
Waste management is a global concern, and one question often asked is whether the United States exports its waste to other countries. This practice, known as waste exportation, is a complex issue that has both economic and environmental implications.
In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the impact of waste exportation on the environment. Some argue that by exporting its waste, the US is simply transferring the problem to other countries, particularly developing nations with less stringent environmental regulations. This raises questions about environmental justice and the responsibility of wealthier countries to properly manage their own waste.
Proponents of waste exportation argue that it can be a cost-effective solution for the US. By exporting waste to countries with lower labor and waste disposal costs, the US can save money and preserve landfill space. However, critics argue that this practice can lead to the exploitation of workers in developing countries and exacerbate social and environmental inequalities.
Overall, the issue of waste exportation is a complex one. It raises questions about environmental responsibility, economic efficiency, and social justice. Finding a sustainable solution to waste management is crucial in order to protect our planet and ensure a better future for generations to come.
- Does the US export its waste?
- Environmental Impact of Waste
- Land Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Global Waste Economy
- Waste Generation
- Waste Management Strategies
- Waste Export Regulations
- Basel Convention
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
- Exceptions and Restrictions
- US Waste Export Statistics
- Reasons for US Waste Export
- Environmental and Ethical Concerns
- Controversies and Criticism
- Future Outlook and Solutions
- Q&A:
- Does the US export a lot of waste to other countries?
- Which countries does the US export its waste to?
- Why does the US export its waste to other countries instead of handling it domestically?
- Are there any negative consequences of the US exporting its waste to other countries?
Does the US export its waste?

The United States is one of the largest producers of waste in the world, generating millions of tons of waste each year. However, it also exports a significant amount of its waste to other countries.
One of the main reasons why the US exports its waste is because it is often cheaper and more convenient to send it to other countries. Some countries, especially those in Southeast Asia, have lower labor and environmental standards, which makes it more cost-effective to dispose of waste there.
Another reason why the US exports its waste is that it allows the country to avoid dealing with the environmental and health risks associated with waste management. By exporting waste, the US can shift the responsibility to other countries and avoid the costs and challenges of managing it domestically.
The types of waste exported by the US vary, but they often include electronic waste, plastic waste, and hazardous waste. These types of waste can cause significant environmental and health issues if not properly managed.
However, the practice of exporting waste has come under criticism in recent years. Some argue that it is an unethical way for the US to avoid taking responsibility for its waste. Others argue that it exacerbates pollution and other environmental issues in the countries that receive the waste.
In response to the criticism, some countries have started to restrict or ban the import of waste from the US and other countries. These restrictions have led to an increase in domestic waste management efforts in the US, but the country still exports a significant amount of its waste.
In conclusion, the US does export its waste to other countries as it is cheaper and more convenient. However, this practice has faced criticism and some countries have started to restrict or ban the import of waste. The US continues to generate and export a significant amount of waste, which highlights the need for better waste management practices both domestically and internationally.
Environmental Impact of Waste

Waste management is a critical environmental issue that affects countries and regions around the world. The improper disposal of waste can have serious negative consequences for the environment, including pollution of land, air, and water.
Land Pollution
When waste is not properly disposed of, it often ends up in landfills. Landfills are vast areas filled with heaps of garbage that releases harmful gases and toxins into the atmosphere. These gases include methane, a potent greenhouse gas, which contributes to climate change. Landfills can also contaminate surrounding soil and groundwater, making them unsuitable for agriculture or drinking.
Air Pollution
Many waste materials produce harmful emissions when disposed of improperly, leading to air pollution. For example, burning of waste emits toxic substances like dioxins and furans, which are hazardous to human health. These pollutants can cause respiratory problems and contribute to the formation of smog.
Water Pollution
Improper waste disposal can contaminate water sources, including rivers, lakes, and oceans. When waste materials, such as plastics or chemicals, are dumped into bodies of water, they can leach harmful substances into the water, affecting marine life and ecosystems. Water pollution also poses a threat to human health, as contaminated water can lead to the spread of waterborne diseases.
Overall, the environmental impacts of waste are significant and far-reaching. Proper waste management practices, including recycling, reducing waste generation, and implementing secure landfill procedures, are essential to minimize these negative effects and protect the environment for future generations.
Global Waste Economy
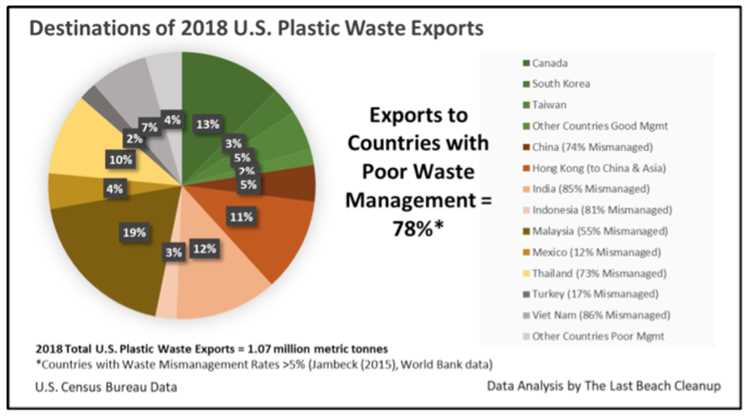
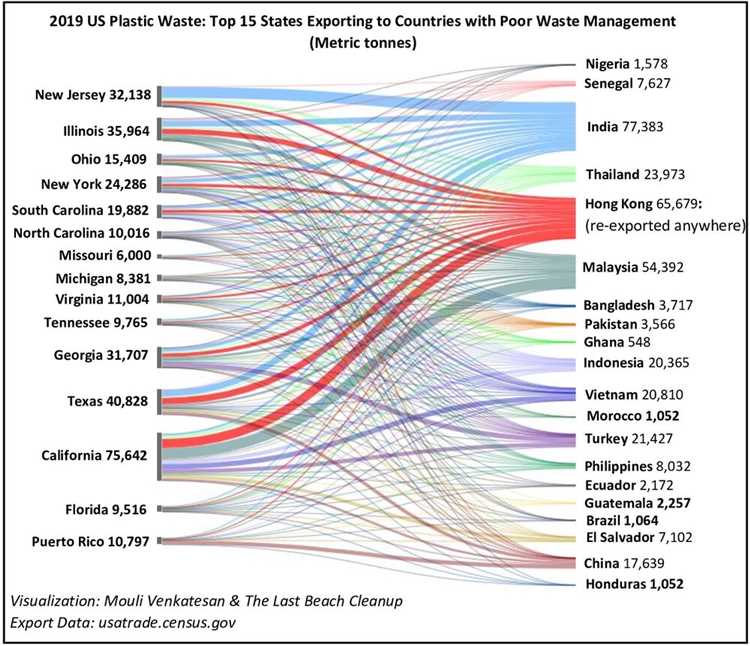
The global waste economy is a complex system that involves the production, disposal, and trade of waste materials across countries and continents. As the world’s population and consumption continue to increase, so does the amount of waste generated.
Waste Generation
Waste generation refers to the creation of waste materials through various human activities such as manufacturing, construction, and daily consumption. Different countries have different levels of waste generation, with industrialized nations generally producing more waste than developing countries. However, waste generation is a global issue that affects all countries and requires effective management strategies.
Waste Management Strategies
Waste management strategies vary across countries depending on their resources and capabilities. Some countries prioritize recycling and waste reduction, while others rely heavily on landfilling or incineration. International cooperation and knowledge sharing are essential for developing sustainable waste management practices.
| Country | Major Waste Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| United States | Landfilling |
| China | Incineration |
| Germany | Recycling |
| Sweden | Waste-to-Energy |
These are just a few examples of waste management strategies employed by different countries. Each strategy has its own advantages and challenges, and no single approach is universally applicable.
However, the global waste economy also involves the trade of waste materials between countries. Some countries, such as the United States, export their waste to other countries for processing and disposal. This practice can have environmental and social consequences in the recipient countries, as they may lack the infrastructure and resources to handle the imported waste properly.
Overall, the global waste economy is a critical issue that requires international collaboration and innovative solutions. It is crucial to find sustainable waste management strategies that minimize environmental impact and promote a circular economy where waste is seen as a valuable resource rather than a burden.
Waste Export Regulations
Exporting waste from the United States to other countries is strictly regulated to ensure proper disposal and protect the environment both domestically and internationally. The export of certain types of waste is subject to various legal requirements and international agreements.
Basel Convention
The Basel Convention, adopted in 1989, is an international treaty that aims to control the transboundary movement and disposal of hazardous waste. The United States is a party to this convention, which sets out specific rules and guidelines for the export and import of hazardous waste.
Under the Basel Convention, hazardous waste can only be exported with the consent of the receiving country and in accordance with their domestic laws and regulations. Prior informed consent (PIC) must be obtained, and proper documentation must be provided, including details about the waste, its origin, and how it will be managed.
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
In addition to the Basel Convention, the export of non-hazardous waste is regulated by the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), a federal law in the United States. The RCRA ensures that non-hazardous waste is managed in an environmentally sound manner, whether it is exported or disposed of domestically.
Under the RCRA, anyone who intends to export non-hazardous waste must notify the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and obtain their consent. The waste must be properly characterized and documented to determine its classification and whether it can be exported. The EPA also conducts inspections and audits to verify compliance with the regulations.
Exceptions and Restrictions
While there are regulations in place to control waste exports, there are also exceptions and restrictions. Some waste materials, such as recyclable commodities, may be exported without prior consent, provided they meet certain conditions and are managed in an environmentally sound manner.
However, certain countries may have their own restrictions on waste imports, and exporters must be aware of these requirements to avoid any legal issues. Additionally, the United States has imposed bans on the export of certain types of waste, such as electronic waste, due to the potential environmental and health risks associated with their improper disposal.
Overall, waste export regulations play a crucial role in ensuring that waste is handled responsibly and that the environment is protected. By adhering to these regulations, the United States aims to prevent the dumping of waste in developing countries and promote sustainable waste management practices globally.
US Waste Export Statistics
The United States is one of the top waste-generating countries in the world, producing millions of tons of waste annually. However, not all of this waste remains within the country’s borders. In fact, the US has been known to export a significant portion of its waste to other countries.
According to recent statistics, the US exports approximately X million tons of waste each year. This waste includes various types, such as plastic, paper, electronic waste, and scrap metal. The main recipients of US waste exports are countries in Asia, particularly China, followed by countries in Southeast Asia.
Reasons for US Waste Export
There are several reasons why the US exports its waste to other countries. One of the main reasons is the lower cost of waste disposal in these countries. Many developing countries have lower labor costs and less stringent environmental regulations, making it more cost-effective for US waste to be processed and disposed of there.
Another reason is the lack of adequate infrastructure for waste management in the US. With limited landfill space and outdated recycling facilities, exporting waste becomes a convenient solution. Additionally, exporting waste can also be seen as a way to reduce domestic pollution levels and the burden on local communities.
Environmental and Ethical Concerns
While waste export may offer short-term benefits, it also raises significant environmental and ethical concerns. The transportation of waste over long distances contributes to carbon emissions and air pollution. Furthermore, the improper disposal or recycling of waste in recipient countries can lead to soil and water contamination.
From an ethical standpoint, exporting waste to countries with less stringent regulations can be seen as a form of environmental injustice. It can result in adverse health effects on the local population and further burden already vulnerable communities.
- The United States exports approximately X million tons of waste each year.
- The main recipients of US waste exports are countries in Asia, particularly China.
- Lower cost of waste disposal and lack of adequate infrastructure are the main reasons for US waste export.
- Waste export raises environmental concerns such as carbon emissions and soil contamination.
- Waste export can also be seen as an ethical issue, as it disproportionately affects vulnerable communities.
Controversies and Criticism
Exporting waste to other countries has been met with a considerable amount of controversies and criticism. Many environmentalists and activists argue that the practice not only contributes to global pollution but also exploits poorer nations.
One of the main criticisms is that the United States is exporting its waste to countries with less stringent environmental regulations. This means that the waste could potentially harm the local environment and the health of the people living in those countries.
Another concern is the carbon footprint associated with shipping waste overseas. Transporting waste over long distances requires significant amounts of energy and can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. This goes against the efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.
Furthermore, the export of waste can create a dependency on foreign countries for waste management. Developing nations that receive the waste may lack the resources and infrastructure to properly dispose of it, leading to long-term environmental and health issues.
In recent years, several incidents have highlighted the negative consequences of waste exports. For example, in 2018, China announced a ban on the import of certain types of waste, including plastic. This decision affected countries like the United States, which had been sending large amounts of plastic waste to China for recycling. Consequently, the ban led to an increase in landfill disposal and the search for alternative destinations for US waste.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| – Reduces landfill usage in the US | – Environmental pollution |
| – Supports recycling industries in other countries | – Exploitation of poorer nations |
| – Lower cost of waste disposal | – Carbon footprint of transporting waste |
| – Creates jobs in waste management sector | – Dependency on foreign countries for waste management |
In response to these controversies, some countries and international organizations have taken steps to address the issue of waste exports. For example, the Basel Convention, an international treaty, aims to regulate the transboundary movement of hazardous waste and ensure its environmentally sound management.
Overall, the export of waste from the United States to other countries has sparked heated debates and raised important environmental and ethical concerns. It is crucial for governments and individuals to work together to find sustainable solutions and reduce the negative impacts of waste exports.
Future Outlook and Solutions
As the global community becomes more aware of the environmental impact of waste disposal, there is an increasing push for countries to find sustainable solutions to their waste management. This includes reducing waste production, implementing efficient recycling programs, and finding alternative methods of disposal.
In the case of the United States, there are several initiatives and steps being taken to address the issue of waste export. One approach is the development of domestic recycling infrastructure and facilities. By investing in recycling infrastructure, the United States can reduce its reliance on exporting waste and instead process it domestically.
Another solution is the implementation of stricter regulations and policies on waste management. The United States can enforce stricter standards for waste disposal, encourage companies to reduce packaging waste, and promote sustainable practices. This would help reduce the amount of waste generated in the first place.
Furthermore, there is a need for increased international cooperation and collaboration to tackle the global waste problem. Countries need to work together to develop sustainable waste management systems, share best practices, and support each other in finding innovative solutions.
Education and awareness are also crucial in changing consumer behavior and promoting responsible waste disposal practices. By educating the public about the importance of waste reduction, recycling, and responsible consumption, individuals can make informed choices and contribute to a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, the future outlook for waste management in the United States and globally is promising. With increased awareness and efforts to find sustainable solutions, it is possible to reduce waste export and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Q&A:
Does the US export a lot of waste to other countries?
Yes, the US exports a significant amount of waste to other countries. In fact, it is one of the largest exporters of waste in the world.
Which countries does the US export its waste to?
The US exports its waste to various countries, including China, India, and Vietnam. These countries often import waste for recycling or disposal.
Why does the US export its waste to other countries instead of handling it domestically?
The US exports its waste to other countries because it can be more cost-effective to send waste abroad for recycling or disposal. Additionally, some countries may have the infrastructure in place to handle certain types of waste more efficiently.
Are there any negative consequences of the US exporting its waste to other countries?
Yes, there can be negative consequences of the US exporting its waste to other countries. Some importing countries may not have adequate regulations or infrastructure in place to properly handle the waste, leading to environmental and health risks. Additionally, the transport of waste over long distances contributes to carbon emissions and global pollution.