
Trees are vital for the health and sustainability of our planet. They provide us with oxygen, absorb carbon dioxide, and support a wide range of ecosystems. However, not all countries are blessed with abundant forests and lush green landscapes.
One country that stands out in terms of having the fewest trees is Somalia. Located in the Horn of Africa, Somalia has been facing numerous environmental challenges for decades, including deforestation and desertification.
The lack of trees in Somalia is primarily due to several factors, such as civil war, illegal logging, and droughts. The ongoing conflict in the country has disrupted environmental conservation efforts, leading to the uncontrolled cutting down of trees for fuel and construction purposes.
The impact of deforestation in Somalia is devastating, as it not only results in the loss of habitat for wildlife but also contributes to soil erosion and desertification. The absence of trees makes the land more vulnerable to arid conditions, causing frequent droughts and scarcity of water resources.
Efforts are being made to address the issue of deforestation in Somalia, including reforestation projects and raising awareness about sustainable land management practices. However, these initiatives face numerous challenges in the midst of ongoing conflicts and political instability.
The situation in Somalia serves as a stark reminder of the importance of trees and the need for global efforts to preserve and restore forests. It highlights the delicate balance between human activities and the environment, emphasizing the urgent need to protect our natural resources for future generations.
- Countries with the Fewest Trees
- Arid Regions with Sparse Vegetation
- Another example is the Atacama Desert in South America
- Deforestation and Environmental Degradation
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Soil Erosion
- Climate Change
- Impact on Wildlife and Biodiversity
- Loss of Habitat
- Disrupted Food Chain
- Conservation Efforts and Reforestation Programs
- Economic and Social Consequences
- International Collaborations and Initiatives
- Question-answer:
- Which country has the fewest trees?
- Why does Iceland have the fewest trees?
- What is the percentage of tree cover in Iceland?
- What are the environmental consequences of having few trees in Iceland?
- Are there any efforts to increase tree planting in Iceland?
- Which country has the fewest trees?
- Why does Qatar have the fewest trees?
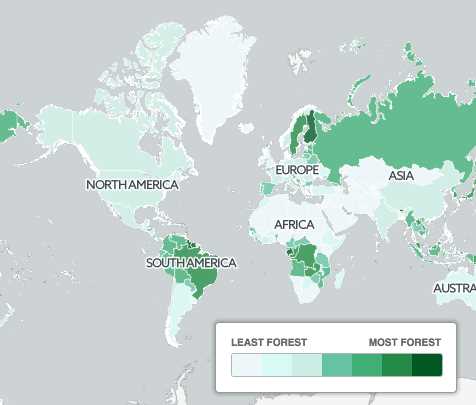
Countries with the Fewest Trees
Forests play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of the planet, providing habitat for wildlife, producing oxygen, and regulating climate. However, there are several countries around the world that have a significantly low percentage of land covered by trees.
One such country is Haiti, which has been severely deforested due to unsustainable agriculture practices, charcoal production, and logging. It is estimated that less than 2% of Haiti’s land is covered by trees, making it one of the countries with the fewest trees in the world.
Another country with a low tree cover is Iceland. Despite its name, Iceland has a harsh climate that prevents the growth of many trees. Less than 1% of Iceland’s land is covered by forests, and the majority of these are small and young. The lack of trees in Iceland has significant implications for soil erosion and biodiversity.
In addition, the Maldives, a small island nation in the Indian Ocean, is also facing a severe lack of tree cover. With limited land area and rising sea levels, the Maldives has been prioritizing development and infrastructure over reforestation efforts. As a result, less than 1% of the Maldives’ land is covered by trees.
These countries, along with others like Bermuda, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates, serve as reminders of the importance of preserving and protecting forests worldwide. Deforestation not only contributes to climate change but also threatens the livelihoods of local communities and the survival of countless species.
Efforts are being made globally to combat deforestation and promote reforestation, but it will require collective action and sustainable practices to reverse the trend and increase tree cover in these countries with the fewest trees.
Conclusion
While there are several countries with a low percentage of tree cover, Haiti, Iceland, and the Maldives are among the countries with the fewest trees. Taking steps to preserve and restore forests in these countries is vital for the well-being of the planet and future generations.
Arid Regions with Sparse Vegetation
Arid regions with sparse vegetation refer to areas with extremely dry climates and low plant cover. These regions are characterized by limited rainfall, high evaporation rates, and insufficient water resources to support abundant plant life. As a result, the vegetation in these areas is scarce and mostly consists of drought-resistant plants and shrubs.
One example of an arid region with sparse vegetation is the Sahara Desert in Africa, known as the largest hot desert in the world. The Sahara experiences extremely high temperatures and receives very little rainfall, leading to the presence of only a few specialized plant species adapted to survive in such harsh conditions. These plants have features like deep root systems to tap into underground water sources and waxy coatings on their leaves to minimize water loss through evaporation.
Another example is the Atacama Desert in South America
The Atacama Desert is considered one of the driest places on Earth, with some parts of the desert not receiving any rainfall for several years. The aridity of this region is attributed to a combination of factors, including the cold ocean currents that prevent moisture from reaching the land and the presence of the Andes Mountains, which create a rain shadow effect. As a result, the Atacama Desert has very few plants and is often compared to Mars due to its similarity in terms of extreme dryness and lack of vegetation.
In addition to deserts, other arid regions with sparse vegetation can be found in parts of Australia, such as the Great Victoria Desert, the Arabian Peninsula, including the Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter), and the high-altitude regions of Tibet in Asia. These areas are characterized by unique ecosystems adapted to survive in extremely harsh and dry conditions.
In conclusion, arid regions with sparse vegetation are fascinating landscapes that showcase the resilience and adaptability of plant life to survive in extreme dryness. These regions are home to plants specially adapted to conserve water and make the most of limited resources, creating unique and diverse ecosystems.
Deforestation and Environmental Degradation
Deforestation is the process of clearing or removing forests or trees from a particular area. It has become a major environmental concern due to its negative effects on the ecosystem and climate. Deforestation contributes to environmental degradation in several ways:
Loss of Biodiversity
Forests are home to a wide range of plant and animal species. When trees are cut down, these species lose their habitats, leading to a loss of biodiversity. The destruction of forests disrupts food chains and reduces the availability of resources for both animal and human populations.
Soil Erosion
Trees serve as a protective cover for the soil, preventing erosion. When forests are cleared, the soil becomes exposed to rain and wind, leading to accelerated erosion. The removal of trees also reduces the ability of the soil to retain water, increasing the risk of drought and desertification.
Climate Change
Forests act as important carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Deforestation releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the air, contributing to the greenhouse effect and climate change. The loss of trees also reduces the evaporation of water, leading to changes in local and regional weather patterns.
Deforestation and environmental degradation are closely linked, as the destruction of forests has far-reaching consequences for the planet. It is crucial to address these issues and promote sustainable practices to protect and restore our forests for the well-being of current and future generations.
Impact on Wildlife and Biodiversity
The country with the fewest trees faces significant challenges when it comes to wildlife and biodiversity. The lack of trees directly affects the habitat and food sources available for various animal species, resulting in a decline in their populations. It also disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to negative consequences for biodiversity.
Loss of Habitat
Trees provide essential habitats for a wide range of wildlife, including birds, mammals, insects, and reptiles. They offer shelter, nesting sites, and protection from predators. Without trees, these animals lose crucial habitats they depend on for survival. The loss of habitat can lead to a decline in populations and, in some cases, even extinction.
Disrupted Food Chain

Trees play a vital role in supporting the food chain by providing food and resources for various organisms. They produce fruits, nuts, and seeds that serve as a food source for many animals. Without trees, the availability of these food sources decreases, impacting the entire food chain. This disruption can result in a decline in predator and prey populations, affecting the overall balance of ecosystems.
| Unable to Adapt | Loss of Biodiversity |
|---|---|
| The absence of trees limits the ability of wildlife species to adapt and survive in changing environmental conditions. Trees offer shelter from extreme temperatures and provide protection during harsh weather. Without this natural refuge, animals are more susceptible to the impacts of climate change and other environmental stresses. | The decline in tree cover directly contributes to a loss of biodiversity. Trees support a vast array of plant and animal species, including insects, birds, and mammals. When trees disappear, many of these species lose their habitats and food sources, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and ecological imbalances. |
In conclusion, the country with the fewest trees experiences a negative impact on wildlife and biodiversity. The loss of habitat, disrupted food chains, inability to adapt, and loss of biodiversity are all significant consequences. It is essential to recognize the importance of trees in supporting diverse ecosystems and take actions to promote reforestation and conservation efforts.
Conservation Efforts and Reforestation Programs

Despite being the country with the fewest trees, efforts are being made to address the issue of deforestation and promote reforestation in [country name]. Various conservation organizations and government initiatives have been implemented to protect and restore the country’s tree cover.
One of the main goals of these conservation efforts is to raise awareness about the importance of trees and forests for the environment. Educational campaigns and outreach programs are being conducted to teach local communities about the benefits of trees and the impacts of deforestation.
In addition to awareness-raising activities, reforestation programs have been established to restore the country’s tree cover. These programs involve planting native tree species in deforested areas and providing them with the necessary care and maintenance to ensure their survival.
The government has also implemented regulations to protect existing forests and prevent further deforestation. These regulations include stricter logging practices, limits on land conversion for agriculture, and penalties for illegal logging activities.
Collaborations between the government, conservation organizations, and local communities are crucial for the success of these conservation efforts. Through partnerships and community engagement, sustainable solutions can be developed to address the country’s deforestation challenges.
- Conservation organizations are working on creating protected areas and establishing sustainable forest management practices.
- Community-led initiatives are being encouraged, where local people are involved in tree planting and forest protection activities.
- Efforts are being made to promote agroforestry, which combines agricultural activities with tree planting to improve soil fertility and provide a sustainable source of income.
- International collaborations and financial assistance are sought to support large-scale reforestation projects and capacity-building efforts.
By implementing these conservation efforts and reforestation programs, [country name] aims to restore its tree cover and mitigate the environmental impacts of deforestation. The goal is to create a more sustainable future for the country and protect its unique biodiversity.
Economic and Social Consequences
The country with the fewest trees faces a number of economic and social consequences as a result of the lack of vegetation.
One of the most significant economic impacts is the loss of income from forestry-related industries. Without a significant tree population, the country is unable to benefit from timber production, which can be a valuable source of revenue. Additionally, industries that rely on wood as a raw material, such as furniture manufacturing, may struggle to obtain a sustainable supply.
The lack of trees also has a negative impact on tourism, as many travelers are attracted to destinations with lush forests and natural beauty. Without an abundance of trees and green spaces, the country may struggle to attract tourists, resulting in a loss of revenue from the hospitality industry.
Furthermore, the absence of trees can lead to environmental and social issues. Trees play a crucial role in regulating the local climate, providing shade, and reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Without trees, the country may experience higher temperatures, increased air pollution, and a decline in overall air quality. This can have serious health implications for residents, leading to respiratory issues and other related illnesses.
Socially, the lack of trees can also impact the quality of life for individuals living in the country. Trees provide a range of benefits, such as providing habitat for wildlife, contributing to biodiversity, and offering recreational spaces for communities to enjoy. Without trees, the natural beauty and ecological balance of the country may be compromised, affecting the overall well-being and happiness of its residents.
In conclusion, the country with the fewest trees faces significant economic and social consequences. From the loss of income from forestry-related industries to the impact on tourism, as well as environmental and social issues, the absence of trees has far-reaching implications. It is crucial for the country to prioritize reforestation efforts and sustainable forestry practices to mitigate these consequences and ensure a more prosperous and sustainable future.
International Collaborations and Initiatives
Addressing the urgent need to combat deforestation and promote reforestation, countries around the world have come together to form international collaborations and initiatives. These efforts aim to share knowledge, resources, and technologies to protect and restore forests globally, including in countries with the fewest trees.
One such collaboration is the Forest Carbon Partnership Facility (FCPF), which brings together governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector to support countries in reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. Through financial incentives and technical assistance, the FCPF helps countries develop and implement strategies for sustainable forest management.
Another key initiative is the Bonn Challenge, a global effort to restore 350 million hectares of deforested and degraded land by 2030. Led by governments, the Bonn Challenge encourages countries to make ambitious commitments to forest landscape restoration and provides a platform for international collaboration and knowledge sharing.
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) also plays a crucial role in fostering international collaborations to address deforestation. The REDD+ initiative, a mechanism under the UNFCCC, aims to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation while promoting sustainable forest management and enhancing carbon stocks.
Collaborations and initiatives like these are essential for tackling deforestation and promoting reforestation worldwide. By working together, countries can leverage their collective expertise and resources to combat the alarming decline in global forest cover and ensure a sustainable future for our planet.
Question-answer:
Which country has the fewest trees?
The country with the fewest trees is Iceland.
Why does Iceland have the fewest trees?
Iceland has the fewest trees because of its harsh climate and volcanic activity, which make it difficult for trees to grow.
What is the percentage of tree cover in Iceland?
The percentage of tree cover in Iceland is less than 1%, one of the lowest in the world.
What are the environmental consequences of having few trees in Iceland?
The environmental consequences of having few trees in Iceland include soil erosion, decreased biodiversity, and reduced carbon sequestration.
Are there any efforts to increase tree planting in Iceland?
Yes, there are efforts to increase tree planting in Iceland through government initiatives and reforestation projects, but it is a challenging task due to the harsh conditions.
Which country has the fewest trees?
The country with the fewest trees is Qatar. This small country in the Middle East has very limited vegetation due to its arid climate and lack of water sources.
Why does Qatar have the fewest trees?
Qatar has the fewest trees mainly because of its arid climate and scarce water sources. The country’s hot and dry conditions make it difficult for trees to survive and thrive. Additionally, Qatar has a very limited water supply, which further limits the growth of trees and other vegetation.