
Plastic pollution has become a pressing global concern in recent years, as the detrimental impact of plastic waste on the environment has become increasingly apparent. But have you ever wondered how long it takes for plastic to decompose? The answer may surprise you.
Plastic is a synthetic material that is designed to be durable and long-lasting. This durability is what makes plastic such a useful material for so many applications, from packaging to construction. However, it is also what makes plastic such a persistent pollutant in the environment.
On average, it takes hundreds of years for plastic to decompose. This means that every plastic bag, bottle, and straw you use will likely outlive you and several generations after you. This is a sobering thought, considering the sheer volume of plastic waste that is generated every day.
Plastic decomposition is a slow process, as it is not biodegradable like organic materials such as food waste or paper. Instead, plastic breaks down into smaller and smaller pieces over time, a process known as photodegradation. This means that even though plastic may appear to disappear, it never truly goes away.
So, the next time you reach for that plastic bag or disposable cup, think about the long-lasting impact it will have on the environment. Consider opting for reusable alternatives and contributing to the fight against plastic pollution. Together, we can work towards a future where plastic waste is a thing of the past.
- How Long Does Plastic Take to Decompose?
- The Impact of Plastic Pollution on the Environment
- The Different Types of Plastic and Their Decomposition Times
- 1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
- 2. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
- 3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- 4. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
- 5. PP (Polypropylene)
- 6. PS (Polystyrene)
- 7. Others
- Factors That Affect the Decomposition of Plastic
- The Consequences of Slow Plastic Decomposition
- Ways to Reduce Plastic Waste and Speed Up Decomposition
- The Importance of Proper Plastic Disposal and Recycling
- Q&A
- How long does it take for plastic to decompose?
- Why does plastic take so long to decompose?
- What are the environmental impacts of plastic decomposition?
- Are there any solutions to the problem of plastic decomposition?
- How can I reduce my use of plastic?
- Why is plastic decomposition important?
- How long does it take for plastic to decompose?
How Long Does Plastic Take to Decompose?
Plastic is known for its durability and long-lasting nature, which is why it has become such a prevalent material in our daily lives. However, this strength also means that plastic takes an incredibly long time to decompose. In fact, some types of plastic can take hundreds, if not thousands, of years to fully break down.
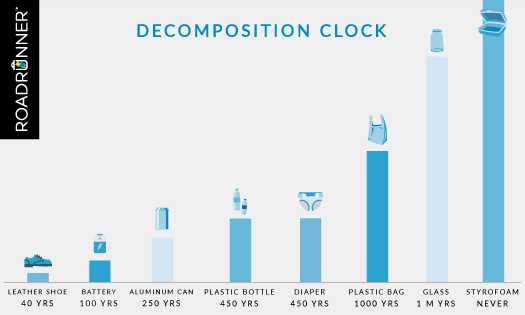
The exact length of time it takes for plastic to decompose depends on a variety of factors, including the type of plastic, the environmental conditions, and the size and thickness of the plastic item. For example, a thin plastic bag can take anywhere from 10 to 20 years to decompose, while a plastic bottle can take up to 450 years.
One of the primary reasons plastic takes so long to decompose is that most plastics are not biodegradable. Unlike organic materials, such as food or paper, plastics do not break down naturally and instead persist in the environment for an extended period of time.
Another factor that contributes to the slow decomposition of plastic is its resistance to natural processes like weathering and erosion. Plastics are designed to be highly resistant to water, air, and sunlight, which helps them maintain their structure and strength over long periods of time. However, this resistance also means that plastics do not easily degrade when exposed to the elements.
Additionally, the widespread use of plastic and improper disposal practices, such as littering and inadequate recycling, contribute to the accumulation of plastic waste in the environment. This further exacerbates the issue of plastic pollution and prolongs the decomposition process.
While efforts are being made to reduce plastic consumption and develop more sustainable alternatives, it is crucial to recognize the long-lasting impact that plastic waste can have on the environment. By reducing, reusing, and recycling plastic, we can help minimize the amount of plastic that ends up in landfills and oceans, ultimately reducing the time it takes for plastic to decompose.
It is important to raise awareness about the harmful effects of plastic pollution and work towards finding solutions to mitigate its long-term consequences. By making conscious choices and adopting eco-friendly habits, we can all play a part in preserving our environment for future generations.
The Impact of Plastic Pollution on the Environment
Plastic pollution has become a global environmental crisis, impacting the ecosystems and biodiversity of our planet. The widespread use of plastic products and the improper disposal of plastic waste have led to devastating consequences for the environment.
Plastics take hundreds of years to decompose, resulting in piles of plastic waste that accumulate in landfills, oceans, and natural habitats. This accumulation leads to severe consequences for marine life, as plastic debris can be mistaken for food and ingested by marine animals. This ingestion not only causes intestinal blockages but can also lead to the death of these animals.
Moreover, plastic pollution has a significant impact on terrestrial animals as well. Wild animals often confuse plastic waste for food, leading to malnutrition and starvation. Plastic pollution can also impact the reproductive abilities of certain species, further endangering their populations.
Plastic products and packaging also contribute to air and water pollution. The production and incineration of plastics release harmful chemicals and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. When plastics are not properly disposed of, they can leach chemicals into the soil and water, contaminating ecosystems and endangering both wildlife and human health.
The long-lasting nature of plastics and their widespread use mean that plastic pollution is not only an aesthetical problem but also a threat to the overall health of our planet. It is crucial that individuals, businesses, and governments take action to reduce plastic waste, promote recycling and sustainable alternatives, and create policies that mitigate the environmental impact of plastic pollution.
In conclusion, plastic pollution poses a grave threat to the environment, impacting ecosystems, biodiversity, and human health. It is imperative that we address this crisis by adopting sustainable practices and reducing our reliance on single-use plastics. By doing so, we can help protect our environment and secure a healthier future for generations to come.
The Different Types of Plastic and Their Decomposition Times
Plastic is a synthetic material that is used in a wide range of products due to its versatility and durability. However, it is also an environmental concern because of its slow decomposition rate. Different types of plastic have different decomposition times, with some taking hundreds of years to break down.
1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
PET is commonly used in food and beverage containers, as well as in polyester clothing and carpet fibers. It is estimated that it takes around 500 years for PET plastic to decompose in the environment. Recycling PET is important to reduce its impact on the environment.
2. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
HDPE is used in a variety of products, including bottles, containers, and plastic bags. It has a shorter decomposition time compared to PET, taking around 20-30 years to break down. Recycling HDPE is an effective way to reduce its environmental impact.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is commonly used in pipes, flooring, and electrical cables. It has a very long decomposition time, estimated to be around 100-1000 years. PVC recycling is important to prevent it from accumulating in the environment and releasing harmful chemicals.
4. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
LDPE is used in various products such as plastic bags, squeezable bottles, and coatings. It decomposes over a period of around 20-30 years. Promoting the recycling of LDPE can help reduce its environmental impact.
5. PP (Polypropylene)
PP is commonly used in packaging, ropes, and automotive parts. It takes around 30-40 years to decompose in the environment. Recycling PP can contribute to reducing its environmental footprint.
6. PS (Polystyrene)
PS is used in disposable food containers, insulation materials, and packaging foam. It can take up to 500 years to decompose. Proper disposal and increasing recycling efforts are essential to prevent PS from persisting in the environment.
7. Others

There are other types of plastic, such as polycarbonate (PC) and polyurethane (PU), which have long decomposition times ranging from 500 to 1000 years. Proper waste management and prioritizing recycling are crucial for minimizing the impact of these plastics on the environment.
| Plastic Type | Decomposition Time |
|---|---|
| PET | 500 years |
| HDPE | 20-30 years |
| PVC | 100-1000 years |
| LDPE | 20-30 years |
| PP | 30-40 years |
| PS | up to 500 years |
| Others | 500-1000 years |
It is important to remember that even though plastic may eventually decompose, it does not fully disappear. It breaks down into smaller pieces called microplastics, which continue to pose a threat to the environment and wildlife. Therefore, reducing plastic consumption, promoting recycling, and finding sustainable alternatives are crucial steps in combating plastic pollution.
Factors That Affect the Decomposition of Plastic
Although plastic is known for its long lifespan, several factors can influence the rate at which it decomposes. Understanding these factors can help us develop strategies to minimize plastic waste and its negative impact on the environment.
Type of plastic: Different types of plastics have varying decomposition rates. For example, some types of plastics are designed to be more durable and resistant to decomposition, while others break down relatively quickly. The most common types of plastic found in landfills, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, can take hundreds of years to decompose.
Environmental conditions: The environment in which plastic waste is located plays a significant role in its decomposition rate. Factors such as temperature, sunlight exposure, moisture, and oxygen availability can all impact how quickly plastic breaks down. Warmer temperatures and abundant sunlight generally speed up decomposition, while cooler temperatures and limited sunlight can slow it down.
Size and shape: The size and shape of plastic items also affect decomposition. Smaller plastic particles have a larger surface area relative to their volume, allowing microorganisms and enzymes to break them down more efficiently. In contrast, larger plastic objects may take longer to decompose due to their bulk and reduced surface area.
Chemical additives: Many plastic products contain additives that can influence decomposition rates. For example, some plastics incorporate stabilizers, flame retardants, or plasticizers to enhance their properties. These additives can both slow down or accelerate decomposition, depending on their composition and concentration.
Proximity to other materials: Other materials present near plastic waste can impact its decomposition rate. For instance, if plastic is buried deep in a landfill without access to oxygen, decomposition may be significantly slower. Additionally, the presence of decomposing organic materials, such as food waste, can accelerate plastic degradation by providing a food source for microorganisms.
Human intervention: The actions and choices of individuals and society as a whole can greatly affect the decomposition of plastic. Proper waste management, recycling, and reducing plastic consumption can all contribute to slowing down the accumulation of plastic waste in the environment. On the other hand, improper disposal and littering can exacerbate the problem and lead to increased plastic pollution.
In conclusion, the decomposition of plastic is influenced by various factors, including the type of plastic, environmental conditions, size and shape, chemical additives, proximity to other materials, and human intervention. By understanding these factors, we can make more informed decisions and take steps to reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste.
The Consequences of Slow Plastic Decomposition
Plastic pollution is a significant environmental problem that affects ecosystems worldwide. One of the main reasons for this is the slow decomposition rate of plastic. Unlike other materials like paper or food waste, plastic can take hundreds of years to fully break down.
This slow decomposition has serious consequences for the environment. As plastic accumulates in landfills and bodies of water, it can have detrimental effects on wildlife. Marine species such as sea turtles, dolphins, and birds often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement. This can result in suffocation, starvation, and even death for these animals.
The presence of plastic particles in the ocean also affects the entire marine food chain. Small pieces of plastic, known as microplastics, are consumed by tiny organisms, which are then consumed by larger fish and marine mammals. This process, known as bioaccumulation, can lead to a build-up of toxins in the bodies of these animals, posing a threat to their health and survival.
In addition to harming wildlife, plastic pollution also impacts human health. Some chemicals used in the production of plastics, such as bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, have been linked to various health issues, including cancer, reproductive problems, and developmental disorders. When plastic waste breaks down into smaller particles, these chemicals can leach into the environment and contaminate water sources and food supplies.
Furthermore, the economic consequences of plastic pollution are significant. The cost of cleaning up plastic waste, restoring ecosystems, and mitigating the impact of plastic pollution on industries such as tourism and fishing can be immense. Additionally, the degradation of natural landscapes and the loss of biodiversity can have long-term economic implications for communities reliant on these resources.
In conclusion, the slow decomposition of plastic has profound consequences for the environment, wildlife, human health, and the economy. It is crucial that we take immediate action to reduce plastic waste, promote recycling and eco-friendly alternatives, and raise awareness about the importance of responsible plastic consumption. Only then can we mitigate the impacts of plastic pollution and preserve the planet for future generations.
Ways to Reduce Plastic Waste and Speed Up Decomposition
Plastic pollution is a major environmental concern, but there are several ways we can reduce plastic waste and help speed up the decomposition process:
- Reduce Single-Use Plastic: One of the most effective ways to reduce plastic waste is to avoid using single-use plastics such as plastic bags, straws, cutlery, and bottles. Instead, opt for reusable alternatives like tote bags, stainless steel straws, and refillable water bottles.
- Recycle Properly: Make sure to separate your plastic waste and recycle it properly. Check the recycling guidelines in your area and follow them accordingly. This will help maximize the chances of plastic being recycled and prevent it from ending up in landfills or polluting oceans.
- Choose Biodegradable Alternatives: Look for products that are made from biodegradable materials or have shorter decomposition times. For example, opt for biodegradable shopping bags made from cornstarch or compostable plates and cutlery.
- Avoid Microplastics: Microplastics are tiny plastic particles that are harmful to the environment and can take centuries to decompose. Avoid using products that contain microbeads or microplastics, such as certain exfoliating scrubs and toothpaste.
- Support Plastic-Free Initiatives: Support initiatives that aim to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable practices. This can include advocating for plastic bag bans, participating in beach clean-ups, or supporting brands that use eco-friendly packaging.
- Compost Organic Waste: If you have a composting system, ensure that only organic waste goes into it. Plastic contaminates compost and slows down the decomposition process. By keeping plastic out of your compost, you can speed up the decomposition of organic materials.
- Spread Awareness: Educate others about the harmful effects of plastic pollution and the importance of reducing plastic waste. Spread awareness through social media, community events, or by discussing the topic with friends and family.
By implementing these measures and encouraging others to do the same, we can make a significant impact in reducing plastic waste and speeding up the decomposition of plastics.
The Importance of Proper Plastic Disposal and Recycling
Proper plastic disposal and recycling are crucial for reducing the negative impact of plastics on our environment. Plastic waste is a major contributor to pollution, with an estimated 8 million metric tons of plastic entering our oceans every year. This poses a serious threat to marine life and ecosystems.
When plastic is not disposed of correctly, it can take hundreds of years to decompose, releasing harmful chemicals into the soil and water. These chemicals can contaminate our food, water sources, and even the air we breathe, leading to serious health issues for humans and animals.
Recycling plastic is one of the most effective ways to reduce plastic waste. It helps to conserve resources, reduce energy consumption, and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. By recycling plastic, we can transform it into new products and reduce the demand for virgin plastic production.
However, it is not enough to simply toss plastic into a recycling bin. Proper sorting and preparation are essential to ensure that plastic can be effectively recycled. Different types of plastics require different recycling processes, and contamination can render the recycling process ineffective.
Additionally, not all types of plastic are easily recyclable. Some plastics, such as single-use water bottles or plastic bags, are often made from low-quality plastic that is more difficult to recycle. Reduce the use of such plastics and opt for reusable alternatives whenever possible.
Ultimately, proper plastic disposal and recycling require a collective effort. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in promoting responsible plastic waste management. By properly disposing of and recycling plastic, we can protect our environment, reduce pollution, and preserve natural resources for future generations.
Q&A
How long does it take for plastic to decompose?
Plastic takes hundreds of years to decompose, with some estimates suggesting it can take up to 1,000 years.
Why does plastic take so long to decompose?
Plastic takes a long time to decompose because it is made from polymers that are very resistant to natural processes of degradation.
What are the environmental impacts of plastic decomposition?
Plastic decomposition has several negative environmental impacts, including releasing harmful chemicals into the soil and water, and endangering marine life.
Are there any solutions to the problem of plastic decomposition?
Yes, there are several solutions to the problem of plastic decomposition, including recycling, reducing plastic use, and finding alternative materials.
How can I reduce my use of plastic?
You can reduce your use of plastic by using reusable bags, bottles, and containers, avoiding single-use plastics, and recycling whenever possible.
Why is plastic decomposition important?
Plastic decomposition is important because plastic waste is causing significant harm to the environment. It takes a very long time for plastic to decompose, and during that time it can release harmful chemicals and pollutants into the soil and water. By understanding how long it takes for plastic to decompose, we can better understand the impact of our plastic waste and work towards reducing it.
How long does it take for plastic to decompose?
The time it takes for plastic to decompose varies depending on the type of plastic. Some plastic items, such as plastic bags, can take anywhere from 10 to 1000 years to decompose. Other types of plastic, such as plastic bottles, can take up to 450 years to decompose. It’s important to note that even when plastic does decompose, it breaks down into smaller pieces called microplastics, which can still have harmful effects on the environment.