Microplastics, tiny pieces of plastic less than 5mm in size, have become a concerning global issue due to their ubiquity in the environment. These particles originate from various sources, such as the fragmentation of larger plastic items or the release of microbeads from personal care products. While the presence of microplastics in marine environments has been extensively studied, their presence in drinking water remains a topic of growing interest.
Studies have found that microplastics can contaminate drinking water sources, including both tap water and bottled water. These particles can enter water systems through a variety of pathways, such as industrial wastewater discharge, atmospheric deposition, and the breakdown of plastic bottles during the bottling process. The potential health effects of consuming microplastics through drinking water are still being researched, but it is generally agreed that the presence of these particles in such a vital resource raises concerns.
Scientists and researchers have developed various methods to detect and analyze microplastics in drinking water samples. These methods typically involve filtration and microscopy techniques, where the water sample is passed through a filter to concentrate the microplastics, which are then examined under a microscope for identification and quantification. Newer techniques, such as Raman spectroscopy and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, have also been employed to enhance the detection capabilities and improve the accuracy of microplastic analysis.
The presence of microplastics in drinking water is a complex issue that requires further investigation and understanding. As the demand for clean and safe drinking water continues to rise, it is essential to determine the extent of microplastic contamination and its potential implications for human health. By conducting thorough research and implementing effective strategies to reduce plastic waste and pollution, we can move towards a future where microplastics are no longer a threat to our drinking water sources.
- Importance of Investigating Microplastics in Drinking Water
- 1. Health Implications:
- 2. Environmental Impact:
- Methods used to Detect Microplastics
- Potential Health Risks linked to Microplastics Consumption
- Possible Chemical Exposure
- Possible Physical Damage
- Research Findings on Microplastic presence in Drinking Water
- Measures to Reduce Microplastic Contamination
- Future Research and Recommendations
- 1. Standardized Testing Methods
- 2. Educating and Raising Awareness
- 3. Developing Filtration Technologies
- 4. Long-term Health Studies
- Q&A:
- Why are microplastics a concern in drinking water?
- How do microplastics end up in drinking water?
- What methods are used to detect microplastics in drinking water?
- Are microplastics found in tap water or only in bottled water?
- What are the potential health risks of consuming microplastics in drinking water?
- What are microplastics and why are they a concern?
- How can microplastics end up in drinking water?
Importance of Investigating Microplastics in Drinking Water
Water is essential for human life, and ensuring its safety and purity is of utmost importance. In recent years, concerns have been raised about the presence of microplastics in drinking water and the potential health risks associated with their consumption. Microplastics are tiny plastic particles, less than 5 millimeters in size, that result from the breakdown of larger plastic items or are intentionally manufactured in small sizes for various purposes.
The investigation of microplastics in drinking water is crucial for several reasons:
1. Health Implications:

There is growing evidence suggesting that microplastics can enter the human body through ingestion or inhalation and have the potential to cause adverse health effects. These tiny particles can carry harmful chemicals and toxic substances, which could accumulate in human tissues over time. By understanding the presence and concentration of microplastics in drinking water, we can better assess the associated health risks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
2. Environmental Impact:
The presence of microplastics in drinking water is not only a concern for human health but also for the environment. Microplastics can enter water bodies through various sources, such as wastewater treatment plants, industrial discharges, or the fragmentation of larger plastic debris. They can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, marine life, and overall biodiversity. Investigating the presence of microplastics in drinking water can help identify the sources of contamination and guide efforts to prevent further pollution.
Overall, investigating microplastics in drinking water is essential for protecting human health, preserving the environment, and ensuring the provision of clean and safe drinking water for everyone. It enables us to understand the scale of the issue and take appropriate actions to minimize the potential risks associated with microplastic contamination.
Methods used to Detect Microplastics
There are several methods commonly used to detect the presence of microplastics in drinking water. These methods rely on various techniques to isolate and identify microplastic particles.
1. Filtration: One of the most commonly used methods is filtration, where water samples are passed through a fine mesh filter to capture any microplastic particles present. The filter is then examined under a microscope to identify and quantify the microplastics.
2. Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy techniques, such as Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, are used to identify the chemical composition of microplastic particles. The unique spectral signatures of different types of plastics can be compared to reference libraries to determine the presence of microplastics.
3. Microscopy: Microscopy techniques, including optical microscopy and electron microscopy, are used to visually detect and characterize microplastics. Optical microscopy relies on light microscopy techniques to examine the size, shape, and color of microplastic particles, while electron microscopy provides higher magnification and resolution for detailed analysis.
4. Raman spectroscopy: Raman spectroscopy is a powerful technique that can be used to identify microplastics based on their molecular structure. It measures the scattering of laser light by the sample, providing information about the chemical composition of the microplastic particles.
5. Flow cytometry: Flow cytometry is a technique that can be used to count and measure the size of particles in a water sample. By tagging microplastic particles with fluorescent dyes, they can be differentiated from other particles and detected using a flow cytometer.
6. Micro-FTIR mapping: Micro-FTIR mapping combines FTIR spectroscopy with microscopy to provide detailed spatial information about the distribution of microplastics in a sample. It allows for the identification of microplastics and their location within a water sample.
7. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR techniques can be used to detect the presence of specific microplastic types by amplifying and identifying their unique DNA markers. This method can provide information about the types of microplastics present in a water sample.
These methods, used individually or in combination, are essential in understanding the extent of microplastic contamination in drinking water and contribute to efforts in assessing potential health risks associated with microplastic ingestion.
Potential Health Risks linked to Microplastics Consumption
Microplastics, small plastic particles measuring less than 5 millimeters, have been detected in various sources of drinking water, including tap water, bottled water, and even well water. These tiny particles can come from a variety of sources, such as the breakdown of larger plastic debris and fibers from synthetic clothing.
While research on the health effects of microplastics is still limited, some studies suggest potential risks associated with their consumption. The presence of microplastics in drinking water raises concerns about the potential transfer of harmful chemicals and toxins present in plastics.
Possible Chemical Exposure

Microplastics have a high surface area, allowing them to adsorb and concentrate various chemicals present in the environment. When these particles are ingested, they may release these chemicals, which can pose a potential risk to human health. Some of the chemicals that may be associated with microplastics include phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), flame retardants, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs).
These chemicals have been linked to a range of health issues, including endocrine disruption, reproductive problems, developmental disorders, and an increased risk of certain cancers. While the exact effects of microplastics ingestion on human health are still being studied, it is important to recognize the potential for chemical exposure.
Possible Physical Damage
In addition to chemical exposure, the physical presence of microplastics in the digestive system can also raise concerns. These tiny particles can accumulate in the gastrointestinal tract and potentially cause irritation or inflammation. There is also a possibility of the particles crossing the gastrointestinal barrier and entering the bloodstream.
Once in the bloodstream, microplastics could potentially accumulate in various organs and tissues, leading to long-term health effects. The potential physical damage caused by microplastics ingestion is an area that requires further research and exploration.
Overall, while the full extent of the health risks associated with microplastics consumption is not yet fully understood, it is important to recognize the potential for harm. Further research and monitoring are necessary to fully comprehend the impact of microplastics on human health. In the meantime, individuals can reduce their exposure to microplastics by using alternative materials, such as glass or stainless steel, and supporting efforts to reduce plastic pollution.
Research Findings on Microplastic presence in Drinking Water
Microplastics, tiny plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size, have become a major concern in recent years. These particles can come from a variety of sources, including clothing, cosmetics, and the breakdown of larger plastic items. Their small size makes them difficult to filter out, and they have been found in various bodies of water around the world.
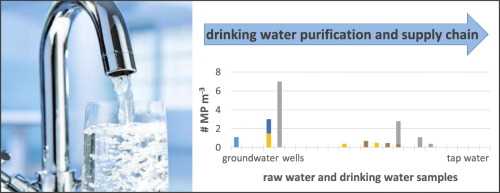
A number of studies have been conducted to determine if microplastics are present in drinking water. Researchers have collected water samples from various sources, including taps, bottled water, and wells, to analyze for the presence of microplastics. The findings of these studies have been both alarming and concerning.
Several studies have found that microplastics are indeed present in drinking water. In one study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO), microplastics were detected in 93% of the samples taken from tap water in numerous countries. The study also found that the concentration of microplastics varied, ranging from a few particles per liter to several hundred particles per liter.
In another study conducted by the Plastic Soup Foundation, microplastics were found in various brands of bottled water. The study revealed that 90% of the samples tested positive for microplastics, with an average of 325 particles per liter.
These findings have raised concerns about the potential health risks associated with consuming microplastics through drinking water. While the long-term effects are still not fully known, researchers have suggested that exposure to microplastics may lead to various health problems, such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and the absorption of toxic chemicals.
In conclusion, research findings have indicated that microplastics are indeed present in drinking water. The extent of their presence and the potential health risks they pose are topics that require further investigation. It is crucial to develop effective filtration systems and regulations to minimize the presence of microplastics in drinking water and protect public health.
Measures to Reduce Microplastic Contamination
The presence of microplastics in drinking water has raised concerns about potential health risks and environmental impacts. To mitigate this issue, various measures can be taken to reduce microplastic contamination:
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Source Control | One of the most effective ways to reduce microplastic contamination is to minimize the release of plastic particles into the environment. This can be achieved through proper waste management, recycling initiatives, and the implementation of policies to reduce plastic production and consumption. |
| 2. Improved Wastewater Treatment | Wastewater treatment plants play a crucial role in removing microplastics from water sources. Upgrading existing treatment processes and implementing advanced technologies can help to enhance the removal efficiency of microplastic particles. |
| 3. Filtration Systems | Integrating filtration systems into drinking water treatment plants can effectively remove microplastics. Advanced filtration technologies, such as membrane filtration and activated carbon filters, are capable of capturing microplastic particles and preventing their entry into the drinking water supply. |
| 4. Education and Awareness | Raising public awareness about the presence and potential risks of microplastics in drinking water can encourage individual actions to reduce plastic consumption. Educational campaigns, informational materials, and public outreach initiatives can help to promote responsible plastic use and disposal. |
| 5. Research and Monitoring | Ongoing research and monitoring efforts are crucial for understanding the extent of microplastic contamination and developing effective mitigation strategies. Robust monitoring programs and scientific studies can provide valuable data to guide policy-making and inform decision-making processes. |
By implementing these measures, it is possible to reduce microplastic contamination in drinking water and safeguard human health and the environment from the potential risks associated with microplastics.
Future Research and Recommendations

To further investigate the presence and impact of microplastics in drinking water, future research should focus on the following areas:
1. Standardized Testing Methods
Developing standardized testing methods for the detection and quantification of microplastics in drinking water is crucial. This will allow for more accurate and reliable data across different studies, making comparisons and analysis easier.
2. Educating and Raising Awareness
Educational campaigns should be conducted to raise awareness about the presence of microplastics in drinking water and their potential health risks. This will help to encourage individuals and communities to take action in reducing plastic waste and pollution.
In addition, educating individuals about the sources of microplastics and their impact on the environment will promote responsible plastic consumption and disposal practices.
3. Developing Filtration Technologies
Research should also focus on developing effective filtration technologies that can remove microplastics from drinking water at various scales, including domestic and municipal levels.
This will enable the implementation of efficient and cost-effective solutions to reduce microplastic contamination and ensure the safety of drinking water.
Furthermore, testing the effectiveness of different filtration methods and materials in removing microplastics of various sizes and types will be essential in refining and optimizing filtration technologies.
4. Long-term Health Studies
Long-term health studies should be conducted to investigate the potential health effects of consuming microplastics in drinking water. This research should include both animal and human studies to assess the risks and establish guidelines for safe levels of microplastics in drinking water.
Additionally, examining the interaction between microplastics and other chemical contaminants commonly found in water sources is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the potential health risks.
Overall, addressing these research areas will contribute to a better understanding of microplastics in drinking water and guide the development of effective mitigation strategies to ensure the safety and quality of this essential resource.
Q&A:
Why are microplastics a concern in drinking water?
Microplastics are a concern in drinking water because they are small plastic particles that may be harmful to human health. If ingested, these particles can potentially cause a range of health issues.
How do microplastics end up in drinking water?
Microplastics can end up in drinking water through various sources such as plastic pollution in rivers and oceans, as well as the breakdown of larger plastic items like bottles and bags. They can also be introduced during the water treatment process.
What methods are used to detect microplastics in drinking water?
Various methods are used to detect microplastics in drinking water, including filtration techniques, spectroscopy, and microscopy. These techniques allow scientists to identify and analyze the presence of microplastics in a water sample.
Are microplastics found in tap water or only in bottled water?
Microplastics can be found in both tap water and bottled water. Studies have shown that microplastics are present in various water sources, including rivers, lakes, and groundwater. They can also be introduced during the bottling process.
What are the potential health risks of consuming microplastics in drinking water?
The potential health risks of consuming microplastics in drinking water are still being studied, but research suggests that they may have harmful effects on human health. These particles can accumulate in the body and potentially cause inflammation, hormonal disruptions, and other adverse health effects.
What are microplastics and why are they a concern?
Microplastics are tiny particles of plastic, smaller than 5mm in size. They are a concern because they can enter the environment through various means, including the breakdown of larger plastic items and the shedding of microfibers from synthetic textiles. Once in the environment, microplastics can be consumed by animals and can potentially make their way up the food chain, including into our drinking water.
How can microplastics end up in drinking water?
Microplastics can end up in drinking water through a variety of sources. They can enter the water supply during the treatment process, as some microplastics may not be filtered out completely. Additionally, microplastics can also enter drinking water sources through run-off from landfills, where plastic waste is often disposed of improperly.