples of regions where recycling practices have not yet gained significant traction. Promoting sustainable waste management and implementing recycling systems in these areas could help mitigate environmental impact and promote a circular economy.
Reasons for Not Recycling
While recycling has become a common practice in many countries around the world, there are still some nations that do not prioritize recycling. There could be several reasons why these countries do not have a well-established recycling system in place.
Lack of Infrastructure
One of the main reasons for not recycling in certain countries is the lack of proper infrastructure. Recycling requires a system of waste collection, sorting, and processing facilities, which requires significant investment. Some countries may not have the financial resources or the technology to develop and maintain a recycling infrastructure.
Low awareness and Education
Another reason for the lack of recycling in some countries is low awareness and education about the benefits of recycling. If the population is not aware of the environmental and economic advantages of recycling, they may not feel motivated to participate in recycling programs. Lack of education about proper recycling practices can also result in contamination of recycling streams, making proper recycling difficult.
Additionally, some countries may have a cultural perception that recycling is not a priority or may have other pressing environmental or social issues that take precedence over recycling initiatives. Without a strong public push for recycling, governments may not see the need to invest in recycling infrastructure.
It is important to note that while some countries may not have a comprehensive recycling system, efforts are being made globally to encourage recycling practices. Through international collaborations, education campaigns, and technological advancements, the hope is that more countries will adopt sustainable recycling practices in the future.
Environmental Implications of Not Recycling
1. Increased Landfill Waste: When countries do not prioritize recycling, the amount of waste sent to landfills increases significantly. Landfills are not designed to break down the materials found in non-recycled items, which leads to a buildup of waste that can take years or even centuries to decompose. This contributes to the pollution of soil, water, and air.
2. Depletion of Natural Resources: Not recycling means missing out on the opportunity to conserve and reuse valuable natural resources. Many products, such as paper, plastic, and metals, require significant amounts of energy and resources to produce. By not recycling, countries continue to extract and consume these finite resources, causing further environmental damage.
3. Increased Energy Consumption and Pollution: Recycling often requires less energy compared to the production of new materials. When countries do not recycle, they miss out on the energy savings that come with recycling. Instead, more energy is consumed during the extraction, processing, and manufacturing of new materials, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
4. Harm to Wildlife and Ecosystems: Non-recycled items can end up in natural habitats, posing a serious threat to wildlife. Animals can become entangled in plastic waste or mistake it for food, causing injury and death. The pollution caused by not recycling can also disrupt ecosystems and harm biodiversity.
5. Climate Change Impact: The failure to recycle contributes to climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions from the production and disposal of non-recycled items, as well as the loss of carbon storage capacity in landfills, contribute to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This leads to global warming and the associated impacts, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Overall, not recycling has severe environmental implications, affecting both the present and future generations. It is crucial for countries to prioritize recycling to reduce waste, conserve resources, and mitigate the negative impacts of human activity on the environment.
Economic Impact of Not Recycling
Not recycling has significant economic consequences for countries that fail to prioritize this practice. These impacts can be seen in various sectors of the economy and can result in long-term financial challenges.
1. Wasted Resources
When countries do not recycle, valuable resources are wasted. Materials such as paper, plastics, glass, and metals are not utilized efficiently, leading to the need for more extraction of raw materials. This extraction process is often costly and can have negative environmental consequences, further exacerbating the economic impact.
2. Increased Waste Management Costs
Not recycling leads to increased waste management costs. Countries that do not have efficient recycling programs must rely on landfill or incineration methods to dispose of waste. These methods are not only less environmentally friendly but also require significant financial investment. The costs associated with waste management can burden local governments and taxpayers, leading to the allocation of resources away from other essential services.
3. Missed Economic Opportunities
The failure to recycle can result in missed economic opportunities. Recycling industries have the potential to create jobs and stimulate economic growth. By not investing in recycling programs, countries miss out on the chance to develop a sustainable and thriving recycling sector that could contribute to job creation and increased revenue.
4. Environmental Cleanup Costs
Without proper recycling measures in place, countries may face higher environmental cleanup costs. Improperly managed waste can lead to pollution of land, water, and air. Cleaning up these polluted areas can be a significant financial burden, as it often requires specialized techniques and technologies. Additionally, the damage caused by pollution can have long-term effects on ecosystems and natural resources, which can further impact the economy.
In conclusion, not prioritizing recycling has various economic consequences. From wasted resources to increased waste management costs and missed economic opportunities, countries that do not recycle face long-term financial challenges. Implementing efficient recycling programs can help mitigate these impacts and create a more sustainable and prosperous future.
Efforts to Improve Recycling Rates in Non-Recycling Countries
While many countries around the world have made significant progress in implementing recycling programs, there are still several nations that are considered non-recycling countries. These countries, often faced with limited resources and infrastructure, struggle to establish efficient recycling systems. However, there are ongoing efforts to improve recycling rates in these non-recycling countries and promote sustainable waste management practices.
Educational Campaigns and Awareness Programs
One of the key strategies to encourage recycling in non-recycling countries is to raise awareness about the importance of recycling and its environmental benefits. Educational campaigns and awareness programs are being implemented to provide information on waste management, sorting practices, and the negative impacts of improper waste disposal. These initiatives aim to change attitudes and behaviors towards recycling, ultimately leading to increased participation rates.
Investment in Recycling Infrastructure
Lack of recycling infrastructure is a major obstacle for non-recycling countries. To address this issue, investments are being made to develop and enhance recycling facilities, such as sorting centers, recycling plants, and collection systems. These efforts aim to improve the capacity and efficiency of waste management systems, making it easier for citizens to recycle and ensuring that collected materials are properly processed.
Additionally, collaborations with private sector companies and organizations are being pursued to establish partnerships and foster technological advancements in recycling. By investing in infrastructure and promoting innovation, non-recycling countries can overcome the challenges they face in establishing effective recycling processes.
Incentive Programs and Policy Changes
Incentive programs have proven to be effective in increasing recycling rates. These programs provide monetary or non-monetary rewards to individuals or communities that actively participate in recycling activities. Non-recycling countries are exploring the implementation of such programs to incentivize citizens and businesses to recycle. Moreover, policy changes are being considered to introduce regulations that require mandatory recycling practices and impose penalties for improper waste disposal. These measures are expected to create a legal framework that promotes recycling and encourages compliance.
In conclusion, while non-recycling countries face significant challenges in establishing recycling systems, efforts to improve recycling rates are underway. These efforts focus on raising awareness, investing in recycling infrastructure, and implementing incentive programs and policy changes. With continued commitment and collaboration, it is possible to transform non-recycling countries into efficient recyclers and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Success Stories of Countries That Transitioned to Recycling
Recycling has become an essential aspect of waste management worldwide, with many countries adopting successful recycling practices. From reducing landfill waste to conserving resources, these countries have made remarkable strides in promoting sustainability and creating a cleaner environment.
Germany: A Pioneer in Recycling
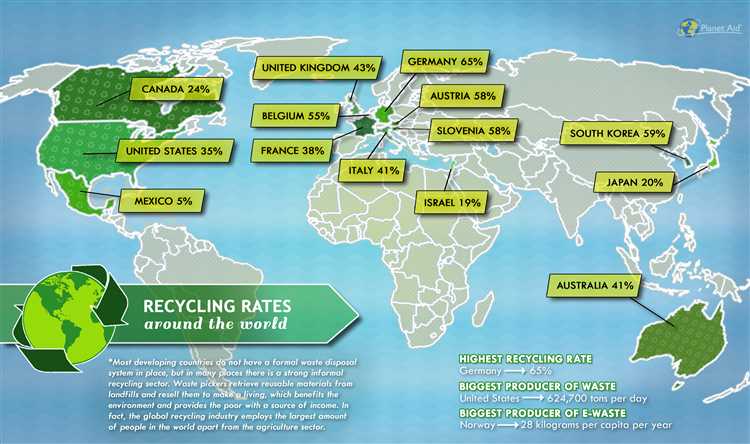
Germany is recognized as a global leader in recycling due to its extensive waste management system. The “Green Dot” program, established in 1991, encouraged manufacturers to take responsibility for the waste their products generate. Through this program, packaging waste is collected and then recycled or used for energy recovery. The country also implemented a dual-bin system, making it easy for citizens to separate recyclable materials from non-recyclables. As a result, Germany has achieved a recycling rate of more than 60% and significantly reduced landfill waste.
Sweden: Achieving Zero Waste Goals
Sweden has made great progress in waste management and recycling, with a goal of zero waste by 2020. The country has implemented a comprehensive waste-to-energy system, where waste is incinerated to produce heat and electricity. Furthermore, Sweden has heavily invested in recycling infrastructure, ensuring that recyclable materials are sorted and processed efficiently. With effective public education campaigns, Sweden has developed a culture of recycling, resulting in a recycling rate of around 99% for household waste.
By prioritizing recycling, Germany and Sweden have successfully transitioned towards sustainable waste management. Through innovative programs and infrastructure, these countries serve as inspiring examples for others striving to achieve higher recycling rates and minimize environmental impact.
Question-answer:
Which countries do not have recycling programs?
There are several countries that do not have comprehensive recycling programs, including Afghanistan, Belize, Cambodia, Haiti, and several countries in Africa.
Why don’t some countries recycle?
There are several reasons why some countries do not have recycling programs. These may include a lack of infrastructure and resources, limited public awareness and education on recycling, and a lack of government support or incentives for recycling initiatives.
What are the consequences of not recycling?
Not recycling can have significant negative consequences for the environment. It leads to increased waste production, depletion of natural resources, pollution of air, land, and water, and contributes to climate change. It also results in the loss of economic opportunities and the potential for creating a circular economy.
How can countries without recycling programs manage their waste?
Countries without recycling programs can manage their waste through other means, such as landfilling, incineration, or exporting the waste to other countries. However, these methods are not as sustainable or environmentally friendly as recycling, and can have negative impacts on human health and the environment.
What can individuals do in countries without recycling programs?
Even in countries without recycling programs, individuals can still make a difference by adopting environmentally friendly practices. This can include reducing waste by reusing items, composting organic waste, and advocating for the implementation of recycling programs. Additionally, consumers can choose products with less packaging or those made from recycled materials.
What countries have the lowest recycling rates?
Some of the countries with the lowest recycling rates include Nigeria, Egypt, Indonesia, and Mexico. These countries face various challenges in implementing effective recycling systems, such as lack of infrastructure and awareness.
Are there any countries that do not have recycling programs at all?
Yes, there are several countries that do not have formal recycling programs in place. Some of these countries include Iraq, Afghanistan, and Sierra Leone. In these areas, waste management practices are often limited, and recycling infrastructure is virtually non-existent.