
When we think about oxygen, the first thing that comes to mind is probably trees and plants. We’ve all been taught in school that plants are responsible for producing oxygen through photosynthesis. However, a recent scientific discovery has revealed that there is another major player in the oxygen game.
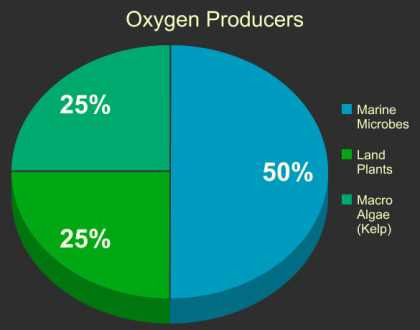
Scientists now believe that the ocean is actually the source of approximately 70% of the Earth’s oxygen. The vast amount of microscopic plants in the ocean, known as phytoplankton, produce oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. These tiny plants are not only essential for the marine ecosystem, but they also play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of oxygen in our atmosphere.
Phytoplankton are responsible for producing more oxygen than all the forests and land plants combined. They are able to thrive in the ocean’s surface waters, where sunlight is abundant. Through the process of photosynthesis, these plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into oxygen and organic compounds that are essential for other marine life.
- New Findings Shed Light on Oxygen Production
- Unraveling the Mystery
- Understanding the Impact
- Understanding the Role of Marine Photosynthesis
- Oceanic Algae and Its Oxygen-Producing Abilities
- Algae and Photosynthesis
- The Role of Phytoplankton
- Exploring the Impact of Phytoplankton on Oxygen Levels
- The Role of Photosynthesis
- Impact on Marine Ecosystems
- The Connection Between Oxygen and Coral Reefs
- Oxygen Production
- Ecosystem Impact
- The Future of Oxygen Production
- Rethinking the Importance of Protecting Ocean Habitats
- The Threats to Ocean Habitats
- The Consequences of Inaction
- The Need for Action
- Q&A:
- What is the source of Earth’s oxygen?
- Why is it important to know the source of Earth’s oxygen?
- How much oxygen do plants produce?
- Can we survive without oxygen from plants?
- What other factors can affect the production of oxygen?
- What is the source of 70% of Earth’s oxygen?
New Findings Shed Light on Oxygen Production
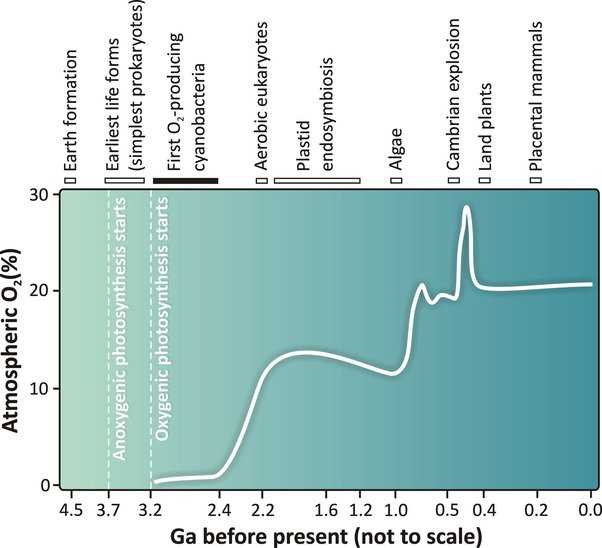
Scientists have made significant discoveries that have shed light on the process of oxygen production on Earth. These findings provide valuable insights into the intricate mechanisms responsible for supplying our planet with oxygen, a key element for supporting life.
Unraveling the Mystery
For decades, researchers have been puzzled by the source of the majority of Earth’s oxygen. However, recent research has revealed that approximately 70% of our planet’s oxygen is produced by marine plants, particularly phytoplankton.
Phytoplankton are microscopic plants that live in the surface waters of the ocean. Through the process of photosynthesis, they convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into energy and oxygen. These incredible organisms have the ability to produce vast amounts of oxygen, playing a crucial role in maintaining Earth’s oxygen-rich atmosphere.
Understanding the Impact
The discovery that phytoplankton is a major contributor to our oxygen supply highlights the importance of preserving and protecting our oceans. Factors such as pollution, overfishing, and climate change can disrupt the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, ultimately affecting the production of oxygen.
Furthermore, these findings have implications beyond Earth. As scientists explore the possibilities of space travel and colonization, understanding the mechanisms of oxygen production becomes essential for sustaining life on other planets.
By continuing to study and investigate the process of oxygen production, researchers hope to gain further insights into the intricate web of life on Earth and beyond.
Understanding the Role of Marine Photosynthesis
In the quest to unravel the mysteries of Earth’s oxygen production, scientists have turned their attention to the role of marine photosynthesis. Photosynthesis, which is the process through which plants and some microorganisms convert sunlight into energy, plays a crucial role in sustaining the oxygen levels on our planet.
While land-based plants are often celebrated for their role in oxygen production, marine photosynthesis actually accounts for a significant portion of the Earth’s oxygen supply. In fact, it is estimated that marine plants, such as phytoplankton and algae, are responsible for approximately 70% of the oxygen we breathe.
The oceans are teeming with microscopic marine plants that are capable of photosynthesis. These plants, known as phytoplankton, are found in abundance in the sunlit surface waters of the ocean. They harness the power of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and organic matter through photosynthesis.
The importance of marine photosynthesis goes beyond oxygen production. Phytoplankton, along with other marine plants, are at the heart of the ocean food web. They serve as the primary food source for many marine organisms, including fish, whales, and other sea creatures. By photosynthesizing and producing oxygen, marine plants support the entire ecosystem of the ocean.
However, the delicate balance of marine photosynthesis is under threat. Human activities such as pollution, climate change, and overfishing are disrupting marine ecosystems and affecting the health and abundance of marine plants. This disruption not only jeopardizes the oxygen supply but also endangers the entire marine food chain and ecosystem.
Understanding the role of marine photosynthesis is vital for the preservation of our planet’s oxygen production and the health of our oceans. Scientists continue to study and monitor phytoplankton and other marine plants to gain insights into their dynamics and response to environmental changes. By working towards a better understanding of marine photosynthesis, we can take actions to protect and restore the crucial role that these organisms play in maintaining the Earth’s oxygen levels.
Oceanic Algae and Its Oxygen-Producing Abilities
The Earth’s oceans are not only home to a vast array of marine life, but they also play a critical role in producing oxygen for our planet. It is estimated that 70% of Earth’s oxygen comes from oceanic algae, making them one of the primary sources of this essential gas.
Algae and Photosynthesis
Algae are simple, photosynthetic organisms that are found in aquatic environments, including both freshwater and seawater. They are capable of converting carbon dioxide into oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. Like plants, algae use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce energy-rich molecules and release oxygen as a byproduct.
What sets algae apart from plants is their ability to thrive in various marine habitats, including the open ocean, coral reefs, and coastal areas. This adaptability allows them to have a significant impact on global oxygen production.
The Role of Phytoplankton
One specific type of oceanic algae called phytoplankton deserves special attention due to its vital role in oxygen production. Phytoplankton are microscopic algae that float near the ocean’s surface, often forming large blooms. These blooms can be visible from space and are responsible for a significant portion of our planet’s oxygen supply.
Phytoplankton’s ability to produce oxygen is directly linked to their ubiquity and high growth rates. They are incredibly efficient at photosynthesis and can rapidly convert carbon dioxide into oxygen, helping to replenish Earth’s atmospheric oxygen levels.
- Phytoplankton also play a crucial role in the carbon cycle by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thus helping to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- They are a vital food source for a variety of marine animals, forming the base of the oceanic food web.
- Some species of phytoplankton can produce toxins, which can have harmful effects on marine ecosystems and human health.
Overall, oceanic algae, particularly phytoplankton, are indispensable contributors to oxygen production on Earth. Their ability to harness sunlight and convert carbon dioxide into oxygen plays a vital role in sustaining the planet’s ecosystems and maintaining a breathable atmosphere for all living organisms.
Exploring the Impact of Phytoplankton on Oxygen Levels
Phytoplankton, tiny plant-like organisms that inhabit the surface waters of the world’s oceans, play a crucial role in maintaining the oxygen balance in our atmosphere. Through the process of photosynthesis, these microscopic organisms convert carbon dioxide into oxygen, accounting for approximately 70% of Earth’s oxygen supply.
The Role of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the primary process by which phytoplankton produce oxygen. Using sunlight and nutrients, they convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This oxygen is then released into the surrounding water and eventually diffuses into the atmosphere, replenishing the oxygen levels in the air we breathe.
The photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton not only influences the concentration of oxygen in the atmosphere, but it also impacts the carbon cycle. Carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas responsible for climate change, is absorbed during photosynthesis and transformed into organic compounds, effectively reducing its concentration in the atmosphere.
Impact on Marine Ecosystems
Phytoplankton form the foundation of the marine food chain, providing sustenance for a wide array of marine organisms. Their photosynthetic activity produces organic matter, which serves as a food source for zooplankton, small fish, and other marine animals. Changes in phytoplankton populations can have cascading effects on marine ecosystems, affecting the abundance and distribution of various species.
Furthermore, fluctuations in phytoplankton populations can directly impact oxygen levels in the ocean. Excessive growth of phytoplankton, known as an algal bloom, can deplete oxygen levels in the water, leading to hypoxia or even anoxic conditions. These oxygen-deprived zones pose a threat to marine life, as many organisms rely on dissolved oxygen for survival.
Understanding the impact of phytoplankton on oxygen levels is crucial for assessing the health of our oceans and the stability of our atmosphere. Ongoing research and monitoring efforts are vital for predicting and mitigating potential disruptions to these delicate ecosystems.
The Connection Between Oxygen and Coral Reefs

Coral reefs are not only breathtakingly beautiful, but they also play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of oxygen on Earth. These vibrant underwater ecosystems are home to a diverse array of marine life, including fish, plants, and invertebrates.
Oxygen Production
One of the key contributions of coral reefs to oxygen production is through photosynthesis. Coral polyps contain tiny symbiotic algae called zooxanthellae, which live inside their tissues. These algae use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose through photosynthesis.
Furthermore, the calcium carbonate skeletons of coral reefs serve as a natural reservoir for carbon dioxide, absorbing it from the surrounding water. By sequestering carbon dioxide, coral reefs help reduce the levels of this greenhouse gas in the ocean, ultimately benefiting the entire planet.
Ecosystem Impact
The health of coral reefs is intricately linked to the overall health of the marine ecosystem. When coral reefs thrive, they provide shelter, food, and breeding grounds for numerous species. As more species benefit from the protection and resources provided by coral reefs, the overall productivity of the ecosystem increases. This, in turn, leads to an increase in oxygen production.
However, coral reefs are facing unprecedented threats, including rising ocean temperatures, pollution, and overfishing. These stressors can cause coral bleaching, a phenomenon where the coral expels the zooxanthellae due to stress, resulting in the coral’s death. The loss of coral reefs not only leads to a decline in biodiversity but also negatively impacts oxygen production.
The Future of Oxygen Production
Protecting and restoring coral reefs is crucial for maintaining the oxygen balance on Earth. Efforts to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change can help prevent further damage to coral reefs and their ability to produce oxygen. Additionally, implementing sustainable fishing practices and reducing pollution can contribute to the health and resilience of these delicate ecosystems.
| Threats to Coral Reefs | Actions to Protect Coral Reefs |
|---|---|
| Rising ocean temperatures | Reducing carbon emissions |
| Pollution | Implementing sustainable fishing practices |
| Overfishing | Reducing pollution |
By understanding the connection between oxygen and coral reefs, we can appreciate the vital role these underwater wonders play in sustaining life on Earth. It is our responsibility to protect and restore coral reefs for the benefit of future generations.
Rethinking the Importance of Protecting Ocean Habitats
As we now know, the ocean is the source of 70% of Earth’s oxygen. It is not only the home to a vast array of marine species, but it also plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate. However, there has been a lack of awareness and understanding about the importance of protecting ocean habitats.
The Threats to Ocean Habitats
Human activities such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change are posing significant threats to ocean habitats. Overfishing disrupts the balance of marine ecosystems, leading to the decline of important species and the loss of biodiversity. Pollution, including plastic waste and chemical pollutants, not only harms marine life but also contaminates the water we depend on for drinking and recreation. Climate change, with rising temperatures and ocean acidification, is causing coral bleaching and the destruction of coral reefs.
The Consequences of Inaction

If we continue to neglect the protection of ocean habitats, the consequences will be severe. The loss of biodiversity will disrupt the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, potentially leading to the collapse of fisheries and the loss of a vital food source for millions of people. Moreover, the decline of coral reefs will have ripple effects on tourism, coastal protection, and even the development of new medicines.
Furthermore, the oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate by absorbing heat and carbon dioxide. With the destruction of ocean habitats, this natural carbon sink will be compromised, exacerbating climate change and its impacts on global weather patterns.
The Need for Action
It is clear that protecting ocean habitats must be a priority. Governments, organizations, and individuals all need to work together to implement sustainable fishing practices, reduce pollution, and mitigate climate change. This includes creating marine protected areas, implementing stricter regulations on fishing and pollution, and investing in renewable energy sources.
By taking action to protect ocean habitats, we can ensure the continued provision of crucial ecosystem services, maintain biodiversity, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. It is time to rethink the importance of protecting these invaluable habitats and recognize the urgency of the situation.
References:
- “Ocean Acidification.” National Ocean Service, 2022, oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/ocean-acidification.html.
- “Protecting Our Oceans.” World Wildlife Fund, 2022, www.worldwildlife.org/threats/overfishing.
- “Why are the Oceans Important?” NOAA, 2022, oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/why-important.html.
Q&A:
What is the source of Earth’s oxygen?
The source of Earth’s oxygen is photosynthesis, which is primarily carried out by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.
Why is it important to know the source of Earth’s oxygen?
Understanding the source of Earth’s oxygen is important because it helps us comprehend the delicate balance of the planet’s atmosphere and the impact of human activities on it.
How much oxygen do plants produce?
Plants are responsible for producing about 30% of Earth’s oxygen. The remaining 70% is produced by oceans and marine algae through photosynthesis.
Can we survive without oxygen from plants?
No, we cannot survive without oxygen from plants. Oxygen is crucial for respiration and the survival of all living organisms.
What other factors can affect the production of oxygen?
Factors like deforestation, pollution, and climate change can negatively impact the production of oxygen by reducing the number of plants and disrupting ecosystems.
What is the source of 70% of Earth’s oxygen?
The source of 70% of Earth’s oxygen is marine photosynthesis, specifically by microscopic algae and plants called phytoplankton.