
In today’s world, recycling has become a crucial aspect of waste management, as we strive to minimize our impact on the environment. However, not all plastics can be recycled, and it’s essential to understand which ones are not recyclable.
Plastics labeled as recycling code 3 (PVC) or recycling code 6 (polystyrene) are among the most common types of plastics that cannot be recycled. PVC can release toxic chemicals when melted, making it harmful to both humans and the environment. Polystyrene, often used for disposable coffee cups and food containers, is not only non-recyclable but also takes hundreds of years to decompose.
Another plastic that poses significant challenges in the recycling process is biodegradable or compostable plastic. Although it may seem like a more eco-friendly option, it often requires specific conditions to break down properly. These conditions are rarely available in recycling facilities, making it difficult to recycle these types of plastics.
Other non-recyclable plastics include black plastic, plastic bags, and plastic film. Black plastic cannot be sorted by recycling machinery due to its dark color, which prevents the optical sensors from detecting it. Plastic bags and film are often made from low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which is recyclable but requires a separate recycling process that is not commonly available.
Knowing which plastics cannot be recycled is just as important as knowing which ones can be recycled. By avoiding non-recyclable plastics and opting for more sustainable alternatives, we can all contribute to a cleaner and greener future.
- Understanding Non-Recyclable Plastics
- Types of Non-Recyclable Plastics
- The Impact of Non-Recyclable Plastics
- The Environmental Impact of Non-Recyclable Plastics
- 1. Pollution
- 2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- The Importance of Proper Disposal
- Common Examples of Non-Recyclable Plastics
- Alternative Solutions to Non-Recyclable Plastics
- 1. Biodegradable Plastics
- 2. Composting
- Table: Comparing Alternative Solutions to Non-Recyclable Plastics
- Educating Consumers on Non-Recyclable Plastics
- Q&A:
- Are all types of plastics recyclable?
- What are examples of plastics that cannot be recycled?
- Why can’t polystyrene foam be recycled?
- Can plastic bags and films be recycled?
- What should I do with plastics that cannot be recycled?
- What are some common types of plastics that cannot be recycled?
- Why can’t polystyrene be recycled?
Understanding Non-Recyclable Plastics
Plastics have become an integral part of our daily lives, but unfortunately, not all plastics can be recycled. Understanding the different types of non-recyclable plastics is essential for making informed decisions about waste disposal and reducing plastic pollution.
Types of Non-Recyclable Plastics
1. Polystyrene (PS) or Styrofoam:
Polystyrene is a lightweight and versatile plastic commonly used in disposable food containers, packaging materials, and insulation. It is difficult to recycle due to its low density and complex structure.
2. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC):
PVC is a durable plastic that is commonly used in pipes, vinyl flooring, and certain types of packaging. It contains harmful additives, such as phthalates, and its recycling process is complicated, making it non-recyclable in most recycling facilities.
3. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) with Black Color:
PET is a commonly recycled plastic used for water bottles and food containers. However, when PET plastic is black in color, it is difficult for optical sorting machines to detect it, leading to contamination and making it unrecyclable in many recycling programs.
The Impact of Non-Recyclable Plastics
Non-recyclable plastics pose significant environmental challenges. When these plastics end up in landfills or as litter in the environment, they can take hundreds of years to decompose, contributing to pollution and posing health risks to wildlife and humans. Additionally, the production and disposal of non-recyclable plastics contribute to the depletion of natural resources and increase greenhouse gas emissions.
It is crucial to be aware of the non-recyclable plastics we use in our daily lives and find alternative options whenever possible. By reducing our consumption of non-recyclable plastics and choosing eco-friendly alternatives, we can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
The Environmental Impact of Non-Recyclable Plastics
Non-recyclable plastics are a major environmental concern due to their significant impact on the planet. These plastics cannot be recycled or reused, and as a result, they often end up in landfills or are incinerated, contributing to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
1. Pollution
When non-recyclable plastics are disposed of in landfills, they can release harmful chemicals and toxins into the soil and water. These pollutants can have long-lasting effects on ecosystems, contaminating water sources and threatening the health of both humans and wildlife. The accumulation of non-recyclable plastics in the environment also poses a threat to marine life, as marine animals can mistake them for food or become entangled in them.
2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
When non-recyclable plastics are incinerated, they release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to global warming and climate change, exacerbating the already critical environmental crisis. Additionally, the production of non-recyclable plastics requires fossil fuels, further contributing to greenhouse gas emissions during the manufacturing process.
The Environmental Impact of Non-Recyclable Plastics
In conclusion, the environmental impact of non-recyclable plastics is significant and detrimental to our planet. It is crucial that we reduce our reliance on non-recyclable plastics by finding sustainable alternatives and promoting recycling and waste management practices. By taking action to minimize the use and disposal of non-recyclable plastics, we can help protect the environment and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
The Importance of Proper Disposal

Proper disposal of unrecyclable plastics is crucial for the environment and human health. When these plastics are not disposed of correctly, they can contribute to pollution and harm wildlife.
One of the main concerns with improperly disposing of unrecyclable plastics is the risk of them ending up in the ocean. Plastic waste that enters the ocean can have a devastating impact on marine life. Sea turtles, dolphins, whales, and other marine creatures can mistake plastic for food and end up ingesting it, resulting in injury or even death. Additionally, marine animals can become entangled in plastic debris, leading to suffocation or drowning.
Another issue that arises from improper disposal is the release of hazardous chemicals into the environment. Some unrecyclable plastics contain toxic additives that can leach out into soil and water, polluting ecosystems. This can not only harm wildlife but also contaminate the food chain, potentially affecting human health.
Proper disposal can help prevent these harmful consequences. It is essential to follow local waste management guidelines and dispose of unrecyclable plastics in designated landfill or incineration facilities. By doing so, the risk of these plastics entering the environment and causing harm can be minimized.
Furthermore, proper disposal practices can also contribute to efforts to reduce plastic waste and promote a circular economy. By disposing of unrecyclable plastics correctly, they can be separated from recyclable materials, preventing contamination and increasing the efficiency of recycling processes.
In conclusion, the proper disposal of unrecyclable plastics is crucial for protecting the environment and safeguarding human health. By recognizing the importance of proper disposal and following waste management guidelines, we can minimize pollution, protect wildlife, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Common Examples of Non-Recyclable Plastics
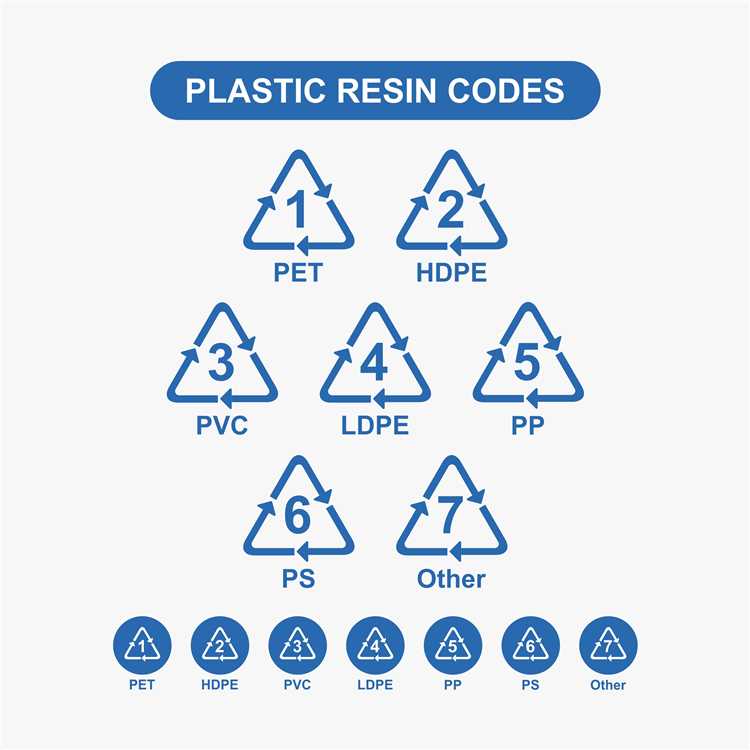
While it is important to recycle plastics whenever possible, not all plastics can be recycled. Understanding which plastics cannot be recycled is crucial for making environmentally conscious choices in our daily lives. Here are some common examples of non-recyclable plastics:
1. Polystyrene (Styrofoam): Polystyrene is commonly used in packaging materials, disposable food containers, and insulation. Unfortunately, it is not commonly accepted in recycling programs due to its low market value and difficulties in the recycling process.
2. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC is commonly used in pipes, flooring, and window frames. Its high chlorine content makes it difficult to recycle, and it also releases toxic chemicals when incinerated.
3. Mixed Plastics: Plastics made of multiple layers or different types of plastic are difficult to recycle because of the challenges associated with separating and processing them. Examples include food packaging with metalized film or juice boxes with plastic and aluminum layers.
4. Biodegradable Plastics: While biodegradable plastics may break down over time, they often require specific conditions (such as high heat or moisture) to do so, making them unsuitable for traditional recycling processes. Additionally, their widespread adoption has been limited due to the lack of proper facilities to handle them.
5. Crinkly Plastic Wrappers: Thin, crinkly plastic wrappers like those used on snack foods or single-use condiments cannot be recycled due to their size and composition. These should be disposed of in the regular waste bin.
6. Plastic Utensils: Disposable plastic utensils like cutlery and straws are usually made from low-quality plastics that are not recyclable. Consider switching to reusable alternatives made from stainless steel or bamboo.
7. Plastic Bags: While some stores offer recycling programs for plastic bags, they are typically not accepted in curbside recycling bins. Reusable cloth bags or paper bags are more eco-friendly alternatives.
By avoiding these non-recyclable plastics and opting for sustainable alternatives, we can reduce our environmental impact and work towards a more sustainable future.
Alternative Solutions to Non-Recyclable Plastics
As the issue of non-recyclable plastics continues to grow, it is important to explore alternative solutions that can help reduce plastic waste and minimize its impact on the environment. While recycling is a crucial part of the solution, it is not always feasible for certain types of plastics. In such cases, innovative approaches are being developed to address the problem.
1. Biodegradable Plastics

One alternative to non-recyclable plastics is the use of biodegradable plastics. These plastics are designed to break down naturally in the environment, reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills or oceans. Biodegradable plastics can be made from plant-based materials such as cornstarch or wheat, making them a more sustainable choice.
2. Composting
Composting is another solution for non-recyclable plastics. Some plastics can be composted in facilities that are equipped to handle biodegradable waste. By composting these plastics, they can be transformed into nutrient-rich soil that can be used for gardening or agriculture.
It is important to note that not all plastics are suitable for composting, so it is necessary to carefully read packaging labels or seek guidance from local composting facilities.
Table: Comparing Alternative Solutions to Non-Recyclable Plastics
| Solution | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Biodegradable Plastics | – Break down naturally | – Higher production costs |
| Composting | – Transform waste into soil | – Limited facilities for composting |
While these alternatives provide some solutions to non-recyclable plastics, it is important to remember the importance of reducing overall plastic consumption. By opting for reusable or sustainable materials whenever possible, we can help minimize the need for non-recyclable plastics and lessen their impact on the environment.
Educating Consumers on Non-Recyclable Plastics
In today’s society, plastic is everywhere. From food packaging to household items, we use and throw away a staggering amount of plastic each day. However, not all plastics can be recycled, and it is essential for consumers to be aware of this fact.
Understanding the different types of non-recyclable plastics is the first step towards making informed decisions as a consumer. Plastics that cannot be recycled include certain types of polystyrene (commonly known as Styrofoam), plastic bags, and certain plastic containers such as those used for motor oil or hazardous chemicals.
One of the main challenges in recycling plastic is identifying which types can be recycled and which cannot. This is why educating consumers plays a crucial role in reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainability. By knowing which plastics are non-recyclable, consumers can make better choices when it comes to their purchases and reduce their impact on the environment.
Another important aspect of educating consumers on non-recyclable plastics is highlighting the alternatives available. For example, instead of using single-use plastic bags, consumers can opt for reusable cloth bags or paper bags. Instead of purchasing beverages in plastic bottles, consumers can choose beverages packaged in glass or aluminum containers.
By providing consumers with viable alternatives, we empower them to make environmentally conscious decisions. It is important for consumers to understand that they have the power to make a difference through their daily choices.
In conclusion, educating consumers on non-recyclable plastics is essential in the fight against plastic pollution. By understanding which plastics cannot be recycled and by providing alternatives, consumers can take an active role in reducing plastic waste and creating a more sustainable future.
Q&A:
Are all types of plastics recyclable?
No, not all types of plastics are recyclable. Some plastics cannot be recycled due to the nature of their composition or the lack of recycling infrastructure to process them.
What are examples of plastics that cannot be recycled?
Some examples of plastics that cannot be recycled include polystyrene foam (commonly known as Styrofoam), plastic bags and films, and certain types of PVC (polyvinyl chloride).
Why can’t polystyrene foam be recycled?
Polystyrene foam is difficult to recycle because it is lightweight and often contaminated with food or other substances. The recycling process for this type of plastic is not cost-effective and there is limited demand for recycled polystyrene products.
Can plastic bags and films be recycled?
No, plastic bags and films cannot be recycled in most curbside recycling programs. They can cause issues at recycling facilities, as they can get tangled in the machinery. However, some grocery stores and retailers offer collection bins for plastic bag recycling.
What should I do with plastics that cannot be recycled?
If you have plastics that cannot be recycled, it is best to dispose of them in the regular trash. However, the best approach is to reduce your consumption of single-use plastics and choose alternative, more sustainable options whenever possible.
What are some common types of plastics that cannot be recycled?
Some common types of plastics that cannot be recycled include polystyrene (PS), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polypropylene (PP).
Why can’t polystyrene be recycled?
Polystyrene cannot be easily recycled because it is made up of a lightweight and rigid foam material which is difficult to sort and process. Additionally, polystyrene has a low market value, making it less economically viable to recycle.