
In recent years, Germany has become a leading example of efficient waste management. The country has developed innovative strategies and implemented comprehensive systems to minimize waste generation, promote recycling, and achieve high rates of waste diversion from landfills.
One of the key reasons for Germany’s success in waste management is its focus on waste prevention. Through strict regulations and policies, the country encourages producers and consumers to reduce waste at the source. This includes packaging reduction, product design that favors recyclability, and promoting the use of reusable products.
Recycling is an integral part of Germany’s waste management system. The country has implemented a dual system, known as the Green Dot, which requires producers to take responsibility for the packaging waste they generate. This system has led to high recycling rates, with the country consistently surpassing EU recycling targets. Furthermore, Germany has established an extensive network of recycling facilities, making it convenient for citizens to recycle different types of materials.
The notion of a circular economy is also deeply ingrained in Germany’s waste management approach. The country promotes the concept of using waste as a resource, emphasizing the importance of recovering valuable materials through processes such as composting, anaerobic digestion, and energy recovery. This not only reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills but also contributes to the generation of renewable energy.
In conclusion, Germany’s waste management strategies set a benchmark for other countries, demonstrating that a combination of waste prevention, recycling, and a circular economy approach can lead to efficient waste management. By prioritizing sustainability and taking a holistic approach, Germany has achieved remarkable results in waste reduction and resource recovery, making it a global leader in this field.
- Germany’s Efficient Waste Management System
- Policies and Regulations
- Recycling Programs
- Waste Separation and Recycling Bins
- Green Dot System
- Waste Separation and Collection
- Waste Separation
- Waste Collection
- Waste-to-Energy Plants
- Circular Economy Initiatives
- Sustainable Packaging
- Resource Recovery and Recycling
- Public Awareness and Education
- Education Initiatives
- Information and Advice
- Q&A:
- What is Germany’s waste management system like?
- How does Germany encourage waste reduction?
- What does Germany do with its organic waste?
- How does Germany ensure proper disposal of hazardous waste?
- Does Germany have any initiatives to promote recycling among its citizens?
Germany’s Efficient Waste Management System
Germany is known for its efficient waste management system, which has become a model for other countries around the world. The key to its success lies in its comprehensive approach that focuses on reducing, reusing, and recycling waste.
One of the cornerstones of Germany’s waste management system is its strict waste separation policies. Household waste is separated into different categories such as paper, plastics, glass, and organic waste. Citizens are required to sort their waste accordingly, and failure to do so can result in fines. This ensures that recyclable materials are not contaminated and can be processed more easily.
In addition to waste separation, Germany also prioritizes waste reduction. The government encourages manufacturers to produce products with less packaging, and consumers are encouraged to bring their own reusable bags and containers when shopping. This helps minimize the amount of waste generated in the first place.
Germany also has an extensive recycling infrastructure. The country has implemented a system where consumers pay a deposit on certain items such as beverage bottles, which is refunded when the items are returned for recycling. This incentivizes consumers to recycle and ensures that valuable materials are not lost in landfills.
Furthermore, Germany promotes the use of renewable energy from waste through its biogas and waste-to-energy plants. These plants convert organic waste into biogas, which can be used for heating or electricity generation. This reduces the dependence on fossil fuels and provides a sustainable solution for waste management.
Overall, Germany’s efficient waste management system is a result of its comprehensive approach that includes strict waste separation policies, waste reduction measures, recycling initiatives, and the use of renewable energy. By adopting similar strategies, other countries can also achieve effective waste management and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Policies and Regulations
Germany has implemented strict policies and regulations to manage waste efficiently and promote sustainability. These policies are based on the principles of waste prevention, reuse, recycling, and proper disposal. The German government has set ambitious targets for waste reduction and recycling rates, and it has established a comprehensive regulatory framework to achieve these goals.
One of the key policies in Germany is the Product Responsibility Act. This act holds manufacturers and importers responsible for the products they introduce to the market, including their packaging. It aims to encourage the production of eco-friendly and recyclable products and packaging materials. Producers are required to take back and recycle their products and packaging or pay a financial contribution towards their proper disposal.
The Recycling and Waste Management Act is another important regulation in Germany. It sets out guidelines for waste management and promotes a circular economy by emphasizing recycling and resource recovery. The act mandates separate collection of different types of waste, such as paper, glass, plastics, and organic waste. It also encourages the use of recycled materials in the production of new products.
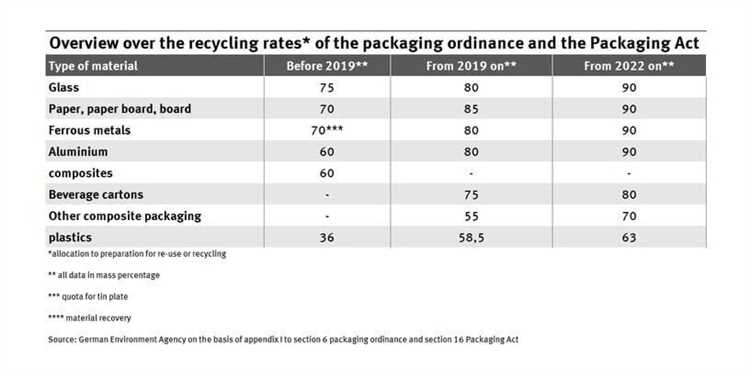
The Packaging Act is specifically focused on reducing packaging waste and promoting recycling. It requires producers to participate in a nationwide dual system for the collection and recycling of packaging materials. The act also sets recycling quotas for different types of packaging materials and promotes the use of eco-friendly packaging solutions.
In addition to these acts, Germany has implemented waste prevention programs at the local level. Municipalities and cities are responsible for waste management and are encouraged to implement measures to reduce waste generation, such as promoting reusable products and supporting initiatives to reduce food waste.
Overall, Germany’s policies and regulations on waste management have been successful in achieving high recycling rates and reducing waste. These measures have helped the country to become a leader in sustainable waste management and serve as an example for other countries to follow.
Recycling Programs
Germany is known for its efficient waste management system, which includes a comprehensive network of recycling programs. These programs are designed to encourage citizens and businesses to recycle their waste and reduce the amount of material going to landfills.
One of the key recycling programs in Germany is the Dual System. This program is responsible for the collection and recycling of packaging waste, such as plastic bottles, cans, and paper. It is funded by the manufacturers and distributors of these products, who are required by law to participate in the program. The Dual System ensures that the collected waste is sorted, processed, and recycled efficiently.
In addition to the Dual System, Germany also has recycling programs for specific materials, such as batteries, electronics, and hazardous waste. These programs provide designated collection points where individuals can drop off their waste for proper disposal or recycling. The government and various organizations work together to educate the public about the importance of recycling these specific materials and the potential environmental and health hazards associated with improper disposal.
Waste Separation and Recycling Bins
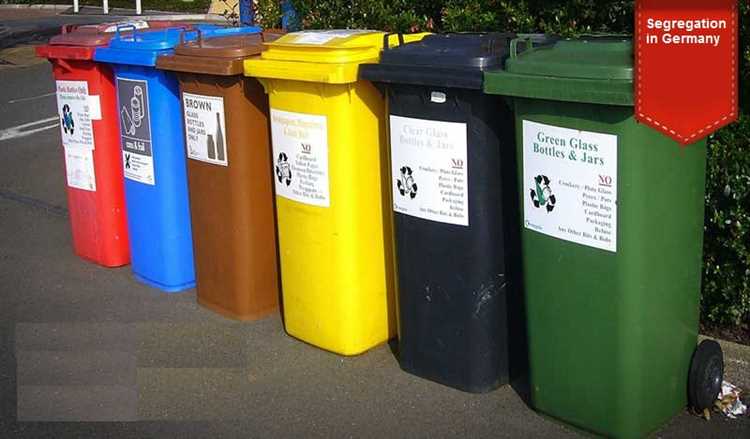
One of the reasons why Germany’s recycling programs are so successful is its emphasis on waste separation. In many cities and municipalities, households are required to separate their waste into different categories, such as paper, plastic, glass, and organic waste. Recycling bins are provided to residents for each specific category, making it convenient to separate and recycle their waste.
Green Dot System
The Green Dot System is another important aspect of Germany’s recycling efforts. It is a financing system that ensures the collection and recycling of packaging waste. The Green Dot symbol, which is shown on product packaging, indicates that the manufacturer or distributor has financially contributed to the waste management and recycling efforts. The revenues generated from the Green Dot System are used to support the recycling programs and infrastructure in Germany.
Overall, Germany’s recycling programs play a crucial role in its waste management strategy. By encouraging the separation and recycling of different types of waste, these programs help reduce the amount of waste going to landfills and conserve valuable resources. They also promote a culture of environmental responsibility and sustainability among citizens and businesses.
Waste Separation and Collection
In Germany, waste separation and collection are integral parts of the country’s efficient waste management system. The German government has implemented strict regulations and guidelines to ensure that waste is sorted properly and collected in an organized manner.
Waste Separation

One of the key aspects of waste management in Germany is the separation of different types of waste. This includes separating recyclables such as paper, plastic, and glass from non-recyclable waste. This is done at both the household and commercial levels, with dedicated recycling bins provided for each type of waste.
The German government has also implemented a comprehensive recycling system known as the “dual system”. Under this system, manufacturers and suppliers of packaged goods are responsible for the collection and recycling of the packaging waste their products generate. This ensures that packaging waste is properly separated and recycled.
Waste Collection
Waste collection in Germany is highly organized and efficient. Each municipality has designated waste collection points where residents can dispose of their waste. These collection points are equipped with separate containers for different types of waste, making it easy for residents to sort their waste properly.
In addition to regular waste collection, Germany also has specific collection systems for hazardous waste, electronic waste, and bulky waste. Hazardous waste, such as chemicals and batteries, can be safely disposed of at designated collection points. Electronic waste, such as old computers and televisions, can be recycled through specialized collection programs. Bulky waste, such as furniture and appliances, can be scheduled for pick-up by contacting the local waste management authorities.
| Type of Waste | Collection Method |
|---|---|
| Recyclables (paper, plastic, glass) | Dedicated recycling bins |
| Packaging waste | “Dual system” through manufacturers and suppliers |
| Hazardous waste | Designated collection points |
| Electronic waste | Specialized collection programs |
| Bulky waste | Scheduled pick-up by local waste management authorities |
Waste-to-Energy Plants

Germany is at the forefront of waste management and has implemented innovative solutions to deal with the increasing amount of waste generated. One of the key strategies employed by Germany is the use of waste-to-energy plants. These plants play a crucial role in the country’s waste management system by converting non-recyclable waste into usable energy.
Waste-to-energy plants use advanced technologies to thermally treat waste and convert it into electricity and heat. The process involves burning the waste at high temperatures in specially designed incinerators. This combustion process not only reduces the volume of waste but also generates energy that can be used to power homes and businesses.
These plants are equipped with sophisticated pollution control systems to ensure that emissions are minimized and comply with strict environmental regulations. They employ a combination of technologies such as scrubbers, filters, and electrostatic precipitators to capture and remove harmful pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere.
In addition to producing energy, waste-to-energy plants also help in the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. By diverting waste from landfill sites, these plants prevent the release of methane gas, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. This makes waste-to-energy plants an environmentally friendly option for managing non-recyclable waste.
Germany has invested heavily in waste-to-energy plants and has a well-developed network across the country. These plants not only serve as an efficient way to manage waste but also contribute to the country’s renewable energy goals. They provide a sustainable solution to waste management while reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Waste-to-energy plants convert non-recyclable waste into usable energy.
- They use advanced technologies to thermally treat waste and generate electricity and heat.
- These plants have pollution control systems to minimize emissions.
- Waste-to-energy plants help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Germany has a well-developed network of waste-to-energy plants.
Circular Economy Initiatives
Germany has been a pioneer in implementing circular economy initiatives to manage waste efficiently. The concept of a circular economy focuses on reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling resources to create a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly society.
Sustainable Packaging
One of the key initiatives in Germany’s circular economy is promoting sustainable packaging. The government has implemented policies to encourage the use of eco-friendly materials for packaging, such as biodegradable and compostable options. This helps reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact of packaging materials.
Furthermore, the “Green Dot” system, introduced in Germany in the 1990s, has been pivotal in the management of packaging waste. This system involves labeling packaging with a green dot symbol, indicating that the manufacturer has financially contributed to the collection and recycling of the packaging. This encourages companies to use less packaging or opt for eco-friendly alternatives.
Resource Recovery and Recycling
Germany places a strong emphasis on resource recovery and recycling. The country has an extensive waste separation system that encourages citizens to sort their waste into different categories, such as paper, plastic, glass, and organic waste. This enables efficient recycling and recovery of valuable resources.
Moreover, Germany has implemented advanced recycling technologies to process waste materials. These technologies include eco-friendly methods such as mechanical and biological treatment, which help recover valuable resources and reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills.
The country also has a well-established infrastructure for collecting and recycling electronic waste, such as old smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices. Recycling initiatives for electronic waste ensure that valuable materials, like gold and copper, are recovered instead of ending up in landfill sites.
In addition, Germany promotes the concept of a circular economy through initiatives like a “circular economy law” that aims to encourage companies to design products that are more durable, repairable, and recyclable. This helps reduce waste generation and promotes a more sustainable approach to product design and manufacturing.
In conclusion, Germany’s circular economy initiatives have played a significant role in managing waste efficiently. The focus on sustainable packaging, resource recovery, recycling, and promoting a circular economy mindset has helped the country minimize waste and create a more sustainable future.
Public Awareness and Education
In Germany, public awareness and education play a crucial role in the efficient management of waste. The government and various organizations have implemented extensive programs to educate the public about the importance of waste reduction, recycling, and proper disposal.
Education Initiatives
A wide range of educational initiatives are in place to teach individuals about waste management. Schools incorporate waste reduction and recycling into their curriculum by including lessons on waste separation, composting, and the importance of recycling. Students are encouraged to actively participate in recycling initiatives and are taught about the environmental benefits of reducing waste.
Additionally, public awareness campaigns are run by the government and environmental organizations to educate the general population about waste management practices. These campaigns utilize various media platforms, including television, radio, and social media, to disseminate information about waste separation, recycling programs, and responsible waste disposal.
Information and Advice
A key aspect of public awareness is providing individuals with accurate and up-to-date information about waste management. The government and waste management authorities offer resources such as websites, brochures, and helplines to help citizens understand the proper methods of waste disposal and recycling.
Furthermore, individuals can access information about the location of recycling centers, collection points, and the types of materials accepted for recycling. This accessibility ensures that individuals can easily find the necessary information to correctly dispose of their waste and participate in recycling efforts.
| Benefits of Public Awareness and Education |
|---|
| 1. Increased Recycling Rates: By educating the public about the importance of recycling and waste reduction, Germany has seen significant increases in recycling rates. Citizens are more aware of the impact of their actions on the environment and are motivated to recycle. |
| 2. Improved Waste Separation: Public education campaigns have helped individuals understand the importance of separating waste into specific categories. This has led to improved waste separation practices, resulting in higher-quality recycled materials. |
| 3. Reduced Contamination: Proper education ensures that individuals are aware of the potential environmental and health risks associated with improper waste disposal. This knowledge reduces the occurrence of contaminated waste, making the recycling process more effective. |
| 4. Sustainable Future: Public awareness and education contribute to a more sustainable future by promoting a culture of responsible waste management. By actively involving the public, Germany aims to create a society that values and prioritizes waste reduction and recycling. |
The success of Germany’s waste management system can be attributed, in part, to the emphasis on public awareness and education. By empowering individuals with knowledge and resources, Germany has achieved impressive waste reduction and recycling rates, setting a positive example for other countries to follow.
Q&A:
What is Germany’s waste management system like?
Germany has a highly efficient waste management system that focuses on recycling and reducing waste. It has implemented a system of waste separation and recycling bins, which helps in sorting different types of waste such as paper, plastics, glass, and organic waste. The country also has a well-established infrastructure for waste collection and disposal.
How does Germany encourage waste reduction?
Germany encourages waste reduction through various measures. One of the main ways is to promote packaging-free shopping by offering consumers the option to bring their own containers and bags. The country also supports the use of refillable bottles for beverages, which significantly reduces the amount of plastic waste. Additionally, Germany has strict regulations on packaging materials and promotes the use of recycled materials in packaging.
What does Germany do with its organic waste?
Germany has a comprehensive system for managing organic waste. Organic waste such as food scraps and garden waste is collected separately from other types of waste. It is then processed through composting or anaerobic digestion. The resulting compost can be used as a fertilizer in agriculture, while the biogas produced during anaerobic digestion can be used as a renewable energy source.
How does Germany ensure proper disposal of hazardous waste?
Germany has strict regulations for the proper disposal of hazardous waste. It requires producers and consumers to separate hazardous waste from other types of waste. There are specialized collection points where hazardous waste can be dropped off, such as recycling centers and hazardous waste depots. These facilities ensure that hazardous waste is handled and disposed of safely to minimize environmental and health risks.
Does Germany have any initiatives to promote recycling among its citizens?
Yes, Germany has several initiatives to promote recycling among its citizens. One such initiative is the introduction of a deposit system for beverage containers. Consumers are offered a refundable deposit when they return empty bottles and cans, which encourages recycling. The country also conducts education and awareness campaigns to inform citizens about the importance of recycling and how to properly sort and dispose of their waste.