
The current linear economic model, based on the principle of “take, make, dispose,” is proving to be unsustainable. The overexploitation of natural resources and the accumulation of waste have led to serious environmental and social problems. To address these challenges, the concept of a circular economy has emerged as a viable solution.
A circular economy aims to minimize waste, reduce the consumption of natural resources, and promote the reuse, repair, and recycling of products. It is a regenerative system that aims to keep materials and products in use for as long as possible, while also creating new business opportunities and economic growth. The European Union has recognized the importance of transitioning to a circular economy and has developed a comprehensive Circular Economy Action Plan.
The Circular Economy Action Plan sets out a roadmap for achieving a sustainable and resource-efficient economy. It focuses on key areas such as sustainable production and consumption, waste management, and the design of products and packaging. The plan also aims to promote innovation, investment, and the development of new business models that support circularity.
Key steps outlined in the Circular Economy Action Plan include setting ambitious targets for waste reduction, promoting the use of recycled materials, and supporting sustainable product design and eco-labeling. The plan also emphasizes the importance of digitalization and the transition to a digital circular economy, where data and technology play a central role in optimizing resource use and supply chains.
By implementing the Circular Economy Action Plan, the European Union aims to reduce its environmental impact, create jobs, and foster sustainable economic growth. It recognizes that the transition to a circular economy requires the involvement and collaboration of various stakeholders, including businesses, governments, and consumers.
Overall, the Circular Economy Action Plan sets out a comprehensive framework for transforming our current linear economic model into a more sustainable and resource-efficient system. It provides a roadmap for achieving a future where waste is minimized, resources are used responsibly, and economic prosperity is achieved in harmony with the environment.
- Circular Economy Action Plan: Key Steps for a Sustainable Future
- The Necessity of a Circular Economy
- Understanding the Circular Economy Concept
- Policy Framework for Transitioning to a Circular Economy
- 1. Legislation and regulations
- 2. Economic incentives
- 3. Education and awareness
- 4. Research and innovation
- 5. Collaboration and partnerships
- Encouraging Sustainable Production and Consumption
- Enhancing Resource Efficiency and Waste Management
- Investing in Research and Innovation
- Q&A:
- What is the Circular Economy Action Plan?
- What are the key steps of the Circular Economy Action Plan?
- What are the benefits of a circular economy?
- How does the Circular Economy Action Plan contribute to sustainable development?
- How can individuals contribute to the circular economy?
- What is the Circular Economy Action Plan?
- What are the key steps of the Circular Economy Action Plan?
Circular Economy Action Plan: Key Steps for a Sustainable Future
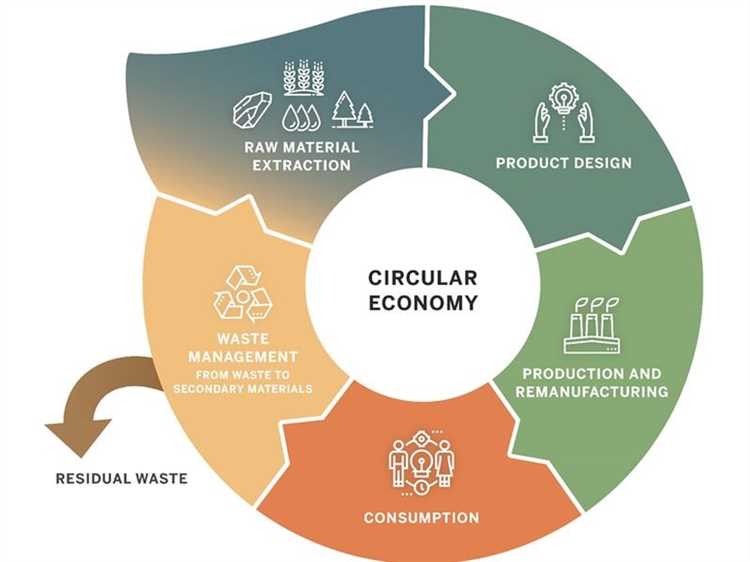
The circular economy is a crucial concept in achieving sustainability and reducing waste in our society. By adopting a circular economy approach, we can transition from the traditional linear model of take-make-dispose to a system that promotes resource efficiency and circularity.
To pave the way for a sustainable future, the Circular Economy Action Plan outlines key steps that need to be taken. These steps include:
- Promoting sustainable product design: Encouraging the development of products that are designed for durability, repairability, and recyclability. This involves incorporating eco-design principles and implementing standards to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
- Transitioning to a regenerative and low-carbon economy: Shifting towards renewable energy sources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This includes promoting the use of renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and investing in sustainable infrastructure.
- Emphasizing resource efficiency and waste reduction: Implementing measures to reduce waste generation and promote the efficient use of resources. This involves implementing recycling and waste management strategies, promoting the reuse of materials, and encouraging practices such as remanufacturing and refurbishment.
- Creating a sustainable and fair food system: Promoting sustainable agriculture, reducing food waste, and ensuring equitable access to nutritious and safe food. This includes supporting organic farming practices, promoting local and seasonal food production, and implementing measures to reduce food waste throughout the supply chain.
- Fostering circular business models and innovative solutions: Encouraging the adoption of circular business models that promote resource efficiency and reduce waste. This includes supporting startups and innovative businesses that develop sustainable products and services, as well as fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Improving knowledge and awareness: Increasing awareness and understanding of the circular economy among businesses, consumers, and policymakers. This involves raising public awareness, providing education and training programs, and sharing best practices and success stories.
By following these key steps outlined in the Circular Economy Action Plan, we can work towards a sustainable future where resources are used efficiently, waste is minimized, and the environment is protected. It is crucial for governments, businesses, and individuals to collaborate and take action to make the circular economy a reality.
The Necessity of a Circular Economy
A circular economy is crucial for achieving a sustainable future. The traditional linear economy, which is based on a take-make-dispose model, is no longer viable due to its significant negative impacts on the environment and limited availability of resources.
In a circular economy, the goal is to keep products, materials, and resources in use for as long as possible by maximizing their value. This is achieved through practices such as recycling, reusing, and repairing. By adopting a circular economy approach, we can minimize waste, reduce the extraction of virgin resources, and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
One of the key advantages of a circular economy is its potential to generate economic growth while also addressing social and environmental challenges. It fosters innovation by encouraging the redesign of products and the development of new business models that prioritize resource efficiency and sustainability.
Implementing a circular economy requires collaboration from various stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and consumers. Governments can play a crucial role by enacting policies that support circularity, such as promoting eco-design, creating incentives for recycling, and implementing waste reduction targets. Businesses can contribute by adopting circular practices throughout their supply chains, exploring new business models, and educating consumers about the importance of the circular economy. Consumers can participate by making conscious purchasing decisions, opting for products that are designed for durability and recyclability, and practicing responsible disposal.
By transitioning to a circular economy, we can not only reduce waste and preserve natural resources but also create a more sustainable and prosperous future for generations to come. It is an essential step towards achieving a greener and more resilient planet.
| Advantages of a Circular Economy | Examples |
|---|---|
| Reduces waste and landfill | Recycling plastic bottles into new products |
| Conserves natural resources | Reusing water in industrial processes |
| Creates new job opportunities | Repairing and refurbishing electronic devices |
| Reduces greenhouse gas emissions | Using renewable energy sources in manufacturing |
Understanding the Circular Economy Concept
The circular economy concept is a sustainable approach to economic development that aims to minimize waste and optimize resource usage. Unlike the traditional linear economy model, which follows a “take-make-dispose” approach, the circular economy seeks to keep resources in use for as long as possible, extracting the maximum value from them, and then recovering and regenerating them at the end of their life cycle.
The key principles of the circular economy include:
- Design for longevity: Products and systems should be designed to last, using durable materials and components that can be easily repaired or upgraded.
- Closed-loop recycling: Materials should be recycled and reused to create new products, minimizing the need for extracting and processing virgin resources.
- Resource efficiency: Energy and raw material inputs should be minimized through more efficient production processes and the use of renewable energy sources.
- Product life extension: Products should be designed to have a longer life cycle through measures such as product sharing, renting, and refurbishing.
- Regenerative systems: The circular economy aims to create systems that regenerate natural resources and support ecosystem health and biodiversity.
The benefits of adopting a circular economy approach are numerous:
- Resource preservation: By keeping resources in use for longer and promoting recycling, the circular economy helps conserve natural resources and reduces the need for extraction.
- Waste reduction: By minimizing waste and encouraging reuse and recycling, the circular economy reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills and incinerators, thereby reducing environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Cost savings: Adopting circular economy principles can lead to cost savings by reducing the need for raw materials, lowering energy consumption, and minimizing waste management costs.
- Economic growth: The circular economy can stimulate economic growth by creating new job opportunities, fostering innovation, and promoting sustainable business models.
- Resilience: By diversifying supply chains and reducing reliance on scarce resources, the circular economy enhances economic and environmental resilience.
In conclusion, embracing the circular economy concept offers a promising pathway towards a sustainable future, where resources are used more efficiently, waste is minimized, and economic growth is decoupled from resource consumption.
Policy Framework for Transitioning to a Circular Economy
Transitioning to a circular economy requires a comprehensive policy framework that addresses key challenges and provides the necessary support for businesses and consumers. The following elements are essential for a successful transition:
1. Legislation and regulations
The government should enact legislation and regulations that promote circular practices and discourage linear ones. This could include setting recycling targets, implementing extended producer responsibility programs, and phasing out single-use plastics. Clear regulations and standards will provide businesses with the necessary guidance and incentives to adopt circular models.
2. Economic incentives
Implementing economic incentives such as tax breaks, grants, and subsidies can encourage businesses to adopt circular practices. This can include tax incentives for recycling and reusing materials, grants for research and development of circular technologies, and subsidies for transitioning to resource-efficient production processes. It is important for governments to create a favorable economic environment that rewards circularity.
3. Education and awareness
Education and awareness programs play a crucial role in transitioning to a circular economy. Governments should invest in public campaigns and educational initiatives that promote the benefits of circular practices and provide guidance on how individuals and businesses can participate. By raising awareness and providing knowledge, governments can facilitate the adoption of circular behaviors and practices.
4. Research and innovation
Investing in research and innovation is essential for developing new technologies and business models that support circularity. Governments should allocate funding for research projects that focus on developing sustainable materials, waste reduction techniques, and innovative recycling methods. By supporting research and innovation, governments can facilitate the development of new solutions that enable the transition to a circular economy.
5. Collaboration and partnerships
Transitioning to a circular economy requires collaboration and partnerships between governments, businesses, and civil society organizations. Governments should facilitate dialogue and cooperation by establishing platforms for knowledge exchange and collaboration. Building partnerships can help address common challenges and leverage resources to accelerate the transition to a circular economy.
| Policy Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Legislation and regulations | Enacting laws and regulations that promote circular practices and discourage linear ones. |
| Economic incentives | Implementing tax breaks, grants, and subsidies to encourage businesses to adopt circular practices. |
| Education and awareness | Investing in public campaigns and educational initiatives to raise awareness about circular practices. |
| Research and innovation | Allocating funding for research projects that focus on developing sustainable solutions. |
| Collaboration and partnerships | Facilitating dialogue and cooperation between governments, businesses, and civil society organizations. |
Encouraging Sustainable Production and Consumption
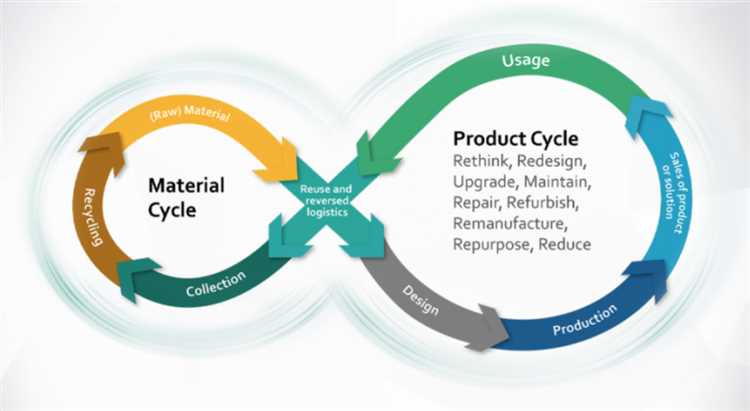
The key to achieving a sustainable future lies in encouraging both sustainable production and consumption. This means shifting towards a circular economy model where resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
One way to encourage sustainable production is to promote eco-design principles. This involves designing products and services with the environment in mind, considering the entire lifecycle of a product from raw materials extraction to disposal. By incorporating these principles, companies can minimize the environmental impact of their products and make them easier to recycle or reuse.
Another strategy is to promote sustainable business practices, such as resource efficiency and green procurement. By optimizing production processes and reducing resource consumption, companies can minimize waste and energy use, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits. Additionally, supporting green procurement practices can drive demand for sustainable products and encourage suppliers to adopt more sustainable practices.
Encouraging sustainable consumption involves raising awareness among consumers about the importance of choosing sustainable products and services. Providing information and education about the environmental impact of different products can help consumers make informed choices. Additionally, implementing incentives, such as tax breaks or subsidies, for sustainable products can incentivize consumers to choose more sustainable options.
Collaboration between all stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and consumers, is crucial for encouraging sustainable production and consumption. Governments can create policies and regulations that promote sustainability, while businesses and consumers can work together to implement and support these initiatives. By working towards a circular economy and embracing sustainable production and consumption practices, we can create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Enhancing Resource Efficiency and Waste Management

Enhancing resource efficiency and waste management is a crucial step towards a sustainable future. In order to achieve a circular economy, it is essential to optimize the use of resources and minimize waste generation.
One way to enhance resource efficiency is through recycling and reusing materials. Recycling reduces the need to extract new raw materials and helps conserve energy. It also reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills or incinerators.
Another important aspect of resource efficiency is improving product design and manufacturing processes. By designing products with recyclability and reusability in mind, we can ensure that materials can be easily recovered and reintroduced into the production cycle.
Waste management is equally important in achieving a circular economy. Proper waste management involves sorting and separating different types of waste to enable better recycling and treatment. It also includes promoting responsible consumption and reducing the generation of waste through eco-design and product innovation.
In addition, waste management strategies should focus on converting waste into valuable resources through techniques such as composting and anaerobic digestion. These processes can turn organic waste into nutrient-rich compost and biogas, which can be used for energy generation.
Furthermore, the implementation of extended producer responsibility schemes can help incentivize manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire life cycle of their products. This includes designing products that are easier to repair, reuse, or recycle, as well as establishing collection and recycling systems.
To enhance resource efficiency and waste management, it is crucial to involve all stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and consumers. Collaboration and cooperation are key to developing and implementing effective strategies and policies that promote the circular economy.
- Promote recycling and reuse
- Improve product design and manufacturing processes
- Implement waste sorting and treatment
- Encourage responsible consumption
- Convert waste into valuable resources
- Establish extended producer responsibility schemes
- Foster collaboration among stakeholders
By enhancing resource efficiency and waste management, we can move towards a more sustainable future and create a circular economy that maximizes the value of resources while minimizing environmental impact.
Investing in Research and Innovation
Investing in research and innovation is crucial for advancing towards a sustainable future. By supporting new ideas, technologies, and processes, we can accelerate the transition to a circular economy. Research plays a key role in providing the necessary evidence-based insights and knowledge to guide decision-making and policy formation.
Through increased investment in research, we can unlock innovative solutions to pressing environmental challenges. This includes finding ways to reduce waste, develop sustainable materials, improve recycling technologies, and enhance resource efficiency. Innovation is essential for transforming traditional linear production models into circular systems that prioritize reuse, repair, and recycling.
Investment in research and innovation also promotes economic growth and job creation. By fostering a culture of innovation, we can stimulate entrepreneurship and create new industries centered around sustainable practices. This not only benefits the environment but also contributes to the overall prosperity and well-being of society.
Additionally, research and innovation foster collaboration among academics, scientists, businesses, and policymakers. By working together, we can share knowledge, best practices, and create networks that facilitate the exchange of ideas. This collaborative approach is essential for addressing complex challenges and developing comprehensive solutions.
Ultimately, investing in research and innovation supports the development and implementation of evidence-based policies and strategies. It enables us to make informed decisions and take proactive measures towards building a sustainable future. By leveraging the power of research and innovation, we can create a circular economy that promotes environmental sustainability, economic growth, and social well-being.
Q&A:
What is the Circular Economy Action Plan?
The Circular Economy Action Plan is a comprehensive strategy developed by the European Commission to promote sustainability and the efficient use of resources. It aims to transition from the traditional linear economy model of “take-make-dispose” to a circular economy model that focuses on reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling.
What are the key steps of the Circular Economy Action Plan?
The Circular Economy Action Plan consists of several key steps. These include setting ambitious goals and targets, promoting eco-design and sustainable production, ensuring the implementation of the waste hierarchy (reduce, reuse, recycle), supporting sustainable business models, investing in research and innovation, and fostering international cooperation.
What are the benefits of a circular economy?
A circular economy offers numerous benefits, including reducing resource depletion, minimizing waste generation, promoting environmental sustainability, creating new job opportunities, improving resource efficiency, increasing economic competitiveness, and enhancing social well-being. It also helps address challenges like climate change and resource scarcity.
How does the Circular Economy Action Plan contribute to sustainable development?
The Circular Economy Action Plan contributes to sustainable development by promoting the transition to a more resource-efficient and sustainable economic model. It helps achieve multiple Sustainable Development Goals, such as responsible consumption and production, climate action, and sustainable cities and communities. By reducing waste and promoting circularity, it aims to create a more sustainable and resilient future.
How can individuals contribute to the circular economy?
Individuals can contribute to the circular economy by adopting sustainable consumption habits, such as reducing waste, reusing products, and recycling materials. They can also support businesses that follow circular principles, participate in repair and sharing initiatives, and stay informed about circular economy practices and initiatives. By making conscious choices, individuals can play a crucial role in promoting a sustainable future.
What is the Circular Economy Action Plan?
The Circular Economy Action Plan is a set of measures proposed by the European Commission to transition to a more sustainable, circular economy. It aims to reduce waste, promote recycling and reuse, and create new economic opportunities.
What are the key steps of the Circular Economy Action Plan?
The key steps of the Circular Economy Action Plan include implementing sustainable product policies, promoting circular business models, fostering sustainable consumption, and strengthening the EU’s global role in the circular economy.
