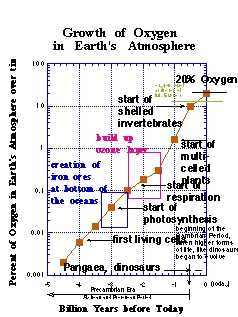
Oxygen is a vital element for sustaining life on Earth. We breathe it in every day without even thinking about it. But have you ever wondered where most of the oxygen comes from? It’s not just the trees and plants that are responsible for producing this essential gas. In fact, recent studies have shown that a surprising source is responsible for 80% of the Earth’s oxygen production, and it’s not what you might expect.
The ocean is the main source of Earth’s oxygen. It may seem hard to believe, but it’s true. Phytoplankton, microscopic plants that live in the upper layers of the ocean, play a crucial role in this process. These tiny organisms produce oxygen through photosynthesis, a process that uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. In fact, phytoplankton are responsible for producing more oxygen than all of the trees and plants on land combined.
But how exactly do these tiny plants produce so much oxygen? The answer lies in their incredible numbers. Phytoplankton are present in vast quantities in the ocean, and their growth is fueled by nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. As they multiply and flourish, they create what scientists call “blooms,” which are large, visible patches of phytoplankton on the surface of the water. These blooms can stretch for miles and are often so dense that they can be seen from space.
So why is this discovery important? Understanding the role of the ocean in oxygen production is crucial for maintaining the balance of our planet’s atmosphere. With climate change and increasing pollution levels, the health of the ocean’s phytoplankton is under threat. Changes in water temperature, nutrient availability, and ocean acidification can all have a detrimental effect on these tiny plants, which could, in turn, disrupt the delicate balance of oxygen production on Earth.
- Unlocking the Secret: Discovering the Main Source of Earth’s Oxygen
- Photosynthetic Bacteria: Nature’s Oxygen Producers
- Quantifying the Impact: Unveiling the Numbers
- The Mystery of Oxygen Production: Unraveling the 80% Enigma
- The Invisible Warriors: Meet the Unsung Heroes Behind Oxygen Creation
- The Threats Facing Phytoplankton
- The Importance of Preserving Phytoplankton
- Blue Gold: The Key Role of Our Oceans in Oxygen Production
- The Green Machine: Revealing the Surprising Contribution of Plant Life
- The Power of Photosynthesis
- The Lungs of the Planet
- Balancing Act: Understanding the Delicate Oxygen-Ecosystem Relationship
- The Marvel of Photosynthesis
- The Oxygen-Ecosystem Relationship
- Q&A:
- What is the main source of Earth’s oxygen?
- How much of Earth’s oxygen is produced by photosynthesis?
- What organisms perform photosynthesis?
- What is the process of photosynthesis?
Unlocking the Secret: Discovering the Main Source of Earth’s Oxygen
For centuries, scientists and researchers have puzzled over the main source of Earth’s oxygen. Recently, a breakthrough discovery has shed light on this age-old mystery. Through extensive research and analysis, scientists have determined that photosynthetic bacteria are the primary contributors to oxygen production on our planet.
Photosynthetic Bacteria: Nature’s Oxygen Producers
Photosynthetic bacteria, also known as cyanobacteria, are microscopic organisms that play a crucial role in oxygen production. These bacteria possess specialized pigments that allow them to convert sunlight into energy through a process called photosynthesis.
During photosynthesis, photosynthetic bacteria absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen as a byproduct. This process occurs in various environments, including oceans, freshwater bodies, and even in the soil.
Quantifying the Impact: Unveiling the Numbers
The extent of photosynthetic bacteria’s contribution to Earth’s oxygen production is truly remarkable. Recent studies estimate that these bacteria are responsible for approximately 80% of the oxygen generated on our planet.
To put this into perspective, the Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” produces approximately 6% of Earth’s oxygen. While the Amazon rainforest is undeniably important, the role of photosynthetic bacteria in oxygen production is even more significant.
| Oxygen Source | Percentage of Oxygen Production |
|---|---|
| Photosynthetic Bacteria | 80% |
| Amazon Rainforest | 6% |
| Other Sources (Plants, Algae, etc.) | 14% |
These findings have significant implications for our understanding of Earth’s oxygen cycle. The discovery of the primary role played by photosynthetic bacteria not only enhances our knowledge of the biosphere but also emphasizes the importance of preserving and protecting these vital organisms.
In conclusion, the unlocking of the secret behind the main source of Earth’s oxygen brings us a step closer to comprehending the intricate workings of our planet. Photosynthetic bacteria, with their remarkable ability to convert sunlight into oxygen, are the unsung heroes responsible for sustaining life as we know it.
The Mystery of Oxygen Production: Unraveling the 80% Enigma
Oxygen is an essential element for sustaining life on Earth, but have you ever wondered where the majority of Earth’s oxygen comes from? Recent scientific studies have revealed that approximately 80% of the oxygen in our atmosphere is produced by marine plants.
Marine plants, including algae and phytoplankton, are tiny organisms that live in oceans and other bodies of water. Through a process called photosynthesis, these plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and carbohydrates. The oxygen released during photosynthesis is then released into the atmosphere, contributing to the oxygen levels that support life on Earth.
This discovery has brought about a paradigm shift in our understanding of oxygen production. Previously, it was believed that the majority of oxygen came from terrestrial plants like trees and shrubs. However, recent research has shown that marine plants play a critical role in oxygen production.
Why are marine plants so important in oxygen production? One reason is their vast numbers. The oceans cover approximately 70% of Earth’s surface, providing a significant habitat for marine plants to thrive. Additionally, marine plants have a high growth rate and can reproduce rapidly, contributing to a continuous production of oxygen. Their ability to efficiently photosynthesize and release oxygen also contributes to their significance in the oxygen cycle.
Furthermore, the oxygen produced by marine plants has a global impact. It is transported by ocean currents and wind patterns, spreading across the Earth and sustaining life in diverse ecosystems. From the largest marine mammals to the tiniest microorganisms, the oxygen produced by marine plants is crucial for the survival of countless species.
Despite the recent advances in understanding oxygen production, there is still much to learn. Researchers continue to study the intricate interactions between marine plants, the oceans, and the atmosphere to gain a deeper understanding of this vital process.
In conclusion, the mystery of oxygen production has been partially unraveled with the discovery that marine plants contribute to approximately 80% of the oxygen in our atmosphere. This revelation highlights the importance of these tiny organisms and their role in sustaining life on Earth. As we continue to explore and study our planet, we may uncover even more fascinating secrets about this essential element and its production.
The Invisible Warriors: Meet the Unsung Heroes Behind Oxygen Creation
Phytoplankton may be small, but they play a crucial role in the oxygen production process. These microscopic organisms, often referred to as the invisible warriors, are responsible for about 50% of the oxygen we breathe. They live in oceans, lakes, and other bodies of water, harnessing the power of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and nutrients into oxygen through photosynthesis.
Although the sheer number of these tiny organisms may seem inconsequential, their collective effort is monumental. Phytoplankton blooms can cover massive areas of the ocean surface, creating what is often called the “ocean’s lungs.” These blooms not only provide oxygen but also serve as a vital food source for marine life, forming the foundation of the marine food chain.
Surprisingly, phytoplankton is not just limited to remote, open waters. They can also be found in freshwater lakes and rivers, where they contribute significantly to the oxygen content of these ecosystems. In fact, research has shown that phytoplankton in lakes and rivers are responsible for nearly 30% of global oxygen production.
The Threats Facing Phytoplankton
Despite their critical role, phytoplankton is facing numerous threats that jeopardize their existence and, consequently, Earth’s oxygen production. Climate change, pollution, and the destruction of their habitats are all factors that affect these invisible warriors.
Warmer temperatures, caused by climate change, can lead to the disruption of the delicate balance necessary for phytoplankton’s survival. Higher temperatures can cause increased evaporation, leading to more saline and nutrient-depleted water conditions that are not favorable for these organisms. Additionally, ocean acidification, another consequence of climate change, poses a threat to phytoplankton’s ability to produce oxygen.
Pollution, especially excess nutrient runoff from agriculture and industrial activities, can also have detrimental effects on phytoplankton populations. Excessive nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, can lead to harmful algal blooms, which can result in oxygen-depleted dead zones in aquatic environments.
The Importance of Preserving Phytoplankton
Understanding the vital role that phytoplankton plays in oxygen production is crucial for our planet’s future. By taking steps to reduce pollution, combat climate change, and protect their habitats, we can ensure the continued existence of these unsung heroes.
| Threats to Phytoplankton | Actions to Preserve Phytoplankton |
|---|---|
| Climate change | – Reducing greenhouse gas emissions |
| Pollution | – Implementing better waste management practices – Encouraging sustainable agriculture |
| Habitat destruction | – Establishing protected areas – Supporting conservation efforts |
By recognizing and appreciating the invisible warriors behind oxygen creation, we can all contribute to preserving the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems and ensure a future where Earth continues to provide us with the oxygen we need to thrive.
Blue Gold: The Key Role of Our Oceans in Oxygen Production
Oceans cover more than 70% of Earth’s surface, making them a vital source of oxygen production. While trees and plants on land have long been recognized for their role in producing oxygen, the contribution of our oceans should not be underestimated.
It is estimated that oceans are responsible for about 50% of the oxygen produced on Earth. This significant contribution is mainly achieved through photosynthesis carried out by phytoplankton, microscopic organisms that float near the surface of the ocean.
Phytoplankton, often referred to as the “grass of the sea,” use sunlight and nutrients present in the water to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen through photosynthesis. They are considered the primary producers in the marine ecosystem and form the base of the ocean food chain.
Not only do phytoplankton produce oxygen, but they also play a crucial role in regulating the global climate. They absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the effects of greenhouse gas emissions and ocean acidification.
Unfortunately, the health and abundance of phytoplankton are being threatened by various factors, including climate change, pollution, and overfishing. These factors can disrupt the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem and have long-term consequences for oxygen production and carbon sequestration.
Preserving the health of our oceans and protecting phytoplankton populations is essential for maintaining the oxygen levels that support life on Earth. It requires collective efforts, including reducing carbon emissions, preventing pollution, and establishing marine protected areas.
Next time you take a breath, remember that the oceans are not just a source of beauty and wonder, but also the unsung heroes behind the oxygen we need to survive.
The Green Machine: Revealing the Surprising Contribution of Plant Life
Plants, from towering trees to tiny green algae, contribute about 80% of the world’s oxygen production. This fact may come as a surprise, as we usually associate oxygen production with marine ecosystems. However, plants are essential in sustaining life as we know it.
The Power of Photosynthesis
Plants harness the power of photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. During this process, they take in carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen as a byproduct. This exchange is crucial for the maintenance of our planet’s oxygen levels.
While marine and freshwater ecosystems do contribute to oxygen production, it is the abundant plant life on land that takes the lead. Trees, shrubs, grasses, and even microscopic plants like phytoplankton all contribute their bit to keeping our atmosphere oxygen-rich.
The Lungs of the Planet
Forests, in particular, play a vital role in oxygen production. The Amazon Rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the planet,” is responsible for producing a significant amount of the world’s oxygen. Trees in the rainforest act as giant oxygen generators, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through photosynthesis.
However, it’s important to note that the oxygen produced by plants does not accumulate indefinitely in the atmosphere. Oxygen is continually being consumed by living organisms and natural processes, ultimately maintaining a delicate equilibrium.
Understanding the significant contribution of plant life to Earth’s oxygen production reminds us of the importance of conserving and protecting our natural ecosystems. By preserving forests and promoting sustainable practices, we can ensure a healthy balance of oxygen in the air we breathe.
Balancing Act: Understanding the Delicate Oxygen-Ecosystem Relationship

Oxygen, a vital component of Earth’s atmosphere, is continuously produced and consumed by various biological and physical processes. The delicate balance between oxygen production and consumption is crucial for the maintenance of life on our planet.
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants and some bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into oxygen and glucose, is the primary source of oxygen production on Earth. This incredible process is responsible for approximately 80% of the oxygen in our atmosphere.
The Marvel of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis not only produces oxygen but also plays a critical role in maintaining the delicate balance of atmospheric gases. During this process, plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the air. This oxygen then becomes available for other organisms, including humans, to breathe, sustaining life on Earth.
Furthermore, photosynthesis also influences the carbon cycle by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants convert carbon dioxide into glucose, which serves as a source of energy for various organisms.
The Oxygen-Ecosystem Relationship
The oxygen produced by photosynthesis is used by aerobic organisms for respiration. During respiration, organisms take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. This carbon dioxide can then be reused by plants in the process of photosynthesis, completing the oxygen-ecosystem cycle.
However, human activities, such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, have disrupted this delicate balance. Deforestation reduces the number of plants available to produce oxygen, while burning fossil fuels releases additional carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, increasing greenhouse gas levels and contributing to climate change.
Therefore, it is crucial to understand and appreciate the delicate balance between oxygen production and consumption. By promoting sustainable practices and preserving natural ecosystems, we can help maintain this delicate balance and ensure a stable supply of oxygen for future generations.
In conclusion, the delicate oxygen-ecosystem relationship is a critical aspect of life on Earth. Photosynthesis, the primary source of oxygen production, not only produces oxygen but also regulates the carbon cycle and influences the overall balance of atmospheric gases. It is essential for us to protect and preserve natural ecosystems to maintain this delicate balance and safeguard our planet’s oxygen supply.
Q&A:
What is the main source of Earth’s oxygen?
The main source of Earth’s oxygen is photosynthesis.
How much of Earth’s oxygen is produced by photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is responsible for approximately 80% of Earth’s oxygen production.
What organisms perform photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is mainly carried out by plants, algae, and some bacteria.
What is the process of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen.