Condom usage is a crucial aspect of sexual health and is an effective method of preventing unintended pregnancies and the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, studies have shown that certain age groups may have lower condom usage rates compared to others. Understanding these demographic trends is essential for developing targeted interventions and educational campaigns to address this issue.
One age group that has garnered particular attention in discussions surrounding condom usage is young adults. Research indicates that individuals between the ages of 18 and 24 tend to have lower condom usage rates compared to older adults. This may be attributed to a variety of factors, including a lack of sexual education, limited access to healthcare resources, and a sense of invincibility or low perceived risk of STIs or unintended pregnancies.
Additionally, cultural and societal factors may play a role in influencing condom usage among different age groups. For example, older generations may have grown up during an era when sexual education and awareness were less prevalent, leading to a lack of emphasis on condom use. On the other hand, younger generations may face different societal and cultural pressures, such as the influence of media and peer norms, which can impact their attitudes and behaviors towards condom usage.
Identifying the age group with the lowest condom usage is vital for public health efforts, as it allows for targeted interventions and educational campaigns to be developed. By understanding the underlying reasons behind lower condom usage rates among specific age groups, public health initiatives can be tailored to address these factors and promote healthier sexual practices. Ultimately, improving condom usage rates among all age groups is essential for ensuring the overall sexual health and well-being of individuals.
- Demographic Trends
- The Importance of Condom Usage
- Factors Impacting Condom Usage
- Understanding Demographic Differences
- Identifying the Age Group with the Lowest Condom Usage
- Implications for Public Health
- Q&A:
- What are the current demographic trends in condom usage?
- Which age group has the lowest condom usage?
- Why do young adults have the lowest condom usage?
- What are the consequences of low condom usage among young adults?
- What can be done to increase condom usage among young adults?
- What are demographic trends?
Demographic Trends
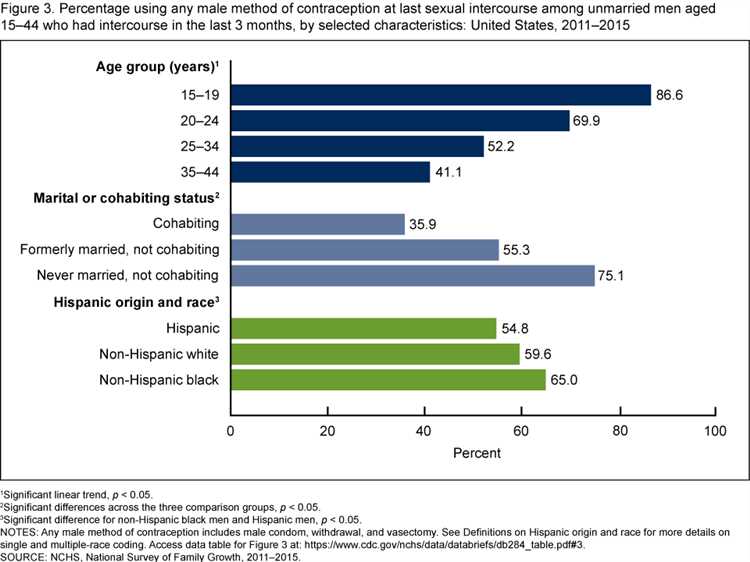
Demographic trends play a crucial role in understanding various aspects of society, including sexual health habits and behaviors. One important factor to consider is the age group with the lowest condom usage.
When analyzing data on condom usage, it is evident that certain age groups demonstrate lower rates of condom use compared to others. These trends can be attributed to various factors, such as access to comprehensive sexual education, beliefs and attitudes towards condoms, and socio-cultural influences.
Research has consistently shown that young adults, particularly those in their late teens and early twenties, have lower condom usage rates compared to older age groups. This can be partially attributed to a lack of sexual health knowledge and experience, as well as a perceived invincibility or a sense of low risk associated with sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies.
Additionally, cultural and societal norms surrounding sexuality and condom use may influence behavior. Factors such as religious beliefs, gender roles, and societal expectations can impact condom usage rates among different age groups. For instance, some conservative cultures may discourage condom use, particularly among unmarried individuals or those in committed relationships.
Moreover, access to sexual health resources and education also plays a significant role in condom usage rates among different age groups. Young adults may have limited access to comprehensive sexual education programs, reliable sources of information, and affordable contraceptive methods, which can contribute to lower condom usage rates.
Efforts to increase condom usage among the age group with the lowest rates should focus on addressing these underlying factors. This can be done through comprehensive sexual education programs that provide accurate and age-appropriate information, destigmatizing sexual health discussions, and improving access to affordable and easily accessible contraceptive methods.
Overall, understanding the demographic trends related to condom usage is crucial for developing targeted interventions and strategies to promote safe and responsible sexual behavior. By addressing the unique challenges faced by different age groups, we can strive towards a society that prioritizes sexual health and well-being for all.
The Importance of Condom Usage
Condom usage is of utmost importance in today’s society, as it plays a crucial role in preventing sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies. Condoms are highly effective in reducing the risk of transmission of STIs, including HIV, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis.
By using condoms consistently and correctly, individuals can protect themselves and their partners from the potential consequences of unprotected sexual activity. Condoms act as a barrier method, preventing the transfer of bodily fluids such as semen, vaginal fluids, and blood, which can contain STIs.
In addition to preventing the spread of STIs, condoms are also an effective form of contraception. They provide a physical barrier that prevents sperm from reaching the egg, thereby reducing the risk of unintended pregnancies. This makes condoms an invaluable tool for individuals and couples who are not ready to start a family or do not wish to have children.
Condom usage is particularly important in populations with low condom usage rates, as it can help address the underlying factors contributing to these trends. Educating individuals about the benefits of condom usage and promoting safe sexual practices is essential in reducing the prevalence of STIs and unintended pregnancies.
Furthermore, condom usage empowers individuals to take control of their sexual health. It allows them to make informed decisions and protect themselves from potential harm. Condoms are easily accessible and affordable, making them a convenient and practical option for individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
In conclusion, condom usage is crucial for individuals to protect themselves and their partners from the risks and consequences of unprotected sexual activity. It is an effective means of preventing STIs and unintended pregnancies and plays a vital role in promoting sexual health and well-being.
Factors Impacting Condom Usage
Several factors contribute to the variation in condom usage among different age groups. These factors include:
- Sexual Education: The level and quality of sexual education significantly impact condom usage. Comprehensive sexual education programs that emphasize condom use as a critical component of safe sex can increase awareness and promote greater condom usage.
- Knowledge and Awareness: Lack of knowledge about condom use can hinder their usage. Many individuals may not be aware of the risks associated with unprotected sex or may have misconceptions about condom effectiveness. Educating individuals about the benefits and proper use of condoms can lead to increased usage.
- Peer Influence: Individuals may be influenced by their peers when it comes to condom usage. Social norms, such as beliefs about condom use among friends and acquaintances, can play a significant role in an individual’s decision to use condoms.
- Cultural and Religious Beliefs: Cultural or religious beliefs that discourage or stigmatize premarital sex or condom use can hinder condom usage among certain age groups. Overcoming these barriers requires addressing cultural and religious beliefs in a respectful and sensitive manner.
- Access and Affordability: Limited access to condoms and their affordability can also impact usage rates. Lack of convenient access to free or affordable condoms can be a significant barrier, particularly for low-income individuals.
- Fear of Stigma and Discrimination: Fear of stigmatization or discrimination due to condom use can discourage individuals from using condoms, particularly in conservative or judgmental communities. Addressing societal attitudes towards condom usage can help create a more supportive environment for condom users.
- Relationship Dynamics: The nature of relationships can influence condom usage. In long-term relationships or committed partnerships, individuals may rely on other contraceptive methods or trust their partners’ fidelity, reducing the need for condom usage.
- Perceived Effectiveness and Satisfaction: Some individuals may perceive condoms as less effective or less pleasurable compared to other forms of contraception. This perception can influence their decision to use condoms. Educating individuals about the effectiveness of condoms and addressing any concerns regarding pleasure and satisfaction can encourage greater condom usage.
Understanding these factors and developing targeted interventions can help increase condom usage among the age groups with the lowest rates, promoting safer sexual practices and reducing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections.
Understanding Demographic Differences

When analyzing condom usage, it is important to understand the demographic differences that may exist among age groups. These differences can help shed light on why some age groups have lower rates of condom usage compared to others.
One important demographic difference to consider is the level of sexual education among different age groups. Younger individuals, such as teenagers and young adults, may have received more comprehensive sexual education that emphasizes the importance of condom usage. On the other hand, older age groups may have received sexual education during a time when condom usage was not as heavily emphasized.
Another factor to consider is the attitudes and beliefs surrounding condom usage within different age groups. Cultural and religious beliefs may influence condom usage, with some age groups having stronger adherence to these beliefs. Additionally, social norms and peer pressure can play a role in influencing condom usage, with younger age groups potentially being more influenced by peer pressure.
Access to condoms is also an important factor to consider. Younger age groups may have easier access to condoms through programs targeted towards sexual health education and resources. Older age groups, especially those who are no longer in school or are not actively seeking sexual health resources, may face challenges in accessing condoms. This lack of access can contribute to lower rates of condom usage.
Lastly, relationship dynamics and sexual behaviors can also vary among different age groups. Some age groups may be more likely to be in long-term relationships or have stable partners, which can impact condom usage. Additionally, certain age groups may engage in riskier sexual behaviors, such as having multiple partners, which can also impact condom usage rates.
By understanding these demographic differences, it becomes clear that a multi-faceted approach is needed to address the issue of low condom usage among certain age groups. It is important to consider educational initiatives, access to resources, and cultural and social factors in order to develop effective strategies that promote safe sexual practices for all age groups.
Identifying the Age Group with the Lowest Condom Usage
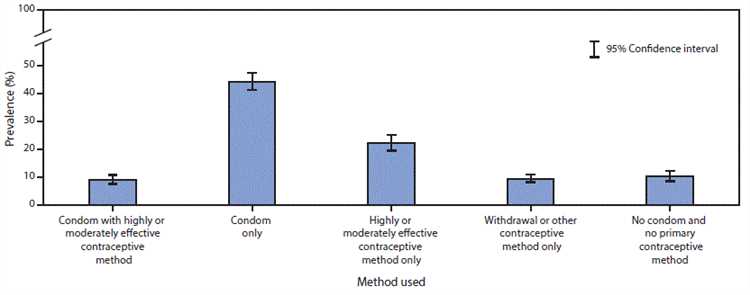
Condom usage is an important aspect of sexual health and preventing the spread of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies. Understanding patterns of condom usage among different age groups can help in developing targeted interventions and educational campaigns to promote safer sexual practices.
Research studies have shown that condom usage varies across different age groups, with some age groups consistently reporting lower rates of condom use compared to others. Identifying the age group with the lowest condom usage can shed light on the specific demographic that requires focused attention and support.
Several factors contribute to variations in condom usage among different age groups. Younger age groups, such as adolescents and young adults, may engage in risky sexual behaviors due to limited knowledge about sexual health, peer pressure, or a sense of invincibility. Older age groups, on the other hand, may exhibit lower condom usage due to lower perceived risk of STIs or a lower prevalence of sexual activity.
One way to identify the age group with the lowest condom usage is through population-based surveys and studies. These surveys collect data on sexual behaviors, including condom usage, among individuals of different age groups. By analyzing the survey data, researchers can determine the age group with the lowest reported condom usage.
Another approach to identifying the age group with the lowest condom usage is through healthcare provider data. Healthcare providers often collect information about sexual behaviors, including condom usage, during routine clinical visits. By analyzing this data, researchers can identify the age group with the lowest condom usage in a specific healthcare setting.
Once the age group with the lowest condom usage is identified, it is important to understand the underlying reasons behind this trend. Research studies and qualitative interviews can provide valuable insights into the barriers and facilitators to condom use among this age group. These insights can inform the development of targeted interventions and educational campaigns to increase condom usage among the specific demographic.
In conclusion, identifying the age group with the lowest condom usage is crucial for addressing gaps in sexual health promotion and education. By understanding the factors contributing to low condom usage in a specific age group, interventions can be developed to improve condom use and ultimately reduce the prevalence of STIs and unintended pregnancies.
Implications for Public Health
The identification of the age group with the lowest condom usage has significant implications for public health. This information provides valuable insights into the potential risks of unprotected sexual activity and the need for targeted interventions and education campaigns. By understanding which age group is least likely to use condoms, public health officials can develop strategies to address this issue and promote safe sexual practices.
It is clear that efforts should be focused on reaching young adults within this age group to improve condom use. Providing accurate and accessible information about the importance of using condoms as a preventive measure against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies can help empower individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual health.
Public health campaigns should also address any barriers that may prevent this age group from consistent condom use. These barriers may include lack of access to affordable condoms, misconceptions about their effectiveness, stigma surrounding condom use, or cultural norms that discourage their use.
Additionally, public health officials should collaborate with community organizations, healthcare providers, and educators to ensure that comprehensive sexual education programs are implemented in schools and other relevant settings. These programs should emphasize the importance of condom use, provide information on STIs and their consequences, and teach individuals about the various contraceptive methods available to them.
By addressing the low condom usage within this age group, public health initiatives can help reduce the transmission of STIs and improve overall sexual health outcomes. It is crucial to recognize that promoting condom use is not only about individual protection but also about protecting the health of the entire community. Increased condom usage can contribute to the prevention of STIs, reduce the rate of unintended pregnancies, and ultimately improve public health outcomes.
In summary, identifying the age group with the lowest condom usage highlights the importance of targeted interventions and education campaigns to promote safe sexual practices. By focusing on reaching young adults within this age group and addressing barriers to condom use, public health initiatives can make significant progress in improving sexual health outcomes and reducing the transmission of STIs.
Q&A:
What are the current demographic trends in condom usage?
The current demographic trends in condom usage show that there is a certain age group that has the lowest condom usage. This age group tends to have higher rates of unprotected sex compared to other age groups.
Which age group has the lowest condom usage?
The age group with the lowest condom usage is typically younger adults between the ages of 18 to 24. This age group tends to engage in riskier sexual behavior and often underestimate the importance of condom use in preventing sexually transmitted infections and unintended pregnancies.
Why do young adults have the lowest condom usage?
There are several reasons why young adults have the lowest condom usage. One reason is the lack of education and information about sexual health and contraception. Many young adults also have a sense of invincibility and believe that they are not at risk for sexually transmitted infections or unintended pregnancies. Peer pressure and a desire for intimacy can also contribute to the low condom usage in this age group.
What are the consequences of low condom usage among young adults?
The consequences of low condom usage among young adults include increased risk of sexually transmitted infections such as HIV/AIDS, gonorrhea, and chlamydia. Low condom usage also contributes to higher rates of unintended pregnancies among this age group. These consequences can have long-term impacts on the health and well-being of young adults.
What can be done to increase condom usage among young adults?
To increase condom usage among young adults, it is important to focus on comprehensive sexual education programs that provide accurate information about sexual health, contraception, and the importance of condom use. Access to affordable and easily accessible condoms is also crucial. Additionally, destigmatizing condom use and promoting open conversations about sexual health can help to increase condom usage among young adults.
What are demographic trends?
Demographic trends refer to the statistical data that provides insights into the characteristics of a population, such as their age, gender, education, and income. These trends help identify patterns and changes in the population, which can be useful for understanding various societal issues.