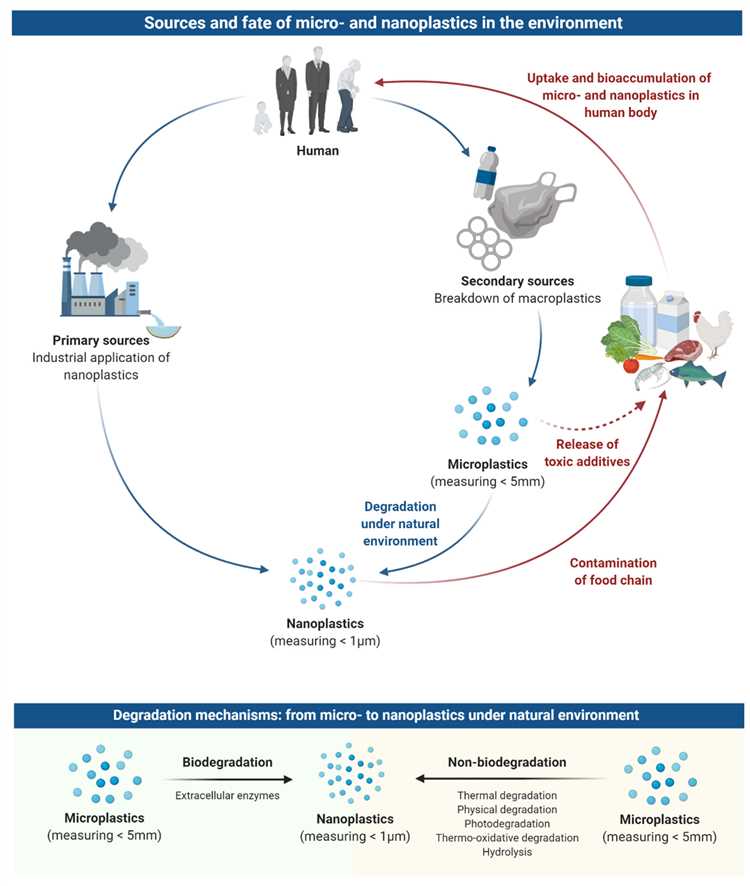
Microplastics are small plastic particles that have become a significant concern in recent years due to their widespread presence in the environment and potential impact on human health. These particles, often smaller than 5mm in size, come from a variety of sources, including the breakdown of larger plastic items and the use of synthetic materials in personal care products.
One question that has been the subject of much debate is whether or not microplastics can be absorbed by the skin. Some studies suggest that the skin may act as a barrier, preventing the absorption of these particles into the body. However, other research has found evidence of microplastics in human tissues, suggesting that absorption may indeed occur.
While more research is needed to fully understand the extent to which microplastics can be absorbed by the skin, there are several factors that may play a role in their potential uptake. These include the size and shape of the particles, the duration and frequency of exposure, and the presence of other substances that may enhance or inhibit absorption.
As microplastics continue to be a topic of concern, it is important for further research to be conducted to determine the potential health risks associated with their absorption through the skin. In the meantime, individuals can take steps to reduce their exposure to microplastics by making conscious choices in their product consumption, such as opting for natural and biodegradable materials whenever possible.
- Is Skin Absorbing Microplastics?
- 1. Hair follicles:
- 2. Skin damage:
- Understanding Microplastics
- How Are Microplastics Absorbed?
- The Potential Health Effects
- The Skin-Plastic Interaction
- Penetration of Microplastics
- Inflammatory Response
- Research and Findings
- Implications for Human Health
- Precautionary Measures
- 1. Avoid the Use of Personal Care Products with Microbeads
- 2. Use Natural Fiber Clothing
- 3. Filter Your Tap Water
- The Future of Microplastics and Skincare
- Question-answer:
- Can microplastics be absorbed through the skin?
- Are microplastics harmful if absorbed through the skin?
- How do microplastics enter our body through the skin?
- Is there a way to protect ourselves from absorbing microplastics through the skin?
- Are there any health risks associated with absorbing microplastics through the skin?
Is Skin Absorbing Microplastics?
Microplastics are tiny plastic particles that are less than 5mm in size. They can be found in many products, such as cosmetics, personal care items, and clothing. Concerns have been raised about the potential health effects of microplastics, including whether they can be absorbed by the skin.
Research has shown that microplastics can indeed penetrate the skin. This means that they can enter the body through the skin’s barrier and potentially have harmful effects on our health. The exact mechanisms by which microplastics are absorbed by the skin are still being studied, but there are several ways in which they can enter:
1. Hair follicles:
Microplastics can enter the body through hair follicles, which are tiny openings in the skin. The size of microplastics allows them to easily penetrate these small openings and reach the deeper layers of the skin.
2. Skin damage:
If the skin is damaged or compromised in any way, it may be more susceptible to the absorption of microplastics. For example, cuts, scrapes, or burns can create openings in the skin that allow microplastics to enter.
Once microplastics enter the body through the skin, they can potentially travel to other areas, such as the lymph nodes or bloodstream. This raises concerns about the potential long-term health effects of microplastics, as they are known to contain harmful chemicals that can leach into the body.
It is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the extent of the absorption of microplastics by the skin and the potential health effects. In the meantime, it is advisable to minimize exposure to microplastics by avoiding products that contain them and opting for natural alternatives whenever possible.
Understanding Microplastics
Microplastics are tiny plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size. They can be found in a variety of products, including cosmetics, clothing, and industrial materials. These particles come from the breakdown of larger plastic items or are intentionally added to products as microbeads.
Microplastics are becoming a growing concern due to their potential negative impact on the environment and human health. They have been found in various ecosystems, including oceans, rivers, and even in the air we breathe. Their small size allows them to be easily ingested by marine life, leading to potential bioaccumulation in the food chain.
The concern over microplastics is not only limited to their ingestion. Research suggests that microplastics can also be absorbed by the human body through various pathways, including ingestion, inhalation, and absorption through the skin. While ingestion and inhalation are relatively well-studied, the extent to which microplastics can be absorbed through the skin is still a subject of ongoing research.
How Are Microplastics Absorbed?
The absorption of microplastics through the skin can occur when individuals come into contact with products containing these particles, such as cosmetics or personal care items. The microplastics present in these products can be transferred to the skin, and under certain conditions, they may be able to penetrate the skin barrier.
Studies have shown that the size and shape of microplastics, as well as the properties of the products they are present in, can influence their ability to penetrate the skin. Smaller particles and those with jagged edges are more likely to penetrate the skin compared to larger, smoother particles.
The Potential Health Effects

The potential health effects of absorbing microplastics through the skin are still not fully understood. Some studies suggest that certain types of microplastics may have the ability to cause inflammation, cellular damage, and disrupt the normal functioning of cells. However, more research is needed to determine the long-term impacts and the extent of these effects.
It is important to note that while the absorption of microplastics through the skin is possible, it should not overshadow the larger issue of reducing plastic pollution at its source. By reducing the production and consumption of single-use plastics and implementing effective waste management strategies, we can help mitigate the presence of microplastics in the environment and protect both human health and the planet.
The Skin-Plastic Interaction
The interaction between the skin and microplastics has been a topic of growing concern in recent years. Studies have shown that microplastics, which are tiny particles of plastic less than 5mm in size, can come into contact with the skin through various sources such as personal care products, clothing, and even the air we breathe.
Penetration of Microplastics
One of the questions that researchers have been trying to answer is whether microplastics can actually penetrate the skin. While the skin acts as a protective barrier, studies have suggested that certain types of microplastics, such as nanoparticles, may be able to penetrate the skin’s outermost layer, known as the stratum corneum.
However, it is important to note that the penetration of microplastics into deeper layers of the skin and their potential effects are still not fully understood. More research is needed to determine the extent of skin penetration and the potential risks associated with it.
Inflammatory Response
Another aspect of the skin-plastic interaction is the potential for an inflammatory response. Studies have suggested that when microplastics come into contact with the skin, they can cause an immune response, leading to inflammation.
This inflammation is believed to be triggered by the body’s response to foreign substances, as microplastics are recognized as foreign materials. Chronic inflammation can have various negative effects on the skin, including redness, itching, and even long-term damage.
Conclusion
While the exact effects of microplastics on the skin are still being studied, it is clear that the skin-plastic interaction is a topic of concern. Understanding how microplastics interact with the skin and the potential risks associated with this interaction is essential for developing strategies to minimize exposure and protect skin health.
Research and Findings
Research on the absorption of microplastics by the skin is still ongoing, and the findings so far are inconclusive. Several studies have been conducted to investigate whether microplastics can penetrate the skin barrier and enter the body.
One study conducted in 2016 by researchers at the University of California found that microplastics were able to penetrate the skin of fish larvae, suggesting that they could potentially be absorbed by the skin of humans as well. Another study in 2020 conducted by scientists at the National Center for Atmospheric Research in the United States found microplastics in human skin samples, indicating that they might be able to penetrate the skin barrier.
However, other studies have provided conflicting results. A study conducted in 2017 by researchers at the Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin found that microplastics did not penetrate the skin of human volunteers. Similarly, a study in 2019 by scientists at the University of Plymouth found no evidence of microplastics entering the bloodstream through the skin.
It is important to note that the studies conducted so far have limitations, and more research is needed to fully understand the potential for skin absorption of microplastics. Factors such as the size and type of microplastics, the condition of the skin barrier, and the duration of exposure may all contribute to the variability in the results.
While the current findings suggest that microplastics may be able to penetrate the skin barrier, it is also important to consider other routes of exposure, such as inhalation and ingestion of microplastics. Further research is needed to determine the overall impact of microplastic exposure on human health.
In conclusion, research on the absorption of microplastics by the skin is still ongoing and inconclusive. While some studies suggest that microplastics can penetrate the skin barrier, others have found no evidence of skin absorption. Additional research is needed to better understand the potential risks and impacts of microplastic exposure on human health.
Implications for Human Health
Microplastics are a significant concern for human health due to their potential to enter the body through various routes of exposure, including ingestion, inhalation, and dermal absorption.
Research has shown that microplastics can accumulate in various organs and tissues, raising concerns about their potential impact on human health.
Ingestion: Microplastics can enter the body through the consumption of contaminated food and water. Studies have found microplastics in a wide range of food items, including seafood, bottled water, and even table salt. Once ingested, these particles can accumulate in the digestive system and potentially disrupt its normal functioning.
Inhalation: Microplastics can also be inhaled, especially in environments with high levels of plastic pollution such as industrial areas or near waste disposal sites. Inhalation of microplastics can result in their deposition in the respiratory system, potentially leading to inflammation, respiratory disorders, and impaired lung function.
Dermal Absorption: Although the main route of microplastic exposure is through ingestion and inhalation, there is also evidence to suggest that microplastics can be absorbed through the skin. Since the skin is the largest organ of the body, any potential absorption of microplastics through this route can have widespread implications for human health.
While the exact impacts of microplastic exposure on human health are still being researched, some studies suggest a variety of potential health effects, including hormonal disruptions, immune system dysfunction, and even an increased risk of certain diseases, such as cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term implications of microplastic exposure on human health.
Overall, the presence of microplastics in the environment and their potential to enter the human body raise significant concerns for human health. Efforts to reduce plastic pollution and find alternative materials are essential to mitigate these risks and protect human health.
Precautionary Measures

While the extent of harm caused by microplastics absorbed through the skin is still being researched, it is always a good idea to take precautionary measures to minimize exposure. Here are some steps you can take:
1. Avoid the Use of Personal Care Products with Microbeads
Microbeads are tiny plastic particles commonly found in exfoliating scrubs, soaps, and toothpaste. Check the labels of your personal care products and avoid those that contain microbeads. Instead, opt for natural exfoliants such as sugar or salt.
2. Use Natural Fiber Clothing
Microplastics can be released from synthetic fabrics during the washing process. To reduce the release of microplastics, choose clothing made from natural fibers like cotton, linen, or hemp. These materials are less likely to shed microplastic particles.
3. Filter Your Tap Water
Microplastics can also be found in tap water. Consider investing in a water filter that is specifically designed to remove microplastics. This can help reduce your exposure to these particles when drinking or cooking with tap water.
Remember, while these measures can help minimize exposure to microplastics, more research is needed to fully understand the potential risks and effects on human health. Stay informed about new findings and continue to make informed choices to protect yourself and the environment.
The Future of Microplastics and Skincare
As the issue of microplastics and their impact on the environment becomes more widely recognized, the future of skincare also faces significant challenges. With the growing awareness of the harmful effects of microplastics on marine life and ecosystems, consumers are starting to demand more sustainable and eco-friendly skincare products.
One of the most promising developments in the future of skincare is the rise of biodegradable and natural alternatives to microplastics. Many companies are now investing in research and development to find innovative solutions that can replace the microplastic particles used in exfoliating scrubs, cleansers, and other skincare products.
These alternatives include natural exfoliants like sugar, salt, and coffee grounds, which are not only safe for the environment but also provide the same exfoliating benefits. Other options being explored include bio-based polymers derived from renewable resources and natural fibers.
In addition to finding alternatives to microplastics, the future of skincare also lies in improving product formulations and manufacturing processes. Companies are working towards reducing the use of plastic packaging and minimizing waste in the production and distribution of skincare products.
Furthermore, advancements in technology are expected to play a significant role in ensuring the safety and sustainability of skincare products. For instance, the development of advanced filtration systems and testing methods can help identify and remove microplastic contaminants from skincare formulations, ensuring that only safe and eco-friendly products reach the market.
| Benefits of Sustainable Skincare | Challenges and Opportunities |
|---|---|
| 1. Reduced environmental impact | 1. Finding effective alternatives to microplastics |
| 2. Healthier for the skin | 2. Development of eco-friendly packaging |
| 3. Positive brand image | 3. Integration of technology in product development |
| 4. Meeting consumer demand for sustainability | 4. Collaboration and knowledge sharing among industry stakeholders |
In conclusion, the future of microplastics and skincare is moving towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly direction. With the increasing demand for greener alternatives, continuous research, and technological advancements, it is possible to create skincare products that are both effective and safe for the environment.
Question-answer:
Can microplastics be absorbed through the skin?
According to recent studies, it is possible for microplastics to be absorbed through the skin. However, the extent of absorption and the potential health effects are still being investigated.
Are microplastics harmful if absorbed through the skin?
The potential health effects of absorbing microplastics through the skin are still not fully understood. Some studies suggest that they might have adverse effects on human health, while others indicate that the levels of absorption may be too low to cause significant harm.
How do microplastics enter our body through the skin?
Microplastics can enter the body through the skin through various routes. They can be present in personal care products like exfoliating scrubs or body washes, or they can be released from synthetic clothing fibers that come into direct contact with the skin.
Is there a way to protect ourselves from absorbing microplastics through the skin?
While more research is needed to determine the best methods of protection, some possible measures include avoiding personal care products with microplastics or choosing natural alternatives, wearing clothing made from natural fibers, and maintaining good skin hygiene.
Are there any health risks associated with absorbing microplastics through the skin?
The potential health risks associated with absorbing microplastics through the skin are still under investigation. Some studies have suggested that microplastics could have adverse effects on human health, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and disruption of hormonal balance. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of these risks.