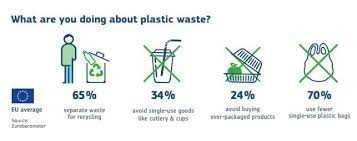
Plastic pollution has become a major global issue, with devastating impacts on our environment and wildlife. Recognizing the urgency of the problem, the European Union (EU) has introduced a comprehensive strategy to address plastic pollution and promote sustainable solutions. This strategy aims to shift towards a circular economy where plastic waste is reduced, reused, and recycled, rather than ending up in landfills or polluting our oceans.
The EU Plastic Strategy encompasses a wide range of initiatives and policies to tackle plastic pollution at every stage of the value chain, from production to disposal. It includes measures to reduce the consumption of single-use plastics, promote the use of sustainable alternatives, and improve waste management and recycling systems. The strategy also encourages innovation and research to find new, more sustainable materials and technologies.
One of the key goals of the EU Plastic Strategy is to ensure that all plastic packaging placed on the EU market is reusable or recyclable by 2030. This ambitious target will require close collaboration between industry, policymakers, and consumers. It will also require investment in new infrastructure and technologies to enable proper recycling and waste management.
By tackling plastic pollution, the EU aims to protect our ecosystems, reduce the carbon footprint of plastic production, and create a more sustainable future. Plastic pollution not only harms marine life but also contributes to climate change, as the production of plastic requires large amounts of fossil fuels. By transitioning to a circular economy, the EU can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote a more sustainable use of resources.
- Understanding Plastic Pollution in the EU
- Benefits of Implementing Sustainable Solutions
- Key Objectives of the EU Plastic Strategy
- 1. Making plastic packaging more sustainable
- 2. Increasing recycling rates for plastics
- Progress and Achievements So Far
- Future Challenges and Initiatives
- Q&A:
- What is the EU Plastic Strategy?
- Why is plastic pollution a significant issue?
- What are the goals of the EU Plastic Strategy?
- What actions will the EU take to achieve the goals of the Plastic Strategy?
Understanding Plastic Pollution in the EU

Plastic pollution is a pressing issue in the European Union (EU) that requires urgent attention. Plastic waste has become a significant environmental problem, affecting marine and terrestrial ecosystems, as well as human health.
The EU produces approximately 25 million tons of plastic waste annually, making it one of the largest plastic waste generators in the world. A significant portion of this plastic waste ends up in landfills, incinerators, or worse, as litter in the environment.
Plastic pollution has detrimental effects on marine life. Marine animals, such as turtles, birds, and fish, often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement. This not only threatens their well-being but also disrupts the natural balance of ecosystems. Microplastics, tiny plastic particles that result from the breakdown of larger plastics, have been found in various marine species, including fish and shellfish, raising concerns about their potential impact on human health when consumed.
Plastic pollution also affects terrestrial ecosystems. Plastic litter, when discarded on land, can contaminate soil and water, posing risks to plants and animals. The accumulation of plastic waste in rivers and lakes can result in clogging and flooding, exacerbating the damage caused by extreme weather events.
The EU is taking action to address plastic pollution through its Plastic Strategy, a comprehensive plan aimed at reducing single-use plastics, promoting recycling, and fostering a more sustainable plastic industry. The strategy includes measures such as banning certain single-use plastic items, promoting eco-design and recyclability of plastic products, and improving waste management infrastructure.
- Implementing effective waste management systems to reduce plastic leakage into the environment.
- Promoting research and innovation for sustainable plastic alternatives and recycling technologies.
- Encouraging consumer behavior changes, such as reducing plastic consumption and adopting reusable products.
- Collaborating with international partners to tackle plastic pollution on a global scale.
By understanding the magnitude and impacts of plastic pollution in the EU, policymakers and stakeholders can develop targeted strategies and initiatives to combat this issue effectively. Through collective efforts and a shift towards a circular economy, the EU can mitigate plastic pollution and promote sustainable solutions for a cleaner and healthier environment.
Benefits of Implementing Sustainable Solutions

Implementing sustainable solutions to tackle plastic pollution offers numerous benefits for both the environment and society as a whole:
| Environmental Benefits | Social Benefits |
|
|
By implementing sustainable solutions, the European Union and its member states can lead the way in reducing plastic pollution and creating a more sustainable future for all.
Key Objectives of the EU Plastic Strategy
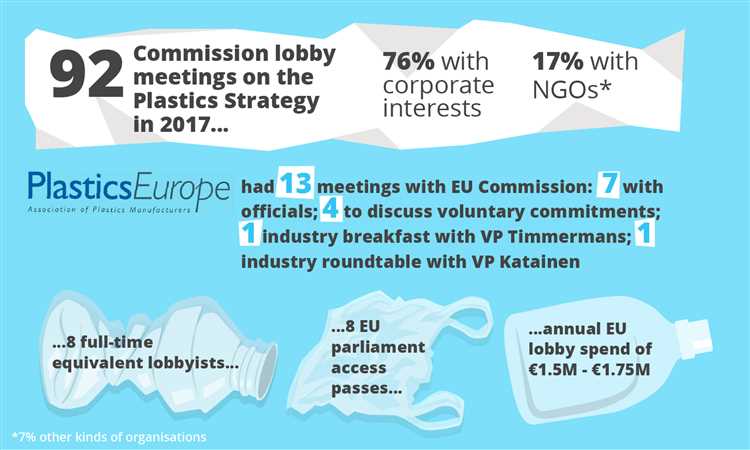
The EU Plastic Strategy was created to address the urgent issue of plastic pollution and to promote sustainable solutions. The strategy focuses on several key objectives that aim to reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste and foster a circular economy.
1. Making plastic packaging more sustainable
One of the main objectives of the EU Plastic Strategy is to ensure that plastic packaging is more sustainable. This involves encouraging the use of recyclable materials, promoting the use of eco-design principles, and improving the overall recyclability and reusability of plastic packaging. The strategy also aims to reduce the consumption of single-use plastics, such as plastic bags and straws, by promoting alternative packaging options.
2. Increasing recycling rates for plastics
Another important objective is to increase the recycling rates for plastics across Europe. The strategy sets a target of recycling at least 50% of plastic packaging waste by 2025 and 55% by 2030. To achieve this, the EU aims to improve the collection, sorting, and recycling infrastructure, as well as promote the use of recycled plastics in products. The strategy also seeks to reduce landfilling and incineration of plastic waste, which contribute to pollution and climate change.
| Recycling targets for plastic packaging waste | 2025 | 2030 |
|---|---|---|
| Target recycling rate | 50% | 55% |
By setting clear recycling targets, the EU aims to create a more sustainable and circular plastic economy.
Overall, the key objectives of the EU Plastic Strategy focus on reducing plastic pollution, promoting sustainable packaging, and increasing recycling rates. By implementing these objectives, the EU aims to protect the environment, reduce waste, and foster a more circular economy.
Progress and Achievements So Far
The EU Plastic Strategy, implemented in 2018, has made significant progress in tackling plastic pollution and promoting sustainable solutions. Since its inception, the strategy has achieved several milestones and accomplished notable achievements.
One major accomplishment is the EU’s ban on single-use plastics, which came into effect in July 2021. This ban prohibits the use of items such as plastic cutlery, plates, straws, and cotton buds, which are among the most commonly found plastic items in Europe’s seas and beaches. By banning these items, the EU aims to reduce the overall plastic waste and prevent further pollution of marine ecosystems.
Another noteworthy achievement is the establishment of a system for Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR). Under this system, producers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including the management of the waste generated by these products. By holding producers accountable, the EU aims to incentivize the development of more sustainable and circular business models.
Furthermore, the EU Plastic Strategy has fostered increased innovation and research in the field of plastic alternatives. The strategy has provided funding and support for the development of bio-based and biodegradable plastics, as well as alternative materials like cellulose and mushroom-based packaging. These innovations have the potential to reduce plastic pollution and offer more sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic packaging.
Additionally, the EU has implemented measures to promote the recycling of plastic waste. The strategy includes a target to recycle 55% of all plastic packaging waste by 2030. To achieve this goal, the EU has implemented stricter recycling standards and improved waste collection and sorting systems. These efforts aim to increase the overall recycling rates and reduce the amount of plastic waste sent to landfills.
Overall, the EU Plastic Strategy has shown significant progress and achieved several milestones in its mission to tackle plastic pollution and promote sustainable solutions. Through the ban on single-use plastics, the establishment of Extended Producer Responsibility, the support for innovation in plastic alternatives, and the promotion of plastic recycling, the EU is paving the way towards a more sustainable and circular economy.
Future Challenges and Initiatives
The EU Plastic Strategy is an important step towards tackling plastic pollution, but there are still several challenges that need to be addressed in the future. One of the main challenges is the lack of a unified approach across member states for plastic waste management. Many countries still have different recycling systems and regulations, which leads to inefficiencies and inconsistencies.
To overcome this challenge, the EU plans to establish a harmonized framework for plastic waste management. This framework will include guidelines for recycling, waste collection, and disposal methods. By creating a standardized approach, the EU aims to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of plastic waste management across member states.
Another challenge is the need for better waste prevention and reduction strategies. While recycling is important, it is not a long-term solution to the plastic pollution problem. The EU recognizes the importance of reducing plastic waste at the source and is implementing initiatives to promote sustainable alternatives.
One such initiative is the promotion of eco-design and the use of alternative materials. By encouraging businesses to design products that are easier to recycle and by promoting the use of biodegradable and compostable materials, the EU aims to reduce the amount of plastic waste generated in the first place.
Furthermore, the EU is investing in research and innovation to develop new technologies and solutions for plastic waste management. This includes funding projects that focus on the development of bioplastics, improved recycling techniques, and advanced waste sorting technologies.
Overall, the EU Plastic Strategy is not just a response to the current plastic pollution crisis, but also a roadmap for a sustainable future. By addressing the challenges and implementing initiatives that promote waste reduction and sustainable solutions, the EU is taking a proactive approach to protect the environment and achieve a circular economy.
Q&A:
What is the EU Plastic Strategy?
The EU Plastic Strategy is a comprehensive plan developed by the European Union to tackle plastic pollution and promote sustainable solutions. It aims to transform how plastic products are designed, produced, used, and recycled in the EU.
Why is plastic pollution a significant issue?
Plastic pollution is a significant issue because it poses a threat to the environment, marine life, and human health. It takes hundreds of years for plastic to break down, and during that time, it can accumulate in ecosystems, harm wildlife, and leach harmful chemicals into the environment.
What are the goals of the EU Plastic Strategy?
The goals of the EU Plastic Strategy are to make all plastic packaging in the EU recyclable or reusable by 2030, reduce the consumption of single-use plastics, restrict the use of harmful microplastics, and promote sustainable alternatives to plastic.
What actions will the EU take to achieve the goals of the Plastic Strategy?
The EU will take several actions to achieve the goals of the Plastic Strategy. These include setting standards for plastic packaging, promoting innovation in plastic recycling technologies, introducing new rules to reduce the consumption of single-use plastics, and working with international partners to combat plastic pollution.