
Plastic has become an integral part of our modern lives, but its impact on the environment cannot be ignored. The production and disposal of plastic products contribute to pollution, climate change, and harm to wildlife. As consumers, we can make a difference by choosing to avoid certain types of plastics and opting for more sustainable alternatives.
1. Single-use plastics: These are the plastics that are used once and then discarded, such as plastic bags, straws, and disposable cutlery. They often end up in landfills or bodies of water, where they take hundreds of years to decompose. By refusing these single-use plastics, we can reduce our carbon footprint and protect the environment.
2. Polystyrene foam: Also known as Styrofoam, this type of plastic is commonly used for packaging and food containers. However, it is difficult to recycle and often ends up in landfills or incinerators, releasing harmful toxins into the air. Opt for alternative materials like paper, cardboard, or biodegradable packaging whenever possible.
3. PVC: Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is a type of plastic commonly found in pipes, vinyl flooring, and shower curtains. Unfortunately, it contains toxic chemicals that can leach into the environment during production, use, and disposal. Look for PVC-free alternatives or choose products made from natural materials like wood or bamboo.
4. Microplastics: These are tiny plastic particles that are less than 5mm in size. They can be found in many personal care products, such as facial scrubs and toothpaste, as well as in synthetic fabrics like polyester. When these products are washed down the drain, the microplastics end up in our waterways, posing a threat to marine life. Avoiding products that contain microplastics can help protect the oceans and the creatures that inhabit them.
5. Plastic packaging: Many products come wrapped in excessive plastic packaging that is unnecessary and wasteful. Look for items with minimal or eco-friendly packaging, or consider buying in bulk to reduce the amount of plastic waste generated. Additionally, bring your own reusable bags and containers when shopping to further minimize plastic packaging.
Making sustainable choices when it comes to plastics is an important step towards protecting our planet for future generations. By avoiding certain types of plastics and opting for alternatives, we can reduce pollution, conserve resources, and contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment.
- Why Avoid Plastics?
- The Environmental Impact of Plastic Waste
- 1. Pollution
- 2. Microplastics
- 3. Wildlife Threat
- 4. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- 5. Long-term Persistence
- Health Risks Associated with Plastic
- Types of Plastics to Avoid
- Single-Use Plastics
- Microplastics
- Sources of Microplastics
- Impact on the Environment
- Reducing Microplastic Pollution
- Choosing Sustainable Alternatives
- 1. Glass
- 2. Stainless Steel
- 3. Bamboo
- Biodegradable Plastics
- Question-answer:
- What are some plastics that I should avoid?
- Why should I avoid using polystyrene?
- Is it important to avoid PVC?
- What can I use instead of PET bottles?
- Are there any alternatives to plastic packaging?
Why Avoid Plastics?
Plastics have become an integral part of our daily lives, but their widespread use comes at a great cost to the environment and human health. There are several compelling reasons to avoid plastics as much as possible:
1. Environmental impact: Plastics are made from non-renewable fossil fuels, such as crude oil and natural gas. The extraction and production of these raw materials contribute to air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change. Plastics also take hundreds of years to break down in the environment, leading to plastic pollution in our oceans, rivers, and landfills.
2. Health risks: Plastics contain harmful chemicals, many of which can leach into food, water, and the environment. Bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, for example, are known endocrine disruptors that can interfere with hormones in the human body. Exposure to these chemicals has been linked to a variety of health problems, including reproductive issues, developmental disorders, and certain types of cancer.
3. Wildlife harm: Marine animals and terrestrial wildlife often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement. Plastic fragments can accumulate in their digestive systems, causing starvation, suffocation, and death. This not only threatens the biodiversity of ecosystems but also impacts the delicate balance of entire food chains.
4. Plastic waste management: Plastic waste represents a significant challenge in terms of waste management. Recycling rates for plastics are low, and many plastic items end up in landfills or incinerators, releasing harmful gases and contributing to air pollution. Plastic waste also contributes to the formation of microplastics, tiny particles that are now found throughout the environment, including in the air we breathe and the food we consume.
5. Sustainable alternatives: Fortunately, there are numerous sustainable alternatives to plastics available today. From reusable water bottles and cloth shopping bags to biodegradable packaging materials, making the switch to these alternatives can greatly reduce our reliance on plastics and help protect the environment.
By avoiding plastics whenever possible, we can minimize our impact on the environment, protect our health, and safeguard the well-being of wildlife and future generations. It is crucial that we all take steps to reduce plastic consumption and embrace more sustainable choices.
The Environmental Impact of Plastic Waste
Plastic waste is a significant environmental problem, with far-reaching consequences for ecosystems and human health. Here are some of the main environmental impacts of plastic waste:
1. Pollution
Plastic waste pollutes our oceans, rivers, and land. According to studies, millions of tons of plastic enter the ocean every year, causing harm to marine life. Many marine animals mistake plastic for food and end up consuming it, leading to injuries, suffocation, and death. Plastic pollution also affects terrestrial ecosystems, as it can leach harmful chemicals into the soil and water.
2. Microplastics
Plastic waste breaks down into tiny particles called microplastics, which can be found everywhere from the deepest ocean trenches to the highest mountain peaks. These microplastics can enter the food chain when ingested by marine animals, and they have been detected in various marine species, including fish and shellfish. Ultimately, microplastics can also make their way into our bodies through seafood consumption.
3. Wildlife Threat
Plastic waste poses a significant threat to wildlife. Animals can become entangled in plastic debris, leading to injury, amputation, or death. Birds, turtles, and marine mammals are particularly vulnerable to these hazards. Plastic waste also disrupts natural habitats, erodes nesting sites, and alters ecosystems, adversely affecting biodiversity.
4. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The production, transportation, and disposal of plastic contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Plastic is primarily made from fossil fuels, which release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases when extracted and processed. Moreover, the incineration of plastic waste can release toxic chemicals and greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change.
5. Long-term Persistence
Plastic waste can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, taking a toll on ecosystems and landscapes. It does not biodegrade like organic materials but instead disintegrates into smaller pieces. These small plastic fragments can remain in the environment for extended periods, continuing to cause harm long after they were discarded or lost.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of plastic waste is extensive and serious. It is crucial to reduce plastic consumption, properly dispose of plastic waste, and promote sustainable alternatives to mitigate these environmental issues.
Health Risks Associated with Plastic
Plastic is a material that has become ubiquitous in our modern world. We use it for everything from packaging food to making household items. However, recent studies have raised concerns about the potential health risks associated with the use of certain types of plastic.
One of the major concerns is related to plasticizers – chemicals added to plastic to make it flexible. Some plasticizers, such as phthalates, are known to be endocrine disruptors. They can interfere with our hormones and have been linked to various health issues, including developmental problems in children, reproductive disorders, and certain types of cancer.
In addition to plasticizers, plastics can also contain harmful additives such as bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is commonly used in plastics and can leach into our food and drinks when the plastic is heated or damaged. It has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, when plastic is incinerated or exposed to high temperatures, it can release toxic chemicals into the air, such as dioxins and furans. These substances are highly carcinogenic and can have long-term impacts on our health.
Moreover, when plastic enters our marine ecosystems, it can break down into microplastics. These tiny particles can be ingested by marine animals and eventually make their way up the food chain, ending up on our plates. Consuming seafood contaminated with microplastics can potentially expose us to harmful chemicals and toxins.
To minimize the health risks associated with plastic, it is important to make sustainable choices. Opt for reusable alternatives, such as glass or stainless steel containers, whenever possible. Look for products labeled as BPA-free or phthalate-free. Avoid heating food or drinks in plastic containers, especially in the microwave. And most importantly, reduce the overall use of plastic by opting for more sustainable and eco-friendly materials.
By understanding the potential health risks associated with plastic and making informed choices, we can contribute to a healthier and more sustainable future.
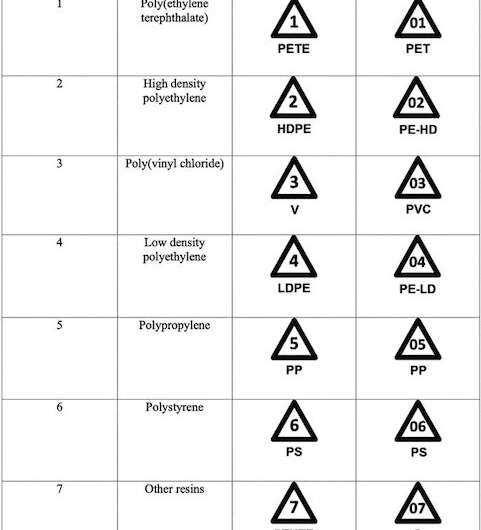
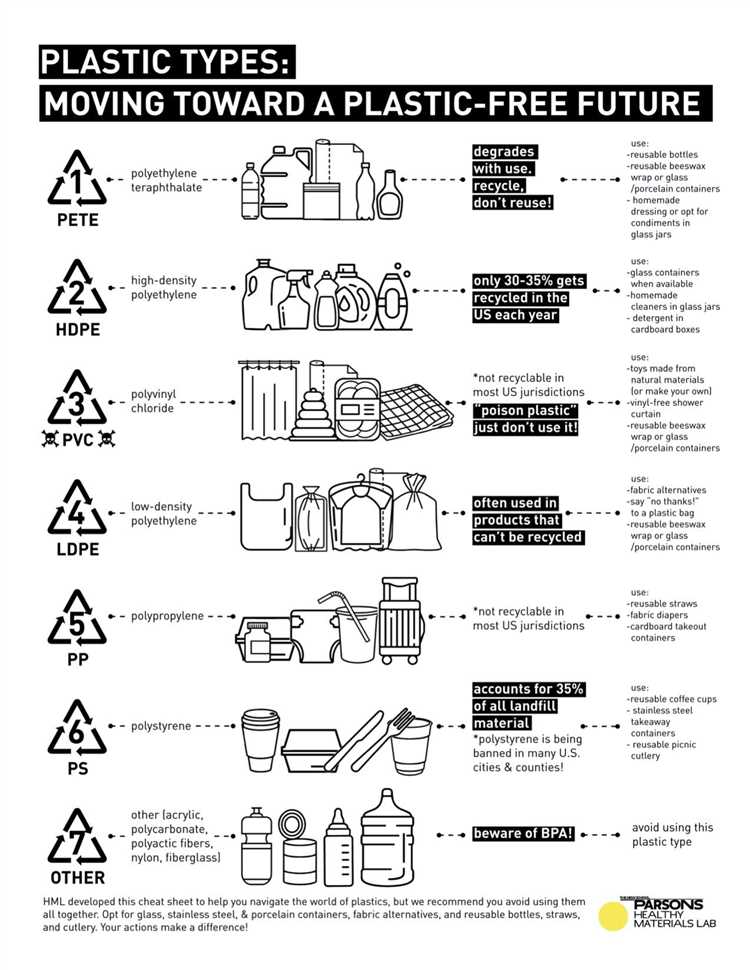
Types of Plastics to Avoid
When it comes to making sustainable choices, it’s important to be aware of the types of plastics that are harmful to the environment. By avoiding these plastics, you can contribute to a cleaner and greener future.
1. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC, also known as vinyl, is commonly used in construction materials, pipes, and packaging. It is not only difficult to recycle, but it also contains harmful additives such as phthalates and lead.
2. Polystyrene (PS): PS, commonly known as Styrofoam, is widely used in food packaging and disposable containers. It is non-biodegradable and can take hundreds of years to break down. PS also poses a threat to marine life when it enters the oceans.
3. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET is commonly used in plastic bottles, food packaging, and polyester fabrics. Although it is recyclable, millions of PET bottles are not recycled and end up in landfills or polluting waterways.
4. Polypropylene (PP): PP is commonly used in food containers, automotive parts, and textiles. Although it has a high melting point, making it suitable for microwave use, it is difficult to recycle and can take hundreds of years to decompose.
5. Polycarbonate (PC): PC is commonly used in water bottles, food storage containers, and eyewear. It contains a harmful chemical called bisphenol A (BPA), which has been linked to health issues such as hormone disruption.
6. Other plastics labeled with the recycling code “7”: Plastics labeled with the recycling code “7” are often made from a combination of different plastics and can contain harmful additives. It is best to avoid these plastics if possible.
By avoiding these types of plastics, you can make a positive impact on the environment and promote a more sustainable future. Consider using reusable alternatives, such as glass or stainless steel, whenever possible.
Single-Use Plastics
Single-use plastics are items that are designed to be used once and then thrown away. These types of plastics have become a major environmental concern due to their high rates of production and disposal. They are typically made from fossil fuels such as petroleum and natural gas, which have significant impacts on the environment during extraction and refinement.
Some common examples of single-use plastics include plastic bags, straws, disposable cutlery, and beverage bottles. These items are often used for a short period of time and then discarded, leading to a significant amount of waste. It is estimated that millions of tons of single-use plastics are produced each year, many of which end up in landfills or in the ocean.
The environmental impact of single-use plastics is significant. Plastics can take hundreds of years to decompose, and as they break down, they release harmful chemicals into the environment. These chemicals can leach into soil and water sources, posing a threat to wildlife and ecosystems.
Fortunately, there are alternatives to single-use plastics that can help reduce waste and environmental harm. For example, reusable shopping bags made from materials like cotton or canvas can be used instead of plastic bags. Stainless steel or bamboo straws can replace disposable plastic straws. And reusable water bottles can replace single-use beverage bottles.
Many governments and organizations are also taking steps to reduce the use of single-use plastics. Some cities have implemented plastic bag bans or fees, while others are encouraging the use of reusable containers for take-out food. These efforts can help to reduce the amount of single-use plastics being produced and disposed of.
| Single-Use Plastic Item | Environmentally Friendly Alternative |
|---|---|
| Plastic Bags | Reusable shopping bags made from cotton or canvas |
| Straws | Stainless steel or bamboo straws |
| Disposable Cutlery | Reusable metal or bamboo cutlery |
| Beverage Bottles | Reusable water bottles made from glass or stainless steel |
By making the switch to reusable alternatives and advocating for policy changes, we can all play a part in reducing the use of single-use plastics and creating a more sustainable future.
Microplastics
Microplastics are tiny particles of plastic that are smaller than 5 millimeters in size. They come from a variety of sources, including the breakdown of larger plastic items, microbeads in personal care products, and fibers from synthetic clothing.
Sources of Microplastics
There are several sources of microplastics:
- Breaking down of larger plastic items: Over time, plastics break down into smaller and smaller pieces due to UV exposure, weathering, and other factors. These tiny particles can then enter the environment.
- Microbeads: Microbeads are tiny plastic beads that were commonly used in personal care products like exfoliating scrubs and toothpaste. They were often too small to be captured by wastewater treatment systems, so they ended up in rivers, oceans, and lakes.
- Synthetic clothing: Many clothing items, such as polyester and nylon, are made of synthetic fibers that shed microplastic particles during each wash. These particles can then be carried by wastewater into the environment.
Impact on the Environment
The presence of microplastics in the environment has raised concerns due to their potential impact on wildlife and ecosystems. Small organisms, such as plankton, may mistake microplastics for food and ingest them. This can lead to blockages in their digestive system or provide a pathway for toxins to enter their bodies. As these microplastics move through the food chain, they can accumulate in larger animals, including fish, birds, and marine mammals.
Additionally, microplastics can transport harmful chemicals, such as pesticides and heavy metals, and release them into the environment. This can have long-term effects on water quality and ecosystems.
Reducing Microplastic Pollution
Reducing microplastic pollution requires a combination of efforts from individuals, businesses, and policymakers. Here are some ways to minimize the release of microplastics:
- Avoid single-use plastics: Single-use plastics, like plastic bags and disposable cutlery, often end up in the environment and contribute to microplastic pollution.
- Choose natural and biodegradable alternatives: Opt for personal care products that do not contain microbeads and clothing made from natural fibers.
- Properly dispose of plastic waste: Recycle or dispose of plastic waste in a way that minimizes its release into the environment.
- Support policies and regulations: Advocate for policies that ban or restrict the use of microplastics in personal care products and promote sustainable practices.
By being aware of the sources of microplastics and taking steps to reduce their release into the environment, we can help protect wildlife, ecosystems, and our own health.
Choosing Sustainable Alternatives
When it comes to reducing our plastic footprint, making sustainable choices is essential. By opting for alternative materials that are eco-friendly and easy to recycle, we can contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment. Here are some sustainable alternatives to consider:
1. Glass
Glass is a versatile and sustainable choice. It is 100% recyclable and can be recycled endlessly without losing its quality. By opting for glass containers, bottles, and jars, you can reduce the amount of plastic waste generated.
2. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a durable and non-toxic alternative to plastic. It is lightweight, easy to clean, and long-lasting. Stainless steel water bottles, lunch boxes, and kitchenware are excellent alternatives to single-use plastics.
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | 100% recyclable, long-lasting | Fragile, heavier than plastic |
| Stainless Steel | Durable, non-toxic, lightweight | More expensive than plastic |
| Bamboo | Renewable, natural, biodegradable | Not suitable for all purposes |
3. Bamboo
Bamboo is a fast-growing and renewable resource that can be used as an alternative to plastic. It is biodegradable, compostable, and provides a natural and eco-friendly option for various products such as utensils, toothbrushes, and kitchenware.
By consciously choosing sustainable alternatives, we can reduce our plastic consumption and make a positive impact on the environment. Remember to always look for materials that are recyclable, non-toxic, and have a lower environmental impact. Small changes can lead to a big difference in creating a more sustainable future.
Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics are a type of plastic that can break down naturally in the environment over time. Unlike traditional plastics, which can take hundreds of years to decompose, biodegradable plastics are designed to degrade in a matter of months or years.
There are different types of biodegradable plastics, including those made from renewable resources such as plant-based materials like cornstarch, sugarcane, or potato starch. These materials can be fermented and converted into a polymer that behaves like traditional plastic but can biodegrade under the right conditions.
Biodegradable plastics are often a more sustainable alternative to traditional plastics because they produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions and require less energy to produce. However, it’s important to note that not all biodegradable plastics are created equal. Some may only biodegrade under specific conditions, such as high temperatures or in industrial composting facilities.
When choosing biodegradable plastics, look for certifications such as the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) certification or the European Standard EN 13432 certification. These certifications ensure that the plastic product will biodegrade properly and meet specific environmental standards.
It’s worth noting that while biodegradable plastics are a step in the right direction, they are not a perfect solution to the plastic pollution problem. The ideal solution is to reduce the overall use of plastic and to opt for reusable alternatives whenever possible.
When disposing of biodegradable plastics, be sure to follow the proper guidelines for your area. Some biodegradable plastics may need to be separated from other waste and sent to a composting facility, while others can be included in regular recycling streams.
In conclusion, biodegradable plastics can be a more sustainable option compared to traditional plastics, as they can break down naturally in the environment. However, it’s important to choose certified biodegradable plastics and to properly dispose of them to ensure they degrade as intended.
Question-answer:
What are some plastics that I should avoid?
Some plastics that you should avoid include polystyrene (commonly known as Styrofoam), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), and PET (polyethylene terephthalate). These plastics are not biodegradable and can have harmful effects on the environment and human health.
Why should I avoid using polystyrene?
You should avoid using polystyrene because it is not biodegradable and it takes hundreds of years to break down. It is also difficult to recycle and often ends up in landfills or polluting our oceans. Polystyrene can release toxic chemicals when heated, which can be harmful to human health.
Is it important to avoid PVC?
Yes, it is important to avoid PVC (polyvinyl chloride) because it is a highly toxic plastic. It releases hazardous chemicals when produced and disposed of, and it is not easily recyclable. PVC products also have a short life span and contribute to the growing problem of plastic waste.
What can I use instead of PET bottles?
Instead of PET bottles, you can use reusable stainless steel or glass bottles. These options are more sustainable because they can be used multiple times and are easily recyclable. They also do not contain harmful chemicals like PET bottles, which can leach into the contents of the bottle.
Are there any alternatives to plastic packaging?
Yes, there are alternatives to plastic packaging. Some sustainable options include using paper or cardboard packaging, reusable fabric bags or containers, and biodegradable materials such as compostable plant-based plastics. These alternatives reduce the amount of plastic waste and minimize the negative impact on the environment.