
Plastic cups are commonly used for serving beverages at parties, picnics, and other events. However, what happens when these cups are exposed to high heat, such as being placed near an open flame or in the microwave? Many people wonder whether melted plastic cups are toxic and if they can release harmful chemicals into the drinks they hold.
The answer to this question is not as straightforward as one might think. While it is true that melting plastic can release potentially toxic chemicals, such as dioxins, the amount of these chemicals that would be released from a plastic cup in normal use is likely to be minimal. The main concern arises when plastic cups are exposed to extremely high temperatures, such as in industrial processes or when burned.
It is important to note that not all plastic cups are created equal. Different types of plastic have different melting points and chemical compositions, which can affect their toxicity when heated. For example, polystyrene cups, commonly used for hot drinks, have a lower melting point than polypropylene cups, which are often used for cold beverages. Therefore, it is possible that polystyrene cups may release more harmful chemicals when melted compared to polypropylene cups.
- Are Melted Plastic Cups Toxic?
- Understanding the Potential Health Risks
- Ingestion
- Inhalation
- Types of Plastics and Their Properties
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- The Effects of Melting Plastic on Chemical Composition
- 1. Release of Toxic Fumes
- 2. Chemical Changes
- Exposure to Harmful Substances
- Importance of Proper Disposal
- Environmental Impact
- Health Risks
- Q&A
- Is it safe to drink from a melted plastic cup?
- What happens if I drink from a melted plastic cup?
- What are the dangers of using melted plastic cups?
- Are there any health risks associated with drinking from melted plastic cups?
- What should I do if I accidentally drank from a melted plastic cup?
- Can melted plastic cups release toxic fumes?
- What are the dangers of using melted plastic cups?
Are Melted Plastic Cups Toxic?
Melted plastic cups can release toxic chemicals when heated. These chemicals can include phthalates, lead, and bisphenol-A (BPA), which are known to be harmful to human health.
When plastic cups are melted, the heat can cause the release of these harmful chemicals into the air. Inhaling these chemicals can lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems, hormonal imbalances, and reproductive disorders.
Additionally, the chemicals released from melted plastic cups can leach into food and beverages if the cups are used for drinking or food storage. This can contaminate the food or drink and result in exposure to these toxic substances.
It is important to note that not all plastic cups are made equal, and the toxicity level can vary depending on the type of plastic used. Some plastics are considered safer than others, but it is always best to avoid heating plastic cups altogether to minimize the risk of exposure to harmful chemicals.
If you need to heat liquids or food, it is recommended to use microwave-safe or heat-resistant containers made of glass or ceramics. These materials do not release harmful chemicals when exposed to high temperatures.
In conclusion, melted plastic cups can indeed be toxic due to the release of harmful chemicals. It is important to be aware of the potential risks and choose safer alternatives for heating and storing food and drinks.
Understanding the Potential Health Risks
When plastic cups are melted, they can release harmful chemicals into the air and the food or beverages that come into contact with them. These chemicals can pose potential health risks if ingested or inhaled over a prolonged period of time. It is important to be aware of these risks and take appropriate precautions to limit exposure.
Ingestion
When melted plastic cups are ingested, either by consuming food or drinks that have been in contact with them or by accidentally swallowing small particles, it can lead to the ingestion of harmful chemicals. These chemicals may include phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), and other additives commonly found in plastic. Studies have shown that long-term exposure to these substances can have negative effects on human health, such as hormone disruption, reproductive issues, and an increased risk of certain diseases.
Inhalation
Melting plastic cups can also release toxic fumes into the air, which can be inhaled and potentially cause respiratory problems. These fumes may contain harmful compounds, such as dioxins, styrene, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Inhaling these substances over time can irritate the respiratory system, trigger allergies, and even contribute to the development of respiratory conditions, including asthma.
It is worth noting that the potential health risks associated with melted plastic cups are greater when the cups are made from low-quality plastics or contain additives that are known to be more hazardous. It is always advisable to use heat-resistant and food-grade plastic containers and cups to minimize the risk of harmful chemical exposure.
To further reduce the potential health risks, it is recommended to avoid using plastic cups for hot liquids, as heat can accelerate the release of harmful chemicals. Opting for alternative materials like glass, ceramic, or stainless steel can provide a safer option for food and beverage consumption. Additionally, it is essential to properly dispose of plastic cups to prevent environmental contamination and reduce the overall impact on human health.
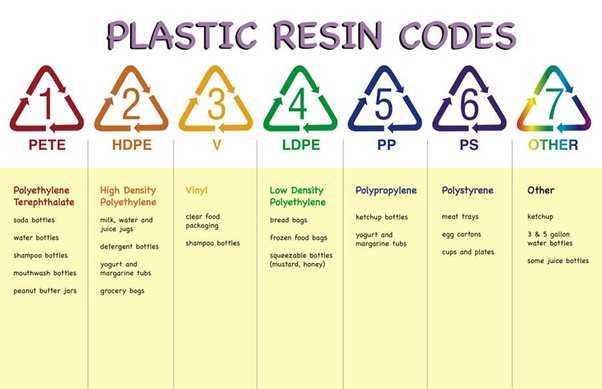
Types of Plastics and Their Properties
Plastics are a versatile material that can be found in a wide range of products, including cups, bottles, packaging materials, and more. Different types of plastics have different properties, making them suitable for different applications. Here are some common types of plastics and their properties:
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is one of the most commonly used plastics and is known for its high strength, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals. It is commonly used in packaging materials, plastic bags, and bottles.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a tough and rigid plastic that is resistant to high temperatures and chemicals. It is often used in food containers, automotive parts, and medical devices.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)

Polyvinyl chloride is a durable and versatile plastic that is resistant to fire, water, and chemicals. It is commonly used in pipes, cables, flooring, and window frames.
Polystyrene (PS)

Polystyrene is a lightweight and rigid plastic that is known for its insulation properties. It is often used in packaging materials, disposable cups, and food containers.
These are just a few examples of the many types of plastics available. Each type of plastic has its own unique properties and is suitable for specific applications. It is important to consider these properties when choosing a plastic for a particular product or use to ensure optimal performance and safety.
The Effects of Melting Plastic on Chemical Composition
Melting plastic can have detrimental effects on its chemical composition. When plastic is melted, the high heat causes the polymer chains to break down, releasing toxic fumes and chemicals into the air.
1. Release of Toxic Fumes
One of the main concerns when melting plastic is the release of toxic fumes. Different types of plastic contain different chemicals, and when these plastics are melted, these chemicals can be released into the surrounding air.
For example, when polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic is melted, it releases chlorine gas, which is highly toxic and can cause respiratory problems, eye irritation, and even damage to the central nervous system.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic, commonly used in water bottles, releases several toxic chemicals when melted, including benzene, which is a known carcinogen.
2. Chemical Changes
In addition to releasing toxic fumes, melting plastic can also cause chemical changes in the plastic itself. The high heat can break down the polymer chains, leading to a loss of structural integrity and changes in the chemical composition of the plastic.
These chemical changes can result in the formation of new compounds that may be toxic or carcinogenic. For example, some studies have shown that melting certain types of plastic can lead to the formation of dioxins, which are highly toxic and can have long-term health effects.
Therefore, it is important to avoid melting plastic, especially in poorly ventilated areas, to minimize the release of toxic fumes and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Exposure to Harmful Substances
When plastic cups are melted, they release harmful substances that can be toxic if ingested or inhaled. These substances include but are not limited to:
Dioxins: Dioxins are highly toxic compounds that can have serious health effects, including reproductive and developmental problems, immune system damage, and certain types of cancer.
Bisphenol A (BPA): BPA is a chemical often found in plastic cups that has been linked to hormone disruption, obesity, and reproductive disorders. It is particularly dangerous for pregnant women and young children.
Phthalates: Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastic cups more flexible and durable. They have been linked to a variety of health issues, including asthma, attention deficit disorder, and certain types of cancer.
Exposure to these harmful substances can occur through direct contact with melted plastic cups, such as when handling hot drinks or microwaving food in plastic containers. Ingesting or inhaling these substances can lead to serious health complications, especially if repeated or long-term exposure occurs.
It is important to always use safe and reliable alternatives to plastic cups, such as glass or stainless steel, to minimize your exposure to these harmful substances.
Importance of Proper Disposal
Proper disposal of plastic cups is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to protect the environment and prevent pollution. When plastic cups are not disposed of correctly, they can end up in landfills or littered in natural habitats. This not only makes the surroundings unsightly, but it also poses a threat to wildlife.
Environmental Impact
When plastic cups are not properly disposed of, they can take hundreds of years to decompose, releasing harmful toxins into the environment. These toxins can contaminate soil and water, affecting the health of plants, animals, and humans. Additionally, improper disposal of plastic cups contributes to the growing problem of plastic waste in our oceans, endangering marine life and causing damage to delicate ecosystems.
Health Risks
Improper disposal of plastic cups also poses health risks. When melted plastic cups are inhaled or ingested, they can release toxic fumes and chemicals. These chemicals can be harmful to human health, causing respiratory problems, allergies, and even certain types of cancers. Proper disposal ensures that these risks are minimized, protecting the well-being of individuals and communities.
To encourage proper disposal of plastic cups, recycling programs and waste management systems should be put in place. These programs not only help to reduce plastic waste and pollution but also promote sustainability and the conservation of resources. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in ensuring that plastic cups and other plastic products are disposed of correctly.
| Advantages of Proper Disposal | Disadvantages of Improper Disposal |
|---|---|
| – Protects the environment | – Pollution of land and water |
| – Preserves wildlife habitats | – Release of harmful toxins |
| – Reduces health risks | – Endangerment of marine life |
| – Promotes sustainability | – Health risks to humans |
Q&A
Is it safe to drink from a melted plastic cup?
Drinking from a melted plastic cup can be toxic because the heat can release harmful chemicals from the plastic into your drink. It is recommended to avoid using melted plastic cups for drinking.
What happens if I drink from a melted plastic cup?
When you drink from a melted plastic cup, you run the risk of ingesting harmful chemicals that have been released from the melted plastic. These chemicals can be toxic and may have adverse effects on your health.
What are the dangers of using melted plastic cups?
Using melted plastic cups can be dangerous because heating plastic can release toxins into the air and into the food or drink that comes into contact with it. These toxins can have negative effects on your health, including respiratory issues and reproductive problems.
Are there any health risks associated with drinking from melted plastic cups?
Yes, drinking from melted plastic cups can pose health risks. When plastic is melted, it can release harmful chemicals such as BPA and phthalates. These chemicals can leach into the drink and may have detrimental effects on your health, including hormone disruption and increased risk of certain diseases.
What should I do if I accidentally drank from a melted plastic cup?
If you accidentally drank from a melted plastic cup, it is important to monitor yourself for any signs of illness or discomfort. If you experience any symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical advice. It is also advisable to avoid using melted plastic cups in the future and opt for safer alternatives.
Can melted plastic cups release toxic fumes?
Yes, when plastic cups are melted, they can release toxic fumes. The fumes are caused by the chemicals in the plastic, such as chlorine, bromine, and phthalates, which can be harmful if inhaled.
What are the dangers of using melted plastic cups?
Using melted plastic cups can pose several dangers. When the plastic melts, it can release toxic fumes, which can be harmful if inhaled. Additionally, the melted plastic can contaminate food or beverages, leading to ingestion of harmful chemicals. It is best to avoid using melted plastic cups and opt for safer alternatives.