Trees are one of the most vital components of our planet’s ecosystem. They provide us with oxygen, regulate our climate, and provide habitats for countless species of animals and plants. But have you ever wondered just how many trees there are on Earth?
Estimating the total number of trees on our planet is a challenging task. With over 3 trillion trees covering the Earth’s land surface, it might seem impossible to count them all. However, scientists have developed various methods to estimate this number.
Remote sensing is one of the techniques used to estimate the global tree population. Satellites equipped with sensors can scan large areas of land and collect data on vegetation cover. By analyzing this data, scientists can estimate the density and extent of forests, allowing them to calculate the number of trees.
Another approach is through ground surveys, where researchers physically count trees within specific plots of land and then extrapolate those numbers to estimate the total tree population. These surveys involve the painstaking task of counting individual trees, which can take years to complete.
While the exact number of trees on Earth remains uncertain, what is clear is their immense value to our planet. Trees play a vital role in maintaining the health of our ecosystems and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Understanding their numbers and distribution is crucial for effective conservation and sustainable management of our forests.
- The Importance of Trees
- Counting Earth’s Trees
- Challenges in Estimating Tree Population
- Methods used to Estimate Tree Population
- 1. Remote Sensing
- 2. Sample Plots
- 3. LiDAR Technology
- 4. Forest Inventory Data
- The Role of Technology in Tree Counting
- The benefits of technology in tree counting:
- The future of tree counting technology:
- Preserving and Restoring Earth’s Tree Population
- Question-Answer:
- How many trees are there on Earth?
- How do scientists estimate the number of trees on Earth?
- What are the benefits of having a large number of trees on Earth?
- Are the number of trees on Earth increasing or decreasing?
- What are the consequences of a decrease in the number of trees on Earth?
- How many trees are there on Earth?
The Importance of Trees
Trees play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of our ecosystems.
- Oxygen: Trees produce oxygen through photosynthesis, which is essential for all living organisms.
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb and store carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biodiversity: Trees provide habitat for a multitude of species, promoting biodiversity and supporting the interconnected web of life.
- Water Cycle: Trees help regulate the water cycle by absorbing rainfall, reducing runoff and erosion, and releasing water vapor into the atmosphere through transpiration.
- Soil Protection: The roots of trees hold the soil together, preventing erosion and maintaining its fertility.
- Air Quality: Trees act as natural air filters, trapping pollutants and improving air quality.
- Shade and Cooling: The canopy of trees provides shade, reducing temperatures in urban areas and helping to cool the environment.
- Wood and Resources: Trees provide valuable wood for construction, fuel, and various other products that support human needs.
- Aesthetics and Recreation: Trees enhance the beauty of landscapes, provide a sense of serenity, and offer opportunities for outdoor activities.
Given their countless benefits, it is crucial to protect and conserve trees to ensure a sustainable and healthy planet for future generations.
Counting Earth’s Trees
Estimating the total number of trees on Earth is a challenging task that scientists have been working on for many years. The sheer size and diversity of our planet’s forests make it difficult to obtain an exact count, but researchers have developed innovative methods to provide estimates.
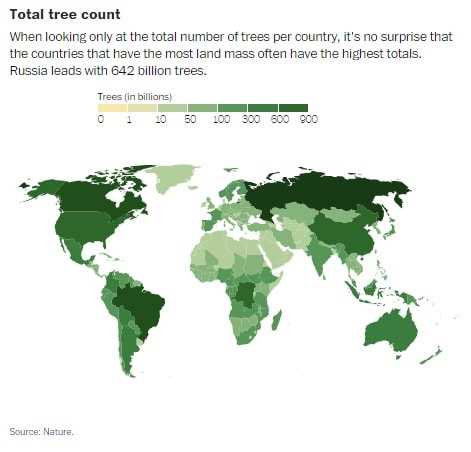
One way scientists estimate tree count is through remote sensing. They use satellite imagery and advanced algorithms to analyze the density and distribution of forests. By measuring the canopy cover and tree height in different regions, they can extrapolate the data to estimate the number of trees worldwide.
Another method is through ground-based surveys. Researchers select specific areas and conduct comprehensive field studies, counting individual trees and collecting data on their characteristics. This data is then used to estimate the tree population in larger areas and extrapolated to cover the whole Earth.
It’s important to note that these estimates are not precise numbers but rather educated guesses. The sheer vastness and complexity of Earth’s ecosystems make it impossible to count every single tree. However, scientists refine their methods and models to improve the accuracy of their estimates.
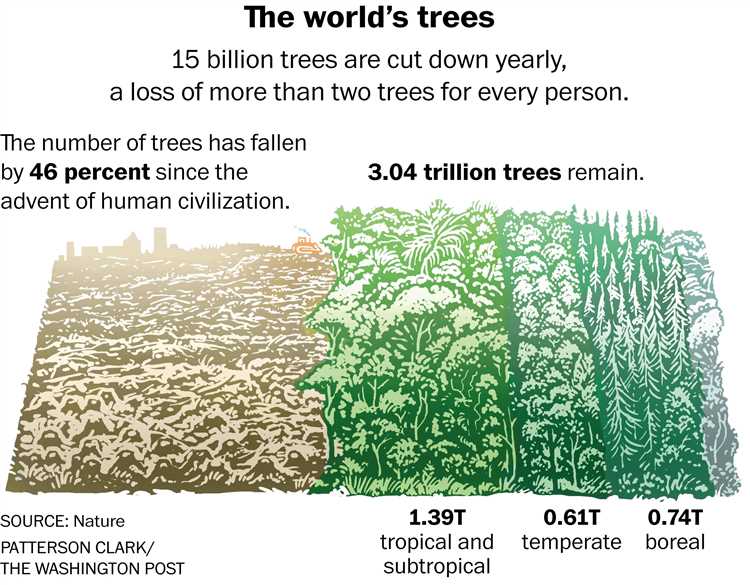
The estimated number of trees on Earth varies, but the most common estimate suggests there are around 3 trillion trees globally. This number represents a significant decline in the past century due to deforestation and habitat loss. Protecting and restoring forests is crucial for preserving biodiversity and mitigating climate change.
In conclusion, while counting every tree on Earth is an impossible task, scientists have developed innovative methods to estimate their numbers. These estimates help us understand the state of Earth’s forests and the importance of protecting and preserving them for future generations.
Challenges in Estimating Tree Population
Estimating the population of trees on Earth is a challenging task due to various factors. These factors include the vastness of the planet, the diversity of ecosystems, and the different methods used for estimation. This section will discuss some of the major challenges in accurately estimating the tree population on our planet.
| 1. Vastness of the Planet: | The Earth is a vast and diverse planet, with different types of ecosystems spread across various geographical regions. Estimating the tree population in each of these regions requires extensive fieldwork and data collection, making it a time-consuming and labor-intensive task. |
| 2. Diversity of Ecosystems: | The Earth is home to a wide range of ecosystems, each with its own unique tree species and characteristics. Estimating the tree population accurately requires comprehensive knowledge of the different tree species and their distribution patterns across each ecosystem. In addition, factors such as climate change and deforestation can significantly impact the tree population, further complicating the estimation process. |
| 3. Different Estimation Methods: | There are various methods used to estimate tree populations, including ground-based surveys, remote sensing techniques, and mathematical modeling. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, making it challenging to compare and consolidate the data obtained from different estimation methods. Additionally, the accuracy of these methods can vary depending on factors such as the size of the study area and the density of trees. |
| 4. Lack of Comprehensive Data: | Despite advances in technology and research, there is still a lack of comprehensive data on tree populations globally. Many regions, especially remote and inaccessible areas, have limited or no data available. This makes it difficult to obtain accurate estimates for the tree population in these areas, leading to gaps in our understanding of the overall global tree population. |
Overall, estimating the tree population on Earth is a complex and ongoing process that requires extensive research, collaboration, and data collection. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for accurately assessing the health of our planet’s forests and implementing effective conservation strategies.
Methods used to Estimate Tree Population
Estimating the total number of trees on Earth is a challenging task due to the vastness of forests and the difficulties in accurately measuring tree populations. However, scientists have developed various methods to estimate tree populations, providing valuable insights into the distribution and density of trees.
1. Remote Sensing
Remote sensing involves using aerial or satellite imagery to assess forest cover and estimate tree populations. This method relies on advanced sensors that can capture data on vegetation density, tree height, and canopy cover. By analyzing the collected data, researchers can extrapolate tree population estimates for large areas.
2. Sample Plots
Another common method is to establish sample plots within forests and measure tree characteristics, such as diameter at breast height (DBH) and species composition. These sample plots are carefully selected to represent different forest types and regions. By extrapolating the data collected from sample plots to the entire forest area, scientists can estimate tree populations more accurately.
Sampling methods can also involve systematic grid sampling, where plots are placed at regular intervals within a forest, or stratified sampling, where plots are selected based on different strata, such as tree size or species.
3. LiDAR Technology
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology uses laser pulses to measure the distance between the sensor and tree crowns. This information can then be used to estimate tree height and calculate tree volumes. LiDAR data combined with ground-based measurements can provide accurate estimates of tree populations, especially in dense forests or areas with challenging terrain.
4. Forest Inventory Data
Forest inventory data collected by forestry organizations also contribute to estimating tree populations. These data include on-the-ground measurements of forest characteristics, such as tree species, diameter, and height. By combining this information with remote sensing data, researchers can derive more precise estimates of tree populations at regional or global scales.
It’s important to note that each method has its limitations and uncertainties. Tree populations are constantly changing due to natural processes, human activities, and environmental factors. Therefore, ongoing research and advancements in technology are necessary to improve the accuracy of tree population estimates.
The Role of Technology in Tree Counting
In the past, estimating the number of trees on Earth was a daunting task that relied solely on manual counting, which was time-consuming and prone to errors. However, with the advent of technology, tree counting has become a more efficient and accurate process.
One of the key technologies used in tree counting is remote sensing. Satellite and aerial imagery provide a bird’s-eye view of vast forest areas, allowing researchers to analyze and interpret the data to estimate tree density and distribution. Advanced image processing algorithms can automatically identify and classify trees, making the counting process faster and more precise.
Additionally, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has revolutionized tree counting by providing detailed 3D measurements of forest structure. LiDAR uses laser pulses to capture the height and shape of trees, enabling scientists to estimate tree volume and biomass. This technology has significantly improved our understanding of forest ecosystems and their carbon storage capacity.
Another technological advancement in tree counting is the use of citizen science and crowdsourcing platforms. These platforms allow individuals from all over the world to contribute to tree counting efforts by submitting observations and photographs of trees in their local areas. This collective effort helps researchers gather large amounts of data, leading to more accurate estimates of tree populations worldwide.
The benefits of technology in tree counting:
1. Efficiency: Technology enables faster and more efficient tree counting, saving time and resources compared to manual methods.
2. Accuracy: Advanced algorithms and remote sensing techniques provide more accurate tree density estimates and improve our understanding of forest ecosystems.
The future of tree counting technology:
As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in tree counting methods. For example, the development of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms may enable computers to automatically analyze satellite imagery and identify and count individual trees with even greater precision. Additionally, the integration of drones with LiDAR technology holds promise for more detailed and comprehensive mapping of tree populations.
Overall, technology has played a crucial role in revolutionizing tree counting, making the process more efficient, accurate, and accessible. These advancements are vital in understanding the state of our planet’s forests and monitoring changes in tree populations over time.
Preserving and Restoring Earth’s Tree Population

Preserving and restoring Earth’s tree population is crucial for the overall health of our planet. Trees play a crucial role in combating climate change, providing habitats for numerous species, and preserving biodiversity.
One of the key initiatives in preserving trees is sustainable forestry practices. These practices involve managing forests in a way that allows them to regenerate and maintain their ecological functions. By selectively harvesting mature trees and planting new ones, we can ensure the long-term health and sustainability of our forests.
Another important aspect of preserving and restoring the tree population is reforestation. Reforestation involves planting trees in areas where forests have been destroyed or degraded. This practice helps to restore habitats for wildlife, mitigate climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide, and prevent soil erosion.
In addition to reforestation, it is also crucial to protect existing forests from deforestation. Deforestation not only leads to the loss of valuable tree species, but it also contributes to increased greenhouse gas emissions and habitat destruction. By implementing policies and regulations that discourage deforestation and promoting sustainable land use practices, we can help to preserve our forests and the ecosystem services they provide.
Another effective strategy for preserving and restoring Earth’s tree population is raising awareness and promoting community involvement. Educating the public about the importance of trees and their role in maintaining a healthy environment can help to foster a sense of responsibility and encourage individuals to take action. This can include initiatives like tree planting events, community clean-ups, and supporting organizations that focus on tree conservation.
| Preservation Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Sustainable forestry practices | Regeneration of forests and maintenance of ecological functions |
| Reforestation | Restoration of habitats, mitigation of climate change, and prevention of soil erosion |
| Protection from deforestation | Preservation of valuable tree species, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, and prevention of habitat destruction |
| Awareness and community involvement | Fostering responsibility, encouraging action, and promoting a sense of environmental stewardship |
By implementing these strategies and working together as a global community, we can preserve and restore Earth’s tree population for future generations to enjoy and benefit from.
Question-Answer:
How many trees are there on Earth?
The exact number of trees on Earth is difficult to determine, but scientists estimate that there are approximately 3 trillion trees.
How do scientists estimate the number of trees on Earth?
Scientists use various methods to estimate the number of trees on Earth. One common method is using satellite imagery to analyze the tree cover in different regions and extrapolate the data to estimate the global tree population.
What are the benefits of having a large number of trees on Earth?
Trees provide numerous benefits to the planet and its inhabitants. They produce oxygen, absorb carbon dioxide, provide habitat for wildlife, prevent soil erosion, and contribute to the overall health and well-being of ecosystems.
Are the number of trees on Earth increasing or decreasing?
The number of trees on Earth is currently decreasing due to deforestation. Human activities such as logging, agriculture, and urbanization are leading to the loss of forested areas, which results in a decline in the global tree population.
What are the consequences of a decrease in the number of trees on Earth?
A decrease in the number of trees on Earth can have negative consequences for the planet. It can lead to increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, loss of biodiversity, disrupted ecosystems, and decreased availability of resources such as timber and clean water.
How many trees are there on Earth?
It is estimated that there are around 3.04 trillion trees on Earth.