
In recent years, China has become more aware of the environmental impact of plastic waste. As one of the world’s largest importers and recyclers of plastic, China played a significant role in the global plastic waste market. However, due to mounting concerns about pollution and the quality of imported plastic waste, China decided to implement stricter regulations on plastic waste imports.
In 2018, China announced a comprehensive ban on the importation of 24 types of solid waste, including various types of plastics. This ban, commonly known as “National Sword”, aimed to reduce the environmental pollution caused by contaminated or low-quality plastic waste. The Chinese government recognized the importance of protecting the environment and promoting sustainable development through the restriction of plastic waste imports.
This ban had a significant impact on the global plastic waste trade, as China had been the top destination for plastic waste exported by developed countries. The sudden halt to China’s acceptance of plastic waste forced exporters to find alternative destinations or invest in advanced recycling technologies. This ban also sparked discussions and initiatives in other countries to address their own plastic waste management strategies.
- China’s Ban on Plastic: A Timeline
- The Environmental Impact of Plastic
- China’s Response: The Plastic Ban
- The Plastic Ban in Action
- Improved Waste Management
- Shift Towards Alternative Materials
- Challenges and Obstacles
- The Plastics Industry
- Changing Mindsets and Behaviors
- The Effects of the Plastic Ban
- The Future of Plastic Use in China
- Question-answer:
- Why did China stop accepting plastic?
- What were the consequences of China’s decision to stop accepting plastic?
- Have other countries followed China’s example and stopped accepting plastic imports?
- What are the alternatives for countries that can no longer export their plastic waste to China?
China’s Ban on Plastic: A Timeline
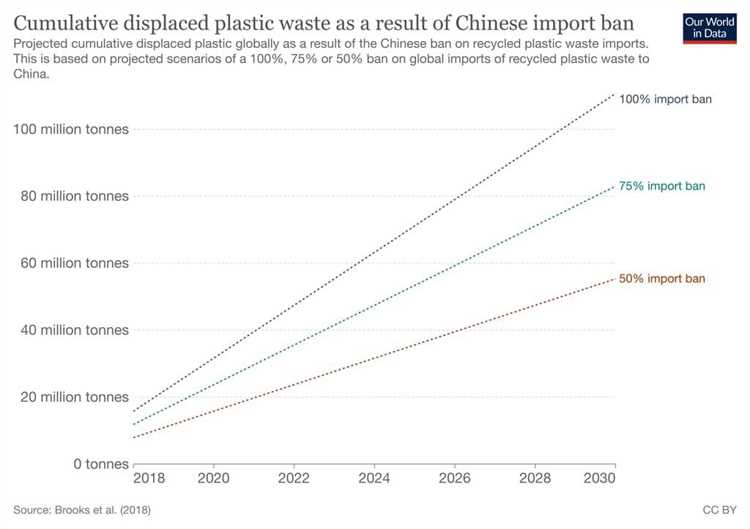
China’s efforts to reduce plastic waste and pollution have evolved over time. Here is a timeline of the major milestones in China’s ban on plastic:
- 2008: China begins implementing a ban on ultra-thin plastic bags that are less than 0.025 millimeters thick. This ban aims to reduce plastic bag usage and encourage the use of reusable bags. Retailers are prohibited from providing free plastic bags to customers.
- 2013: The Chinese government launches a campaign called “Clean Your Plate” to reduce food waste. As part of this campaign, the use of disposable plastic tableware in restaurants is discouraged.
- 2017: The Chinese government announces plans to ban the import of 24 types of solid waste, including certain types of plastic waste. This decision is made in an effort to reduce pollution and improve environmental sustainability.
- 2018: China implements a ban on the import of most types of plastic waste. Previously, China had been the world’s largest importer of plastic waste, but the ban disrupts global recycling systems.
- 2020: China expands its ban on plastic waste by introducing measures to phase out the production and use of single-use plastic items. This ban includes plastic straws, disposable cutlery, and non-degradable plastic bags in major cities by the end of 2020, and nationwide by 2022. The government encourages the use of eco-friendly alternatives.
China’s ban on plastic is an important step in reducing plastic pollution and promoting sustainable practices. While it has created challenges for recycling systems and industries reliant on plastic waste, it also presents opportunities for innovation and the development of more sustainable solutions.
The Environmental Impact of Plastic
Plastic is one of the most widespread and commonly used materials in the world. It has become an integral part of our daily lives, but its environmental impact cannot be ignored.
One of the main concerns is that plastic is not biodegradable. This means that it does not break down naturally over time and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. As a result, plastic waste accumulates in landfills and in natural habitats, posing a risk to wildlife and ecosystems.
Another environmental concern is the production of plastic. The production process requires large amounts of energy and fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Additionally, the extraction of raw materials used to make plastic, such as petroleum and natural gas, has its own environmental consequences.
Plastic pollution is also a major problem in the world’s oceans. It is estimated that millions of tons of plastic end up in the ocean each year, harming marine life and ecosystems. Marine animals can become entangled in plastic debris or mistake it for food, leading to injury, suffocation, and death.
Microplastics, tiny fragments of plastic less than 5mm in size, are another environmental concern. These microplastics can be found in water sources, soil, and even in the air we breathe. They can enter the food chain, potentially exposing humans and other animals to harmful chemicals found in plastic.
Addressing the environmental impact of plastic requires a comprehensive approach. This includes reducing plastic consumption, promoting recycling and proper waste management, and developing more sustainable alternatives to plastic. It is crucial that individuals, businesses, and governments work together to find solutions to this pressing environmental issue.
China’s Response: The Plastic Ban
China’s ban on plastic imports in 2018 sent shockwaves through the global recycling industry. The decision was motivated by China’s environmental concerns and desire to address its own plastic pollution problem.
The plastic ban prohibited the importation of 24 types of solid waste, including various types of plastics, unsorted paper, and textile waste. Previously, China had been the world’s largest importer of plastic waste, accepting millions of tons from countries around the world.
This ban had a significant impact on global recycling efforts, as many countries relied on China as a destination for their plastic waste. With the ban in place, these countries had to find alternative solutions for their plastic waste, such as investing in domestic recycling infrastructure or finding new export markets.
China’s decision to ban plastic imports also forced other countries to re-evaluate their own recycling practices and policies. It highlighted the need for stricter regulations on plastic waste and the importance of developing sustainable recycling systems.
However, the ban also had unintended consequences. Some countries, unable to find alternative solutions for their plastic waste, resorted to illegal dumping or incineration, which exacerbated the plastic pollution problem.
In response to these challenges, China has taken steps to improve its own recycling infrastructure and promote a more sustainable approach to plastic waste management. The country has implemented stricter quality standards for imported recyclables and increased investment in domestic recycling facilities.
China’s ban on plastic imports has had far-reaching effects on the global recycling industry. While it initially caused disruptions and challenges, it has also spurred greater awareness and action on plastic waste management. By taking a proactive approach to addressing its plastic pollution problem, China has set an example for other countries to follow.
The Plastic Ban in Action
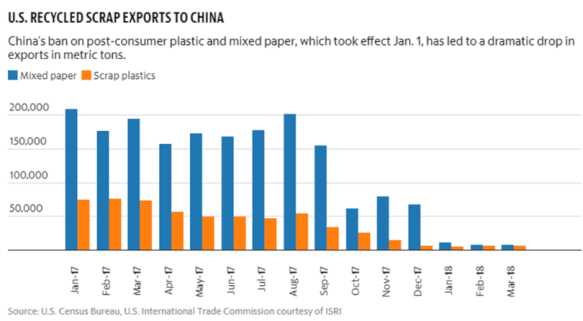
Since China implemented the ban on plastic imports in 2018, the country has seen a significant shift in its waste management and recycling efforts. The ban was enacted in an effort to address the growing environmental concerns and to encourage the development of a more sustainable and circular economy.
The ban has had a profound impact on the global plastic waste trade, as China was once the world’s largest importer of plastic waste. With the ban in place, countries that previously relied on China to process their plastic waste have been forced to find alternative solutions.
Improved Waste Management
The plastic ban has prompted China to prioritize its domestic waste management systems. The country has invested heavily in improving its recycling infrastructure, including the establishment of new recycling facilities and the implementation of stricter recycling standards.
Efforts have also been made to educate the public about the importance of proper waste disposal and recycling. Public awareness campaigns have been launched to encourage individuals to separate and recycle their plastic waste, reducing the overall amount of plastic sent to landfills or illegally dumped.
Furthermore, the ban has led to increased investment in innovative waste-to-energy technologies. China has been exploring ways to convert plastic waste into energy, reducing its reliance on fossil fuels and creating a more sustainable energy source.
Shift Towards Alternative Materials
In addition to improving waste management, the plastic ban has also stimulated innovation in the development and use of alternative materials. Businesses and manufacturers have been encouraged to find alternatives to single-use plastics, such as biodegradable or compostable materials.
This shift towards alternative materials has not only helped reduce plastic waste, but it has also created new opportunities for industries and entrepreneurs. China has witnessed the emergence of new businesses specializing in eco-friendly packaging solutions and sustainable materials.
Overall, the plastic ban in China has been a catalyst for change, prompting a shift towards more sustainable waste management practices and encouraging the development of alternative materials. While there are still challenges to overcome, the ban has undoubtedly had a positive impact on China’s efforts to reduce plastic pollution and promote environmental sustainability.
Challenges and Obstacles

In recent years, China has faced numerous challenges and obstacles in its efforts to manage plastic waste. One of the major challenges is the sheer volume of plastic waste generated by the country’s rapidly growing population and industries. With over 1.4 billion people, China is the world’s most populous nation, and this has contributed to a significant increase in plastic consumption.
Another challenge is the lack of proper waste management infrastructure. China has struggled to keep up with the demand for waste collection and disposal services, especially in rural areas. This has led to widespread illegal dumping and uncontrolled burning of plastic waste, resulting in environmental pollution and health hazards.
Additionally, China has faced obstacles in enforcing regulations and implementing effective policies to curb plastic waste. Despite having strict regulations in place, the country has struggled with enforcement due to corruption, inadequate resources, and limited public awareness about the importance of waste management.
Furthermore, China has also faced resistance from industries and businesses that rely heavily on plastic packaging. These stakeholders often resist efforts to reduce plastic consumption, citing concerns about increased costs and potential loss of competitiveness.
The Plastics Industry
The plastics industry, in particular, has been a major obstacle in China’s efforts to tackle plastic waste. The industry has grown rapidly over the years, driven by the demand for consumer goods and packaging materials. As a result, China has become one of the world’s largest producers and consumers of plastics.
Many plastic manufacturers and packaging companies have been reluctant to switch to more sustainable alternatives, such as biodegradable or recyclable materials. This is due to concerns about costs, technical challenges, and the lack of a well-established market for such products.
Changing Mindsets and Behaviors

Changing mindsets and behaviors towards plastic waste has also proven to be a significant challenge. In a country where convenience is highly valued, single-use plastic products have become deeply ingrained in everyday life. The public’s perception of plastic waste is often limited to its immediate convenience, rather than its long-term impact on the environment.
Addressing this challenge requires not only raising awareness about the environmental consequences of plastic waste but also providing alternative options and promoting sustainable consumer behaviors.
Despite these challenges and obstacles, China has made significant strides in recent years to address plastic waste. The government has implemented various measures, including plastic bag bans, waste sorting programs, and stricter regulations on recycling. However, sustained efforts and continuous innovation will be crucial to overcoming the remaining challenges and achieving a more sustainable approach to plastic waste management in China.
The Effects of the Plastic Ban
Since China stopped accepting plastic waste from other countries, there have been significant effects on both domestic and global levels. Here are some of the effects of the plastic ban:
| Effects | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased domestic recycling efforts | With the ban in place, China has ramped up its efforts to recycle plastic domestically. This has led to the establishment of new recycling facilities and the implementation of stricter recycling policies. |
| Shift in plastic waste exports | Other countries that used to send their plastic waste to China have had to find alternative destinations for their recycling. This has put pressure on these countries to improve their own recycling infrastructure or find new markets for their waste. |
| Rise in illegal plastic waste trade | Unfortunately, the plastic ban has also resulted in an increase in illegal plastic waste trade. Some countries or individuals resort to illegal dumping or exporting plastic waste to developing countries with less stringent regulations. |
| Increase in plastic pollution | Without a reliable outlet for their plastic waste, some countries have resorted to landfilling or incinerating plastic waste, which can contribute to increased plastic pollution. This poses a threat to the environment and human health. |
| Encouragement of sustainable alternatives | The plastic ban has also served as a catalyst for the development and adoption of sustainable alternatives to plastic. This includes the use of biodegradable materials, reusable containers, and the promotion of a circular economy. |
Overall, the plastic ban implemented by China has had wide-ranging effects on waste management systems, recycling efforts, and global plastic pollution. It has highlighted the need for countries to improve their own recycling infrastructure and find sustainable solutions to reduce plastic waste.
The Future of Plastic Use in China
China has made significant strides in addressing its plastic waste problem in recent years. The country has long been one of the largest producers and consumers of plastic, leading to major environmental and health concerns. However, China has taken a series of measures to reduce its plastic footprint and promote more sustainable practices.
One of the key initiatives China has implemented is the ban on importing certain types of plastic waste. In 2018, China implemented a ban on 24 types of solid waste, including various types of plastic. This move aimed to prevent the influx of contaminated and low-quality plastic waste from other countries, which had become a major issue for China’s recycling industry.
In addition to the import ban, China has also introduced stricter regulations on the production and use of plastic. The government has encouraged the development of alternative materials and technologies to replace single-use plastics, such as biodegradable and compostable plastics. Companies are incentivized to adopt these alternatives through tax breaks and other financial incentives.
Another important aspect of China’s approach to reducing plastic use is public awareness and education. The government has launched campaigns to educate the public about the environmental impact of plastic waste and promote sustainable behaviors. This includes encouraging individuals to use reusable bags and containers, as well as promoting recycling and proper disposal of plastic waste.
The future of plastic use in China looks promising as the country continues to prioritize sustainability and environmental protection. The government’s commitment to reducing plastic waste, along with its efforts to develop alternative materials and educate the public, are crucial steps towards a more plastic-free future in China.
However, there are still challenges to overcome. China’s large population and growing middle class pose a significant demand for consumer goods, many of which are packaged in plastic. Balancing this demand with sustainable practices will require further innovation and collaboration between government, industry, and consumers.
Overall, China’s efforts to address its plastic waste problem are commendable and serve as an example for other countries. By implementing strict regulations, promoting alternative materials, and raising public awareness, China is taking decisive actions towards a more sustainable future for plastic use.
Question-answer:
Why did China stop accepting plastic?
China stopped accepting plastic imports in 2018 due to environmental concerns. The country was facing major pollution and waste management issues due to the large volumes of plastic waste being imported.
What were the consequences of China’s decision to stop accepting plastic?
The consequences of China’s decision to stop accepting plastic were significant. Many countries had to find alternative solutions for managing their plastic waste, such as investing in recycling infrastructure or sending the waste to other countries for processing. This decision also led to a decrease in global plastic recycling rates and an increase in plastic waste being incinerated or ending up in landfills.
Have other countries followed China’s example and stopped accepting plastic imports?
Yes, some countries have followed China’s example and implemented stricter regulations on plastic imports. For example, Malaysia and Vietnam have restricted plastic waste imports due to environmental concerns. However, many countries are still struggling to find effective solutions for managing their plastic waste.
What are the alternatives for countries that can no longer export their plastic waste to China?
Countries that can no longer export their plastic waste to China are exploring various alternatives. Some are investing in domestic recycling infrastructure to process the waste locally. Others are seeking new markets for their plastic waste, such as Southeast Asian countries or countries in Africa. However, finding sustainable and economically viable solutions remains a challenge.