
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste is a crucial piece of legislation aimed at addressing the environmental impact of packaging materials. Packaging is an essential part of modern society, ensuring the safe transportation and storage of goods. However, the excessive use of packaging materials has led to significant waste and pollution, prompting the need for regulation.
Under this directive, member states are required to implement measures to reduce the consumption of packaging, promote recycling, and minimize the generation of packaging waste. The directive sets specific targets for the recycling and recovery of packaging waste, with the aim of shifting towards a more sustainable and circular economy.
The directive also encourages producers to design packaging that is reusable, recyclable, and environmentally friendly. It emphasizes the importance of eco-design, promoting the use of materials with a lower environmental impact and encouraging innovative solutions to reduce packaging waste.
Furthermore, the directive establishes extended producer responsibility, holding producers accountable for the management of packaging waste. Producers are required to finance and organize the collection, recycling, and disposal of packaging waste, incentivizing them to adopt more sustainable packaging practices.
By implementing the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste, the European Union aims to create a more sustainable and resource-efficient economy. It recognizes the importance of reducing waste and protecting the environment for future generations. Through this directive, the EU is driving the transition towards a circular economy, where waste is minimized, and resources are used more efficiently. Understanding this directive is key to ensuring compliance and contributing to a greener future.
- The Importance of the EU Directive
- Understanding the Packaging Waste Problem
- Key Objectives of the Directive
- Requirements for Packaging Design and Material
- Extended Producer Responsibility and Recycling Targets
- Implications for Businesses and Consumers
- Implications for Businesses
- Implications for Consumers
- Q&A:
- What is the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste?
- Why was the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste introduced?
- What are the key provisions of the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste?
- How does the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste affect businesses?
The Importance of the EU Directive
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste is a crucial piece of legislation that plays a vital role in managing and reducing waste within the European Union. It sets out guidelines and targets for member states to ensure the sustainable use of packaging materials and the responsible disposal of packaging waste.
By implementing the EU Directive, member states can promote a circular economy by reducing the amount of waste generated and increasing the recycling rates of packaging materials. This helps to conserve natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and prevent pollution.
Furthermore, the EU Directive encourages innovation and the development of eco-friendly packaging solutions. It provides incentives for manufacturers to design packaging that is more easily recyclable and biodegradable, reducing the environmental impact of packaging materials throughout their lifecycle.
The EU Directive also promotes transparency and accountability by requiring member states to report on their progress towards meeting the targets set out in the legislation. This allows for the sharing of best practices and facilitates collaboration between countries to achieve their waste reduction and recycling goals.
In addition, the EU Directive helps to create a level playing field for businesses operating within the European Union. By establishing uniform regulations and standards, it ensures fair competition and prevents unfair advantages for companies that do not adhere to sustainable packaging practices.
In conclusion, the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste is of utmost importance in promoting sustainability, reducing waste, and protecting the environment. Its implementation is a crucial step towards achieving a circular economy and ensuring the long-term well-being of both people and the planet.
Understanding the Packaging Waste Problem
In today’s modern society, packaging has become an integral part of our daily lives. From food to electronics, everything we buy comes in some form of packaging. While packaging serves the important purpose of protecting goods during transportation and storage, its improper management has led to a growing packaging waste problem.
According to studies, packaging waste is a significant contributor to the overall waste generated worldwide. In the European Union alone, it accounts for more than one-third of all municipal solid waste. This excessive amount of packaging waste poses serious environmental and sustainability challenges.
One of the main issues with packaging waste is its disposal. Many consumers dispose of packaging materials without considering the environmental impact. Most packaging, especially plastic, takes hundreds of years to decompose, leading to overflowing landfills and a burden on the environment.
Another problem is the low recycling rate for packaging waste. Despite efforts to promote recycling, many countries struggle to achieve high recycling rates for packaging materials. This is due to various reasons such as inadequate infrastructure, lack of awareness, and limited recycling facilities.
The packaging waste problem also extends to marine pollution. It is estimated that a significant amount of plastic packaging ends up in the oceans and causes harm to marine life. This has raised concerns about the long-term ecological effects and the need for stricter regulations to prevent further pollution.
To address the packaging waste problem, the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste sets out specific targets and measures for reducing packaging waste, increasing recycling rates, and promoting sustainable packaging practices. Through this directive, efforts are being made to shift towards a circular economy model where packaging waste is minimized, and resources are efficiently utilized.
| Impact of Packaging Waste | Solution |
|---|---|
| Overflowing landfills | Increase recycling rates and promote eco-friendly packaging alternatives. |
| Marine pollution | Stricter regulations on packaging materials and improved waste management practices. |
| Low recycling rates | Invest in recycling infrastructure and raise awareness about the importance of recycling. |
In conclusion, the packaging waste problem is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. By understanding the environmental impact of packaging waste and implementing effective measures, we can move towards a more sustainable and waste-free future.
Key Objectives of the Directive
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste has several key objectives with regards to managing packaging waste and promoting sustainable practices. These objectives are:
-
Preventing the generation of packaging waste by promoting the use of environmentally friendly packaging materials and supporting the adoption of reusable packaging.
-
Reducing the overall quantity of packaging waste generated through the implementation of waste prevention measures.
-
Encouraging the recycling of packaging waste through the establishment of recycling targets and the development of recycling infrastructure.
-
Promoting the use of recycled materials in the production of packaging in order to create a circular economy and decrease the dependency on virgin materials.
-
Minimizing the environmental impact of packaging waste through the implementation of ecodesign principles and the reduction of hazardous substances in packaging.
-
Ensuring that producers take responsibility for the management of their packaging waste, including the financing of collection, sorting, and recycling activities.
-
Enhancing transparency and traceability in the management of packaging waste through improved reporting and documentation processes.
By achieving these objectives, the EU Directive aims to improve the sustainable management of packaging waste, promote resource efficiency, and contribute to the transition to a more circular economy.
Requirements for Packaging Design and Material
In order to promote sustainable packaging practices and reduce the environmental impact of packaging waste, the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste imposes certain requirements for packaging design and material.
Firstly, packaging must be designed in a way that minimizes the amount of material used, without compromising its necessary functions. This means that packaging should be lightweight and efficient, while still providing adequate protection for the products it contains.
Furthermore, packaging materials must be chosen with consideration for their environmental impact. The use of recycled or renewable materials is encouraged, as well as the use of materials that are easily recyclable or biodegradable. Packaging should be designed with end-of-life considerations in mind, aiming for a circular economy approach where materials can be reused or recycled.
In addition to material considerations, packaging must also meet certain performance criteria. It must be able to withstand the rigors of storage and transport without compromising the safety or quality of the product. Packaging should also be designed to facilitate efficient disposal and recycling processes, such as by being easy to separate and sort.
Compliance with these requirements is essential for businesses operating within the EU market. Non-compliance can result in penalties and legal action, as well as damage to a company’s reputation. Therefore, it is important for companies to carefully evaluate and adapt their packaging designs and materials in order to meet the directive’s requirements and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Extended Producer Responsibility and Recycling Targets
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste includes provisions for extended producer responsibility (EPR) and sets recycling targets for member states to achieve.
Under EPR, producers are held responsible for the collection, treatment, and recycling of their packaging waste. This means that producers must take steps to ensure that their packaging is designed for recyclability and that they contribute financially to the costs of collection and recycling.
The recycling targets set by the EU directive aim to increase the recycling rates of packaging waste across member states. The targets are specific to different types of packaging materials, such as paper and cardboard, glass, plastic, and metal, and are based on the weight of packaging waste generated.
For example, the directive sets a target for member states to recycle at least 65% of their packaging waste by weight by the year 2025. Additionally, specific targets are set for different packaging materials, such as a minimum recycling rate of 75% for paper and cardboard and 70% for glass.
Member states are required to develop national recycling plans and take measures to achieve the recycling targets set by the directive. These measures may include implementing recycling programs, improving waste collection and sorting systems, and promoting awareness and education about recycling.
By implementing EPR and setting recycling targets, the EU aims to promote the circular economy and reduce the environmental impact of packaging waste. Through these measures, it is hoped that more packaging waste will be recycled, reducing the need for virgin materials and decreasing waste sent to landfill or incineration.
Implications for Businesses and Consumers
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste has significant implications for businesses and consumers. It aims to create a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly approach to packaging, with the ultimate goal of reducing waste and promoting circular economy principles.
Implications for Businesses

For businesses, the directive imposes several requirements and responsibilities. Firstly, they are required to meet certain packaging waste recovery and recycling targets, which vary depending on their country and the type of packaging they produce. This means that businesses will need to invest in recycling infrastructure and processes to ensure compliance.
In addition, the directive promotes the use of environmentally-friendly packaging materials, such as biodegradable or compostable materials, and encourages businesses to minimize the amount of packaging they use. This can have implications for product design, as businesses will need to find ways to reduce packaging without compromising product protection and integrity.
Furthermore, businesses will need to provide clear and accurate information to consumers about the recyclability and environmental impact of their packaging. This includes labeling packaging materials and providing guidance on how to properly dispose of packaging waste. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in fines and reputational damage.
Implications for Consumers
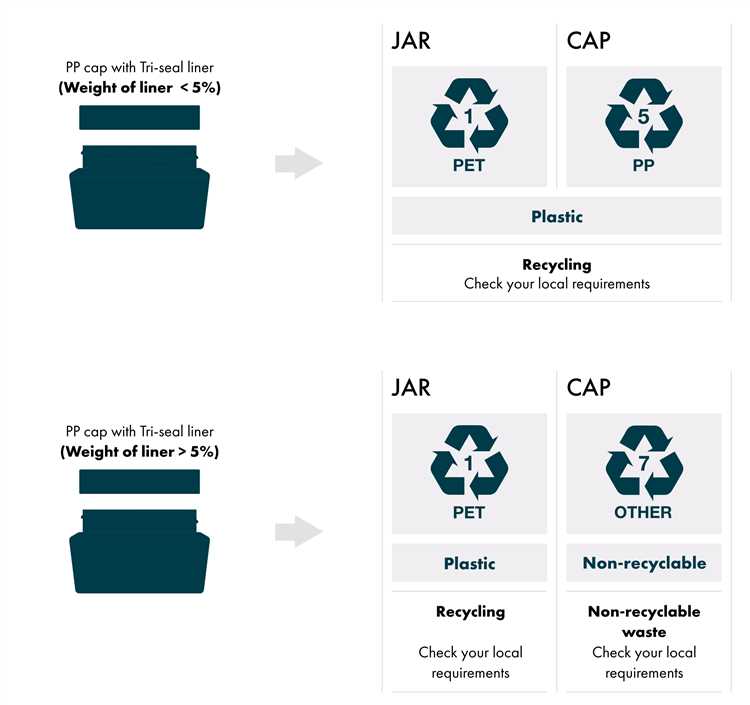
For consumers, the directive aims to increase awareness and encourage responsible recycling behavior. It promotes the use of standardized recycling symbols and labels, making it easier for consumers to identify recyclable packaging materials and understand how to dispose of them properly.
Consumers will also benefit from improved access to recycling facilities and convenient methods for disposing of packaging waste. The directive encourages member states to invest in recycling infrastructure and implement collection systems that are easily accessible to consumers, such as curbside recycling or drop-off points.
Furthermore, the directive incentivizes the use of reusable packaging and encourages consumers to choose products with less packaging or packaging made from recycled materials. This can help reduce waste and promote a more sustainable shopping and consumption behavior.
| Implications for Businesses | Implications for Consumers |
|---|---|
| Meeting packaging waste recovery and recycling targets | Increased awareness and responsible recycling behavior |
| Use of environmentally-friendly packaging materials | Improved access to recycling facilities |
| Minimizing the amount of packaging used | Incentives for reusable packaging |
| Providing clear information to consumers | Promotion of products with less packaging |
Q&A:
What is the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste?
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste is a legislation introduced by the European Union to regulate the management of packaging and packaging waste within its member states. It aims to promote sustainability, reduce environmental impact, and ensure the proper disposal and recycling of packaging materials.
Why was the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste introduced?
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste was introduced to address the growing issues of waste production, environmental pollution, and resource depletion associated with packaging materials. It seeks to establish a circular economy approach, where packaging is designed, used, and recycled in a sustainable and environmentally-friendly manner.
What are the key provisions of the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste?
The key provisions of the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste include setting packaging waste prevention targets, promoting the use of reusable and recyclable packaging materials, establishing recycling and recovery targets for different packaging waste streams, and encouraging eco-design principles for packaging products.
How does the EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste affect businesses?
The EU Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste affects businesses by placing obligations on them to comply with the waste prevention and recycling targets set by the directive. Businesses are required to reduce the environmental impact of their packaging materials, promote recycling and recovery, provide information about packaging materials used, and contribute to the funding of recycling schemes.