The issue of plastic waste pollution has become a pressing concern for many nations, and China has certainly been at the forefront of efforts to address this environmental crisis. In recent years, the Chinese government has implemented several restrictions and regulations on the import and processing of foreign plastic waste, with the aim of reducing pollution and promoting sustainable practices.
One significant move by China was the complete ban on imports of plastic waste from the United States. While this ban has garnered attention and sparked discussions about global recycling practices, there seems to be some confusion about when exactly it went into effect. Understanding the timeline of China’s ban on US plastic is crucial in assessing the implications it has had on the global recycling industry.
Contrary to popular belief, China did not impose a sudden ban on US plastic waste in one fell swoop. Instead, the government implemented a series of gradual measures to limit imports, which eventually led to a near-complete ban. These measures initially began as early as 2017, with stricter regulations and quality controls imposed on the types and quality of plastic waste permitted for import.
By the end of 2018, China had effectively halted the import of most plastic waste from the United States. However, some exceptions were made for certain high-quality materials and specialized processing facilities that met stringent environmental standards. This more gradual approach allowed the Chinese recycling industry and other countries to adapt and find alternative solutions to the sudden halt in waste imports.
- The Background and Context
- The Economic Impact on China
- The Environmental Benefits
- Reduction in Plastic Waste
- Promotion of Sustainable Practices
- Protection of Marine Life
- The Effect on US Exporters
- The International Reaction
- The Future of China’s Plastic Ban
- Q&A:
- Why did China ban US plastic?
- When did China’s ban on US plastic take effect?
- What are the implications of China’s ban on US plastic?
- Has China’s ban on US plastic had any positive effects?
- What are the alternatives for countries affected by China’s ban on US plastic?
The Background and Context
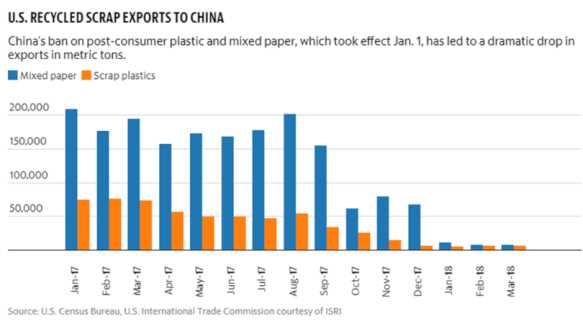
China’s ban on US plastic has become a contentious issue in the global waste management industry. The ban, officially known as the “National Sword” policy, was implemented on January 1, 2018, and caused a major disruption in the global recycling market.
The ban was a response to China’s growing concerns about environmental pollution and the health risks associated with plastic waste. China had been the world’s largest importer of waste for decades, with an estimated 45% of the world’s plastic waste being sent to China for recycling. However, the country was struggling to handle the increasing amount of waste, leading to widespread environmental problems.
The National Sword policy aimed to address this issue by prohibiting the importation of 24 types of solid waste, including various types of plastics. The ban also set strict contamination limits for the accepted materials, making it even more difficult for foreign countries to export their waste to China.
This ban had a significant impact on the recycling industry, especially in the United States. Prior to the ban, the US had been heavily reliant on China to process its plastic waste, with nearly 70% of the country’s plastic waste being exported to China for recycling. As a result of the ban, the US faced a sudden surplus of plastic waste with limited domestic infrastructure to handle it.
The ban also exposed the challenges and vulnerabilities of the global recycling supply chain. With China no longer accepting plastic waste, other countries were forced to find alternative solutions, which often turned out to be more costly and less environmentally friendly.
In response to the ban, the US has been exploring various strategies to address its plastic waste management challenges. This includes investing in domestic recycling infrastructure, promoting sustainable practices, and seeking new markets for its plastic waste.
The ban on US plastic by China serves as a reminder of the urgent need to shift towards a more sustainable and circular economy. While the ban has posed significant challenges to the global recycling industry, it has also created an opportunity for countries to reevaluate their waste management practices and work towards innovative solutions.
The Economic Impact on China
China’s decision to ban US plastic had a significant economic impact on the country. The ban resulted in a shift within China’s recycling industry and affected various sectors of the economy.
Firstly, the ban disrupted China’s plastic waste recycling sector, which heavily relied on imported waste plastic from the United States. With the ban in place, China had to find alternative sources of plastic waste or develop domestic recycling capabilities. This led to increased investment in recycling infrastructure and technology.
Additionally, the ban affected China’s manufacturing industry. Many Chinese manufacturers relied on imported plastic pellets from the United States to produce various goods. With the ban, manufacturers had to search for alternative suppliers or develop new ways to source raw materials, which resulted in increased costs and potential delays in production.
The ban also impacted China’s export market. China was a major exporter of plastic products, but with the ban in place, the country had to find alternative markets for its plastic goods. This led to increased competition and potentially affected China’s export revenues.
Furthermore, the ban had implications for China’s waste management and environmental sectors. Without the import of US plastic waste, China had to address its own waste management issues and develop more sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices.
Overall, while the ban on US plastic had negative consequences for China’s recycling industry, manufacturing sector, and export market, it also pushed China towards investing in domestic recycling capabilities and adopting more sustainable practices. The long-term effects of the ban are still unclear, but it has certainly prompted changes within China’s economy and environmental policies.
The Environmental Benefits
The ban on US plastic by China has brought about significant environmental benefits. Here are some of the positive impacts:
Reduction in Plastic Waste

One of the main advantages of China’s ban is the reduction in plastic waste. The ban has forced countries to look for alternative solutions for their plastic waste, such as recycling or finding new markets. As a result, there has been a decrease in plastic waste being sent to landfills or being improperly disposed of.
Promotion of Sustainable Practices
With the ban in place, there has been a renewed focus on sustainable practices. Countries are now looking for ways to reduce their plastic consumption and promote recycling and reusing. This has led to the development of innovative solutions and technologies that aim to minimize plastic waste and its impact on the environment.
Protection of Marine Life
The ban helps to protect marine life, particularly in coastal areas where plastic waste often ends up. By reducing the amount of plastic waste generated, there is less risk of marine animals ingesting or getting entangled in plastic debris. This helps to preserve the delicate ecosystems and biodiversity that rely on healthy marine environments.
| Environmental Benefits of China’s Ban on US Plastic: |
|---|
| – Reduction in plastic waste |
| – Promotion of sustainable practices |
| – Protection of marine life |
In conclusion, China’s ban on US plastic has had significant environmental benefits. It has led to a reduction in plastic waste, the promotion of sustainable practices, and the protection of marine life. These positive outcomes demonstrate the importance of implementing strict regulations and finding sustainable solutions to address the global plastic pollution crisis.
The Effect on US Exporters
The ban on US plastic waste imports by China has had a significant impact on US exporters. Prior to the ban, China was the largest market for US plastic waste exports, accepting more than 30% of the country’s plastic waste.
Since the ban, US exporters have been forced to find alternative markets for their plastic waste. Many have turned to other countries in Southeast Asia, such as Vietnam, Malaysia, and Thailand, which have seen a surge in plastic waste imports since the ban. However, these countries do not have the same capacity as China to handle large amounts of plastic waste, leading to concerns about environmental and health impacts.
The ban has also led to a decrease in the value of US plastic waste exports. China was willing to pay higher prices for certain types of plastic waste, such as clean and sorted materials, which were in high demand by Chinese manufacturers. Without the Chinese market, US exporters have had to lower their prices and sell to other countries at a lower profit margin.
Furthermore, the ban has highlighted the need for US exporters to improve domestic plastic waste recycling infrastructure. Rather than relying on shipping plastic waste overseas, there is a growing push for the US to invest in recycling facilities and develop a more sustainable method for dealing with plastic waste locally.
Overall, the ban on US plastic waste imports by China has caused significant challenges for US exporters. It has forced them to seek out alternative markets, deal with lower prices, and confront the need for better recycling infrastructure. Moving forward, it is crucial for the US to develop sustainable solutions for dealing with plastic waste to mitigate the effects of future export bans.
The International Reaction

China’s ban on US plastic has caused mixed reactions around the world. While some countries see this as an opportunity to strengthen their own plastic industries, others have raised concerns about the environmental impact of increased plastic production.
European countries, in particular, have expressed their concerns about the ban. They argue that China’s decision could lead to a surge in plastic waste generation within their borders and undermine their efforts to promote sustainable practices. Several European countries, including Germany and the Netherlands, have called for international cooperation to address the issue.
Environmental organizations have also criticized China’s ban, arguing that it does not tackle the root cause of plastic pollution. They argue that instead of banning imports of plastic waste, efforts should focus on reducing plastic consumption and promoting recycling. Greenpeace, for example, has called for stricter regulations on plastic manufacturing and a shift towards a circular economy.
On the other hand, some countries have seen the ban as an opportunity. Malaysia, for instance, has experienced a boost in its plastic recycling industry as it has become a major destination for the US plastic waste previously sent to China. Likewise, India has increased its imports of US plastic waste, capitalizing on China’s ban to boost its own plastic industry.
Overall, the international reaction to China’s ban on US plastic has been mixed. While some countries and organizations see it as an opportunity to address plastic pollution and promote sustainable practices, others have expressed concerns about its potential negative impact on the environment. The debate continues as countries and organizations evaluate the best approach to deal with plastic waste and its consequences.
The Future of China’s Plastic Ban
The ban on US plastic imports implemented by China in 2018 has had a significant impact on both countries’ waste management systems. China’s decision to halt the import of plastic waste from the US shook the global recycling industry and forced countries to re-evaluate their waste policies. However, the future of China’s plastic ban remains unclear.
China’s ban was initially seen as a wake-up call to the rest of the world to reduce plastic consumption and improve recycling infrastructure. It forced countries to find alternative markets for their plastic waste or invest in domestic recycling facilities. Many countries, including the US, have stepped up their efforts to recycle plastic domestically, but progress has been slow and challenging.
One possible future scenario is that China may relax its plastic ban in the future. As countries work towards improving their recycling capabilities and reducing plastic waste, China may reconsider its stance and allow controlled imports of plastic materials. This could provide a temporary solution for countries struggling to manage their plastic waste and give them more time to develop sustainable waste management systems.
Another possible future scenario is that China may continue to enforce its ban on plastic imports indefinitely. This would force countries to find long-term solutions to their plastic waste problem. It may lead to increased investment in recycling infrastructure, the development of new technologies to process plastic waste more efficiently, and a shift towards a circular economy where plastic is reused and recycled rather than discarded.
Regardless of the future of China’s plastic ban, one thing is clear: the global plastic waste problem needs urgent attention. It is essential for countries to reduce plastic consumption, invest in sustainable waste management systems, and develop innovative solutions to tackle plastic pollution. The future of China’s plastic ban relies not only on China’s policies but also on the collective efforts of countries worldwide to address this pressing issue.
In conclusion, the future of China’s plastic ban remains uncertain. It could either be relaxed to allow controlled imports or continue to be enforced indefinitely. Regardless, the global plastic waste problem requires immediate action and collaboration to find sustainable solutions.
Q&A:
Why did China ban US plastic?
China banned US plastic waste as part of its broader effort to reduce pollution and improve environmental sustainability. The country has been facing severe pollution problems due to the large amount of plastic waste it receives from other countries, including the US. By banning US plastic, China aims to shift the burden of handling plastic waste back to the countries that produce it.
When did China’s ban on US plastic take effect?
China’s ban on US plastic took effect on January 1, 2018. However, the decision to implement the ban was made in 2017, giving countries time to adjust their recycling and waste management practices.
What are the implications of China’s ban on US plastic?
The ban on US plastic by China has significant implications for the recycling industry and waste management systems globally. Countries that previously relied on China to process their plastic waste are now struggling to find alternative solutions, leading to an increase in plastic waste stockpiles and landfill use. This ban has highlighted the need for countries to develop their own recycling infrastructure and reduce plastic consumption.
Has China’s ban on US plastic had any positive effects?
Yes, China’s ban on US plastic has had some positive effects. It has forced countries to reevaluate their approach to plastic waste management, leading to increased investment in recycling facilities and technologies. The ban has also raised awareness about the environmental impact of plastic and sparked discussions on how to reduce plastic consumption and promote sustainable alternatives.
What are the alternatives for countries affected by China’s ban on US plastic?
Countries affected by China’s ban on US plastic are exploring various alternatives to manage their plastic waste. Some are investing in domestic recycling infrastructure to process the waste themselves, while others are looking for new export markets to send their plastic waste to. Additionally, there is a growing focus on reducing plastic consumption and promoting sustainable packaging solutions as a long-term solution to the plastic waste problem.