The ubiquitous presence of plastic in our daily lives has undoubtedly made it a symbol of convenience and modernity. However, the detrimental effects of plastic on the environment cannot be overlooked. From polluting our oceans and harming marine life to contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, the impact of plastic pollution is far-reaching and devastating. As a result, many countries and cities around the world have taken the bold step of banning single-use plastics in an effort to mitigate these harmful consequences.
One of the most immediate consequences of banning plastic is the need to find alternative materials for packaging and everyday items. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses and consumers alike. Companies must invest in research and development to find sustainable alternatives that are not only eco-friendly but also economical. Consumers, on the other hand, need to embrace the change and adapt their habits to reduce plastic consumption.
While the banning of plastic may lead to inconvenience in the short term, the long-term benefits cannot be understated. By reducing plastic waste, we can alleviate the burden on landfills and decrease the amount of plastic that ends up in our oceans. This, in turn, will help protect marine life and preserve delicate ecosystems. Furthermore, the reduction of plastic production and consumption will also have positive implications for greenhouse gas emissions, as plastic production is a major contributor to carbon dioxide emissions.
However, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and unintended consequences of banning plastic. For instance, the use of alternative materials may require more resources and energy for production, potentially leading to increased carbon emissions and environmental impact in other areas. Additionally, the transition to alternative materials may be costly, which could have economic implications, particularly for small businesses or developing countries that rely heavily on plastic manufacturing.
- Understanding Plastic Pollution
- The Problem with Plastic
- The Impact on Ecosystems
- Environmental Impact of Plastic
- Social and Economic Consequences
- 1. Job Losses and Economic Disruptions
- 2. Transition to Alternative Materials
- 3. Social and Behavioral Changes
- Q&A:
- What are the consequences of banning plastic?
- How does banning plastic reduce pollution?
- What alternatives to plastic can be used if it is banned?
- What industries will be affected the most by a plastic ban?
- What are some potential challenges in finding alternatives to plastic?
- What are the consequences of banning plastic?
Understanding Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution is a growing environmental issue that poses significant threats to ecosystems and human well-being. The production and consumption of plastic have increased exponentially in recent decades, leading to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills, oceans, and other natural environments.
The Problem with Plastic
One of the key problems with plastic is its durability. While this characteristic makes plastic a versatile and useful material, it also means that plastic takes hundreds of years to decompose naturally. This extended lifespan allows plastic waste to persist in the environment, causing long-term damage and pollution. Single-use plastics, such as plastic bags, bottles, and straws, are particularly concerning due to their high volume of production and low rate of recycling.
The Impact on Ecosystems
Plastic pollution has severe consequences for various ecosystems. When plastic enters bodies of water, it can be mistaken for food by marine animals and birds, leading to ingestion and entanglement. This can ultimately result in injury, suffocation, and even death. Additionally, the presence of plastic debris in water bodies can disrupt habitats, alter the food chain, and affect the overall health and biodiversity of marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
Furthermore, microplastics, which are tiny plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size, have become a widespread concern. They are often found not only in water bodies but also in the air and soil, posing threats to both aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Microplastics have been shown to accumulate in the tissues of organisms, potentially causing harm to their reproductive and immune systems.
In addition to the direct impact on ecosystems, plastic pollution also contributes to climate change. The production and incineration of plastic release greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming and climate instability.
Overall, understanding the scale and consequences of plastic pollution is crucial for developing effective strategies to address this pressing environmental issue. By implementing measures to reduce plastic production and consumption, improving waste management systems, and promoting recycling and sustainable alternatives, we can mitigate the negative impacts of plastic pollution and work towards a cleaner and healthier planet.
Environmental Impact of Plastic
Plastic has become a ubiquitous material in our daily lives, but its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. The production and disposal of plastic have significant consequences for the environment.
One of the main environmental issues with plastic is its long lifespan. Unlike organic materials, plastic takes hundreds of years to decompose. This means that plastic waste will accumulate in landfills, oceans, and other environments for extended periods, causing negative effects on ecosystems and wildlife.
| Environmental Consequences | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Pollution | Plastic pollution is a global problem affecting both land and marine environments. Trash islands, like the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, are a result of plastic waste accumulation in our oceans. This pollution harms marine life and disrupts the natural balance of aquatic ecosystems. |
| 2. Wildlife Impact | Plastic waste poses a severe threat to wildlife. Animals often mistake plastic debris for food and ingest it, leading to health issues and even death. Additionally, animals can become entangled in plastic packaging, causing physical injuries and impairing their ability to move or hunt. |
| 3. Microplastics | Plastic items can break down into tiny fragments called microplastics. These microplastics can be found in water sources, soil, and even the air we breathe. They have the potential to enter the food chain, endangering not just marine life but also humans who consume seafood. |
| 4. Resource Depletion | The production of plastic requires significant amounts of natural resources such as petroleum and natural gas. The extraction and processing of these resources contribute to environmental degradation, including air and water pollution. Moreover, using non-renewable resources for disposable products is highly inefficient and unsustainable. |
| 5. Climate Change | The production, use, and disposal of plastic contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. These emissions occur during the extraction and manufacturing processes, as well as the incineration and decomposition of plastic waste. In the long run, reducing plastic consumption can help mitigate the impact of climate change. |
In conclusion, plastic has extensive environmental implications that need to be addressed. Banning or reducing plastic usage is crucial to protect ecosystems, wildlife, and the overall health of our planet.
Social and Economic Consequences
Implementing a ban on plastic can have significant social and economic consequences. While the impact on the environment is the primary concern, it is essential to consider the effects on various industries and communities.
1. Job Losses and Economic Disruptions
The plastic industry employs millions of people worldwide. Banning plastic products can result in job losses and economic disruptions. Companies that produce plastic items, such as bags, bottles, and packaging materials, might be forced to downsize or shut down entirely. This can lead to unemployment and financial hardship for workers and their families.
Furthermore, the ban can affect related industries that rely on plastic, such as manufacturing and retail. Suppliers of raw materials, machinery, and equipment for plastic production may also suffer from decreased demand. The overall economic impact can be substantial, especially in regions heavily dependent on the plastic industry.
2. Transition to Alternative Materials

As plastic is phased out, a transition to alternative materials must occur. This shift can be challenging and expensive. Businesses and consumers will need to adapt to new materials, potentially leading to increased production costs and consumer prices.
The development and adoption of alternative materials might also face technical and logistical challenges. Research and development will be necessary to find alternatives that are environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and perform the same functions as plastic. Implementing the necessary infrastructure and supply chains for these alternatives can require significant investments.
Additionally, the transition to alternative materials can result in changes in consumer behavior and preferences. Consumers may need to adjust to new packaging and product designs, which can impact their purchasing decisions and loyalty to certain brands.
3. Social and Behavioral Changes
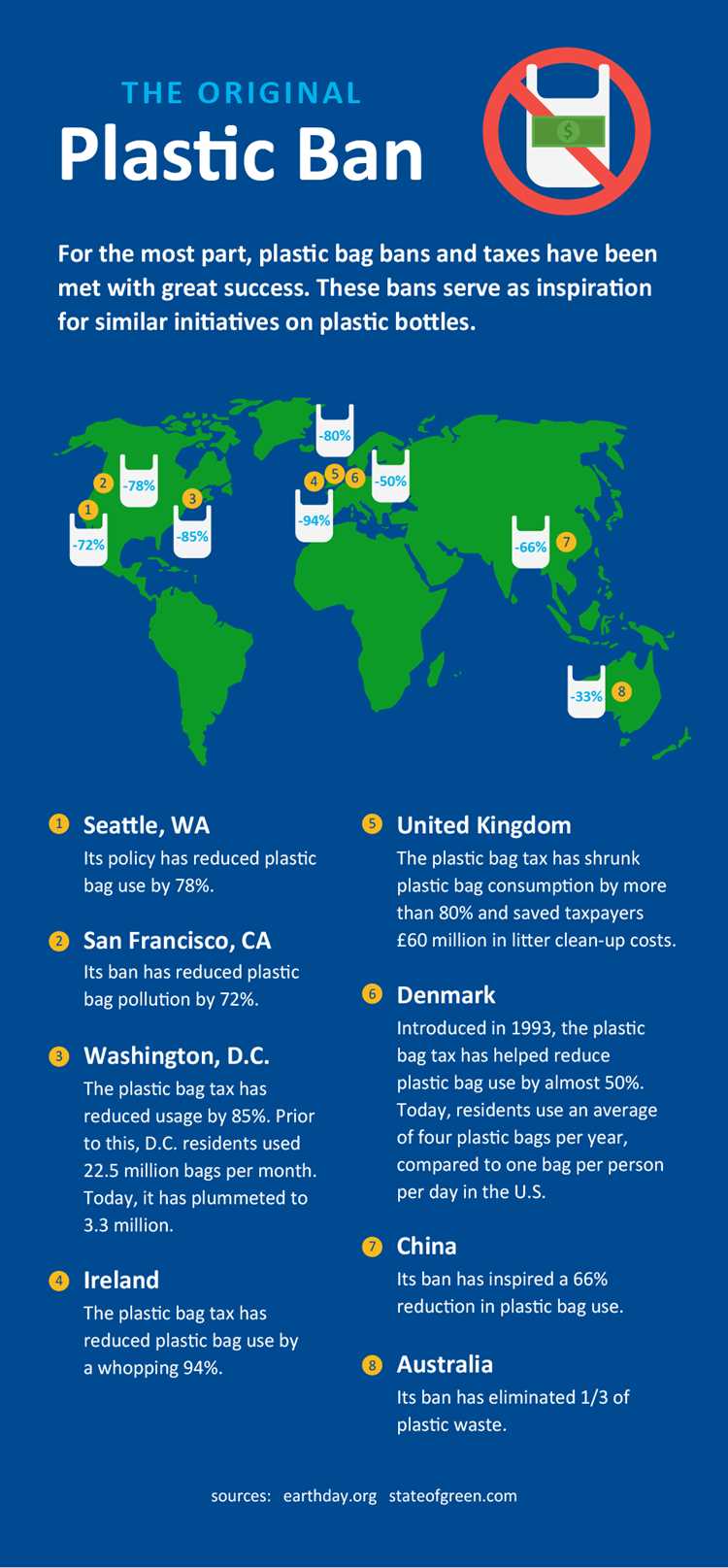
Banning plastic can lead to social and behavioral changes. Consumers might need to adopt new habits, such as carrying reusable bags or using alternative packaging options. These changes can require education and awareness campaigns to ensure widespread adoption.
Public perception and attitudes towards plastic may also change. This can lead to increased environmental consciousness and a shift towards more sustainable practices. Individuals and communities may become more active in reducing waste and advocating for other environmentally friendly initiatives.
Conclusion
While the ban on plastic can yield positive environmental outcomes, it is essential to consider the social and economic consequences. Job losses, economic disruptions, and the transition to alternative materials are some of the key challenges that need to be addressed. However, with appropriate planning and support, these consequences can be mitigated, and a more sustainable future can be achieved.
Q&A:
What are the consequences of banning plastic?
The consequences of banning plastic can be both positive and negative. On one hand, banning plastic can have a positive impact on the environment by reducing pollution and ocean litter. It can also encourage the development of more sustainable alternatives to plastic. On the other hand, banning plastic can have negative economic consequences, as many industries rely heavily on plastic for packaging and manufacturing. Additionally, finding suitable alternatives to plastic that are both cost-effective and environmentally friendly can be a challenge.
How does banning plastic reduce pollution?
Banning plastic can reduce pollution by decreasing the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills, waterways, and oceans. Plastic is non-biodegradable and can take hundreds of years to decompose. By banning plastic, less plastic waste is generated, leading to a decrease in pollution and a cleaner environment.
What alternatives to plastic can be used if it is banned?
If plastic is banned, there are several alternatives that can be used. Some options include paper and cardboard packaging, glass containers, metal utensils, and biodegradable materials such as plant-based plastics. These alternatives are more environmentally friendly as they are biodegradable or can be easily recycled.
What industries will be affected the most by a plastic ban?
Industries such as packaging, manufacturing, and retail are likely to be affected the most by a plastic ban. These industries rely heavily on plastic for packaging and transportation of goods. Finding suitable alternatives to plastic packaging and containers can be a challenge, as they need to be cost-effective, durable, and environmentally friendly.
What are some potential challenges in finding alternatives to plastic?
Finding alternatives to plastic can be challenging due to several reasons. First, the cost of alternatives may be higher than plastic, making it less attractive to businesses. Second, some alternatives may not be as durable or versatile as plastic, limiting their use in certain industries. Finally, scaling up production of alternatives to meet the demand can be a challenge, as it requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology.
What are the consequences of banning plastic?
Banning plastic can have several consequences. On the positive side, it can reduce pollution, protect wildlife, and promote sustainable practices. However, it can also lead to job losses in plastic manufacturing industries and create a need for alternative materials that may have their own environmental impacts.