
Plastics have become an integral part of our modern society, with their use permeating almost every aspect of our daily lives. However, the convenience and versatility offered by plastics come at a steep price. While plastics have undoubtedly improved our lives in many ways, they also have several detrimental effects on our environment and health. In this article, we will explore the three most harmful effects of plastics.
Firstly, one of the most glaring issues with plastics is their impact on our planet’s ecosystems. Plastics are not biodegradable and can persist in our environment for hundreds of years. This leads to a build-up of plastic waste, especially in our oceans, which has devastating consequences for marine life. Sea creatures often mistake plastic for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement, both of which can be fatal. Plastics also leach harmful chemicals into the soil and water, polluting our natural resources and damaging delicate ecosystems.
Secondly, the production and disposal of plastics contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. The process of extracting and refining crude oil, which is used to make plastics, releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Additionally, the incineration of plastics produces toxic gases and contributes to air pollution. Furthermore, the improper disposal of plastic waste, such as landfilling or burning, releases harmful chemicals into the air and soil, further exacerbating the problem.
Lastly, the use of plastics has detrimental effects on human health. Many plastic products contain hazardous chemicals, such as phthalates and bisphenol A, which can leach into the food and beverages we consume, posing a significant risk to human health. These chemicals have been linked to various health issues, including hormone disruption, reproductive problems, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, microplastics, tiny particles of plastic that have infiltrated our food chain and drinking water, have been found in alarming quantities, raising concerns about their potential long-term health effects.
In conclusion, while plastics have undoubtedly revolutionized various aspects of our lives, their detrimental effects on the environment and human health cannot be ignored. It is important for individuals, industries, and governments to take proactive measures to reduce the use of plastics, find alternative solutions, and properly manage plastic waste to mitigate these harmful effects.
- Pollution of Water and Soil
- 1. Water Pollution
- 2. Soil Pollution
- 3. Contamination of Drinking Water
- Endangering Marine Life
- Health Risks for Humans
- 1. Endocrine Disruption
- 2. Respiratory Issues
- 3. Chemical Exposure
- Contribution to Climate Change
- Impact on the Oceans
- Overall Environmental Impact
- Impact on Wildlife
- Q&A
- What are some harmful effects caused by plastics?
- How does plastic pollution affect wildlife and marine life?
- What are some of the toxic chemicals found in plastics?
- How do plastics contribute to greenhouse gas emissions?
- What can individuals do to reduce the harmful effects of plastics?
- What are the harmful effects of plastics?
- How does plastic pollution affect the environment?
Pollution of Water and Soil
Plastics are one of the major sources of pollution in our water bodies and soil. The improper disposal and management of plastic waste contribute to the contamination of these essential resources. Here are the three harmful effects of plastics on our water and soil:
1. Water Pollution
Plastic waste, especially single-use plastics like bottles and bags, make their way into rivers, lakes, and oceans. These plastics break down into smaller pieces called microplastics, which can have devastating effects on aquatic life. Marine animals often mistake these tiny particles for food and end up ingesting them. This can lead to blockages in their digestive systems, malnutrition, and in some cases, even death. Moreover, the toxic chemicals that plastics contain can leach into the water, further polluting it.
2. Soil Pollution
Improper disposal of plastic waste on land can result in soil pollution. Plastics take hundreds of years to break down, and during this process, they release toxic chemicals into the soil. These chemicals can contaminate the soil and affect the organisms living within it. Plastic pollution can hinder the growth of plants and disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem. Additionally, when plastic waste accumulates on the surface, it prevents rainwater from permeating into the soil, leading to waterlogging and reduced fertility.
3. Contamination of Drinking Water

Plastic pollution in water bodies can also contaminate our drinking water sources. Many communities rely on rivers, lakes, and groundwater as their primary sources of drinking water. However, when these sources are polluted with plastic waste, the quality of drinking water is compromised. Harmful chemicals from plastics can seep into the water, making it unsafe for consumption. This poses significant health risks to human beings, as exposure to these chemicals can lead to various diseases, including cancer and hormonal disruptions.
In conclusion, the pollution of water and soil caused by plastics is a serious environmental issue. It not only harms aquatic life and terrestrial ecosystems but also poses health risks to humans. Effective waste management strategies, such as recycling and reducing single-use plastics, are crucial to mitigate these harmful effects and protect our precious resources.
Endangering Marine Life
Plastics pose a significant threat to marine life. Every year, millions of marine animals, including fish, seabirds, turtles, and marine mammals, are harmed or killed by plastic pollution.
One of the main ways plastics endanger marine life is through entanglement. Animals such as seals, whales, and turtles can become entangled in discarded fishing nets, plastic bags, and other debris. This can result in serious injuries, suffocation, or even death.
Ingestion of plastic is another major problem for marine animals. Many species mistake floating plastic for food and end up ingesting it. This can lead to digestive blockages, malnutrition, and starvation. Plastic can also leach harmful chemicals into an animal’s body, causing long-term health problems.
The presence of plastic in the ocean also disrupts marine ecosystems. Coral reefs, for example, are vital habitats for numerous species, but they are highly susceptible to damage from plastic pollution. Floating debris can smother corals, preventing them from receiving the sunlight and nutrients they need to survive.
- Plastics can also introduce invasive species to new areas. Microorganisms and small organisms can attach themselves to floating plastics and hitch a ride to new marine environments. Once they arrive, these invasive species can disrupt the balance of existing ecosystems, outcompete native species, and cause ecological damage.
- Furthermore, plastic pollution in the ocean can contribute to global climate change. Plastics are made from fossil fuels, so their production and disposal release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases are a major contributor to climate change, which has numerous negative effects on marine life, including ocean acidification and rising sea temperatures.
In conclusion, the endangerment of marine life is a significant consequence of plastic pollution. Entanglement, ingestion, disruption of ecosystems, introduction of invasive species, and contribution to climate change are all harmful effects that need to be addressed in order to protect our oceans and the creatures that inhabit them.
Health Risks for Humans
Plastics pose several health risks for humans, some of which are directly related to the toxic chemicals used in their production. These chemicals can leach out of the plastic products and enter our bodies through ingestion, inhalation, or skin absorption.
1. Endocrine Disruption
One of the most concerning health effects of plastics is their potential to disrupt the endocrine system, which is responsible for regulating hormone production and various bodily functions. Many plastics contain phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), and other chemicals known as endocrine disruptors. These chemicals can mimic or interfere with the hormones in our bodies, leading to hormonal imbalances and potentially causing serious health issues such as reproductive and developmental problems, thyroid disruption, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
2. Respiratory Issues
Inhalation of microplastics, which are tiny plastic particles or fibers less than 5mm in size, can have detrimental effects on the respiratory system. These particles can be found in the air we breathe, especially in indoor environments where plastics are commonly used. When inhaled, microplastics can irritate the lungs and cause or worsen respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and even lung cancer.
In addition, burning plastics releases toxic fumes and particles into the air, further contributing to respiratory problems. The toxins released during the incineration of plastics can include dioxins, furans, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are known to be hazardous to human health.
3. Chemical Exposure

Exposure to the chemicals present in plastics can also lead to other negative health effects. For example, certain plastics contain additives such as flame retardants, which are used to make them less flammable. However, these flame retardants are known to be toxic and have been linked to various health problems, including neurological disorders, immune system suppression, and reproductive toxicity.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of plastics can release harmful chemicals into the environment, which can then contaminate our food and water sources. This can result in indirect exposure to these chemicals, further increasing the health risks for humans.
Overall, the health risks associated with plastics highlight the importance of reducing plastic consumption, implementing stricter regulations on plastic production and usage, and exploring alternative materials that are safer for both human health and the environment.
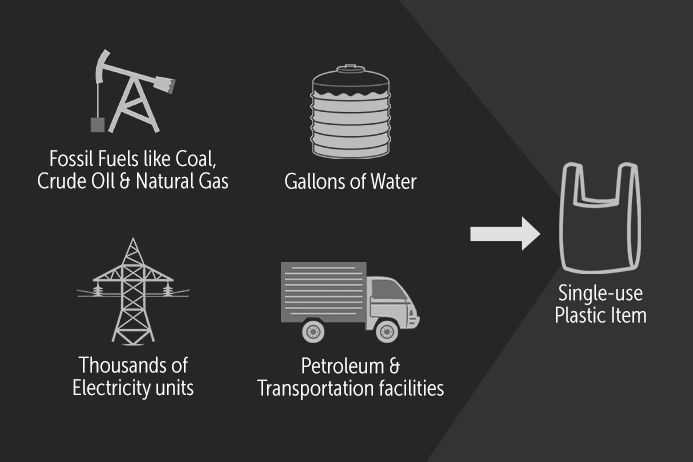
Contribution to Climate Change
Plastics play a significant role in contributing to climate change, primarily through the emission of greenhouse gases during their production and disposal.
Plastics are derived from fossil fuel sources, such as oil and natural gas. The extraction, transportation, and refining of these fossil fuels release substantial amounts of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). These gases are the main contributors to global warming and climate change. As plastics are made from these fossil fuels, the manufacturing process of plastics is inherently carbon-intensive.
Additionally, the disposal of plastics also contributes to climate change. When plastics are incinerated, they release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Incineration is a common waste management method for plastics, especially in areas with limited landfills. Furthermore, when plastics are disposed of in landfills, they can break down over time and release methane. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that has a higher warming potential than CO2, making it a considerable contributor to climate change.
Impact on the Oceans

The contribution of plastics to climate change also has significant implications for the world’s oceans.
As climate change progresses, sea levels rise, and weather patterns become more extreme. These changes have a direct impact on coastal areas, affecting communities and ecosystems. Plastics, being lightweight and buoyant, can be easily carried by wind and rivers, eventually ending up in the ocean.
Moreover, as the sea surface temperature rises due to climate change, certain marine species, such as coral, are under stress and become more vulnerable to diseases. Plastics can exacerbate this problem by providing a suitable environment for pathogens and facilitating the spread of diseases among marine organisms.
Overall Environmental Impact
The contribution of plastics to climate change is part of their wider environmental impact, which affects various ecosystems and organisms on Earth.
Climate change has far-reaching consequences for biodiversity and ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and severe weather events can lead to habitat loss, species extinction, and disruptions in ecological balance. Plastics, as an enabler of climate change, indirectly contribute to these negative environmental impacts.
It is crucial to address the contribution of plastics to climate change to mitigate the adverse effects on both the planet and its inhabitants. Initiatives such as reducing plastic consumption, promoting recycling and circular economy practices, and transitioning to renewable energy sources can help minimize the carbon footprint associated with plastics.
Impact on Wildlife
Plastics have a devastating impact on wildlife, both on land and in the oceans. The abundant use of plastic products, such as bags, bottles, and packaging, has led to an alarming increase in plastic pollution, posing a significant threat to various animal species.
One harmful effect of plastics on wildlife is entanglement. Many marine animals, such as seals, dolphins, and sea turtles, become entangled in plastic debris, such as fishing nets and plastic bags. This can constrict their movements, leading to injuries, suffocation, or even death. Additionally, birds, squirrels, and other land animals can also get entangled in plastic materials, causing similar negative consequences.
Another detrimental effect is ingestion. Marine creatures often mistake plastic pieces for food, especially small particles like microplastics. Sea turtles, for example, may consume plastic bags, thinking they are jellyfish. Ingesting plastic can cause a host of problems, including blockages in the digestive system, nutrient deficiencies, and even death. Seabirds and other marine animals that consume plastics can also suffer from similar harmful effects.
Besides physical harm, plastics also introduce harmful chemicals into the environment, affecting wildlife at the molecular level. Many plastic products contain toxic additives, such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA). These substances can leach out of the plastics, contaminating water and soil. When wildlife is exposed to these chemicals, it can lead to reproductive issues, hormonal imbalances, and even genetic defects.
The impact of plastics on wildlife is significant and widespread. It is crucial for us to reduce plastic use and properly dispose of plastic waste to protect the diverse range of species that share our planet.
Q&A
What are some harmful effects caused by plastics?
Plastics can have several harmful effects on our environment and our health. One of the main effects is pollution. Plastics do not decompose easily and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This leads to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills, oceans, and other ecosystems, causing harm to wildlife and marine life. Another harmful effect is the release of toxic chemicals. Some plastics contain harmful additives, such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA), which can leach into the environment and have adverse effects on human health. Lastly, the production of plastics contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change and global warming.
How does plastic pollution affect wildlife and marine life?
Plastic pollution has a severe impact on wildlife and marine life. Many animals mistake plastic for food and end up consuming it. This can lead to blockages in their digestive systems, causing them to starve or suffer from internal injuries. Marine species such as sea turtles, dolphins, and seabirds are particularly vulnerable to plastic pollution. Additionally, animals can become entangled in plastic debris, such as fishing nets, which can result in injuries and even death. Moreover, the presence of plastic waste in ecosystems can disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems and harm biodiversity.
What are some of the toxic chemicals found in plastics?
Plastics can contain various toxic chemicals, including phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA). Phthalates are commonly used as plasticizers in many plastic products to increase their flexibility and durability. However, these chemicals can leach out of the plastics and enter the environment, posing risks to human health. BPA is another harmful chemical found in plastics, especially in water bottles and food containers. It is known to be an endocrine disruptor and can interfere with hormonal balance in the body. Exposure to these toxic chemicals has been linked to various health problems, including reproductive issues, developmental abnormalities, and certain types of cancer.
How do plastics contribute to greenhouse gas emissions?
The production of plastics involves the extraction, refining, and transportation of fossil fuels, such as crude oil and natural gas. These processes release significant amounts of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2). Additionally, the incineration of plastics also releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change. Therefore, the production and disposal of plastics contribute to the overall carbon footprint and environmental impact.
What can individuals do to reduce the harmful effects of plastics?
There are several actions individuals can take to reduce the harmful effects of plastics. First, reducing the use of single-use plastics, such as plastic bags and straws, can significantly reduce plastic waste. Instead, reusable alternatives like cloth bags and stainless steel straws can be used. Second, recycling plastic waste is crucial to prevent it from ending up in landfills or oceans. Properly sorting and disposing of plastics in designated recycling bins can help ensure they are recycled and given a second life. Finally, supporting and advocating for policies that promote plastic reduction and encourage the use of sustainable alternatives can have a broader impact on reducing the harmful effects of plastics.
What are the harmful effects of plastics?
Plastics have several harmful effects on the environment including pollution, wildlife disturbance, and human health risks.
How does plastic pollution affect the environment?
Plastic pollution has a detrimental impact on the environment, as it takes hundreds of years to decompose. It ends up in landfills or in oceans and can disrupt ecosystems, contaminate soil and water, and harm plants and animals.