Plastic pollution in our oceans has reached alarming levels, with catastrophic consequences for marine life and ecosystems. But what about the impact of this pollution on humans?
Recent studies have raised concerns about the potential health risks of consuming fish contaminated with plastic. Plastics, which take hundreds of years to break down, can be found in various forms in our oceans, including microplastics, tiny particles less than 5mm in size. These microplastics have been found in the stomachs of many marine species, including fish.
But can humans really consume plastic through fish consumption? The answer seems to be yes. Research has shown that microplastics can accumulate in the tissues of fish, including commonly consumed species, such as salmon and tuna. As a result, when we eat fish, we may also unknowingly consume the plastic particles they contain.
- Plastic Consumption by Humans
- The Potential Health Risks
- Reducing Plastic Consumption
- The Impact of Fish Consumption
- How Plastic Gets Into the Ocean
- 1. Land-based Sources
- 2. Rivers
- 3. Coastal Activities
- 4. Offshore Activities
- Accumulation of Plastics in Fish
- Q&A:
- Is it true that humans consume plastic when they eat fish?
- How does plastic pollution in the ocean affect fish?
- Are there any health risks associated with consuming plastic through fish consumption?
- What can be done to reduce plastic consumption through fish consumption?
Plastic Consumption by Humans
Plastic consumption by humans is a growing concern in today’s world. With the increasing production of single-use plastics and their improper disposal, plastic waste is entering our ecosystems and food chains at an alarming rate.
Fish consumption plays a significant role in this issue. As plastic waste accumulates in rivers, lakes, and oceans, marine organisms, including fish, often mistake small plastic particles for food. These plastic particles, known as microplastics, can contain toxins and chemicals that are harmful to both aquatic life and humans.
Studies have shown that microplastics can accumulate in the tissues of fish. When humans consume these contaminated fish, they may unknowingly be ingesting plastic as well. The presence of microplastics in the digestive systems of fish has raised concerns about potential health risks for humans who consume seafood.
The Potential Health Risks
Although the long-term effects of plastic consumption on human health are still being studied, the ingestion of microplastics has been linked to various health issues. The chemicals present in plastic, such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA), have been associated with reproductive problems, hormonal imbalances, and even an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
Furthermore, microplastics can have physical effects on the human body. They may cause inflammation in the digestive system and disrupt nutrient absorption, leading to potential nutritional deficiencies. Additionally, microplastics can accumulate in the respiratory system and worsen respiratory conditions, such as asthma.
Reducing Plastic Consumption
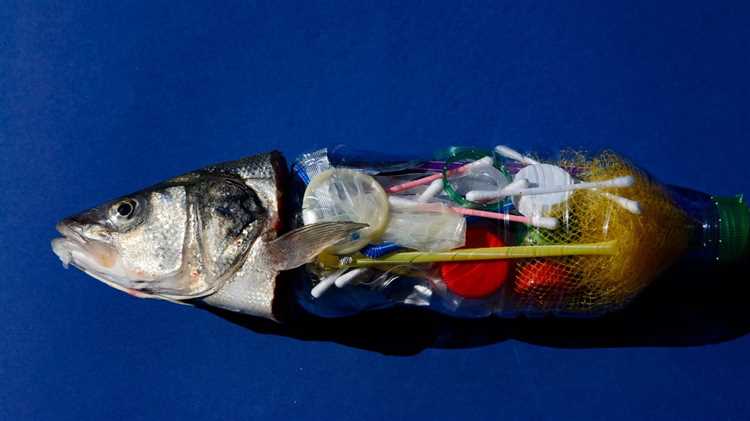

Given the potential health risks associated with plastic consumption, it is crucial to take steps to reduce our plastic usage. Some actions individuals can take include:
- Choosing reusable alternatives to single-use plastics, such as cloth bags instead of plastic bags.
- Properly disposing of plastic waste to prevent it from entering waterways.
- Supporting campaigns and initiatives that promote plastic reduction and recycling.
- Spreading awareness about the issue and educating others on the importance of reducing plastic consumption.
By taking these actions, we can collectively work towards reducing our reliance on plastic and minimizing the impact of plastic consumption on both our environment and health.
The Impact of Fish Consumption
Fish consumption can have a significant impact on both human health and the environment. While fish is generally considered a nutritious food source, there are potential risks associated with consuming fish that have been exposed to plastic pollution.
Plastic pollution in the oceans is a growing concern, with millions of tons of plastic waste entering the water each year. This waste includes microplastics, which are small pieces of plastic less than 5mm in size. These microplastics can be ingested by fish and other marine organisms, and they can make their way up the food chain.
When humans consume fish that have been contaminated with plastic, they may also be ingesting these microplastics. Studies have shown that microplastics can accumulate in the tissues of fish and have the potential to leach harmful chemicals into the food we eat.
While the full impact of consuming plastic through fish consumption is still not fully understood, it is clear that there are potential health risks associated with this type of pollution. Some studies have suggested that exposure to microplastics can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and other negative health effects.
Additionally, the environmental impact of plastic pollution is significant. Plastic waste not only harms marine life, but it also contributes to climate change and pollution. The production and disposal of plastic contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, and the breakdown of plastic in the environment releases harmful chemicals.
To mitigate the impact of plastic pollution on fish and human health, efforts are being made to reduce plastic waste and improve waste management practices. These include initiatives to reduce plastic use, improve recycling and disposal systems, and promote alternative materials.
In conclusion, while fish consumption is generally considered a healthy choice, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with consuming fish that have been exposed to plastic pollution. By taking steps to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable fishing practices, we can help protect both human health and the environment.
How Plastic Gets Into the Ocean
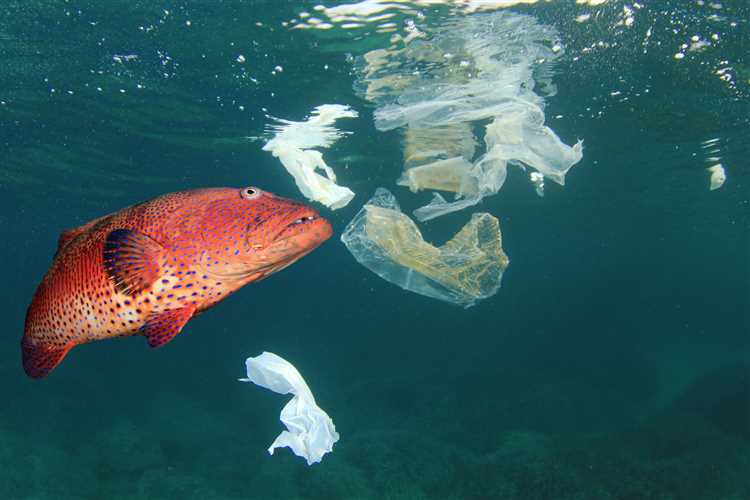

Plastic pollution in the ocean is a major environmental issue that threatens marine life and ecosystems. It is estimated that approximately 8 million metric tons of plastic waste enters the ocean each year. Understanding how plastic enters the ocean is crucial in finding solutions to mitigate and prevent this problem.
1. Land-based Sources
One of the primary sources of plastic in the ocean is land-based pollution. Plastic waste is often improperly disposed of or ends up in waterways through runoff. This can include plastic bottles, bags, packaging materials, and other single-use items. Wind and storm events can also transport plastic waste from landfills and littered areas into rivers, which eventually flow into the ocean.
2. Rivers
Rivers play a significant role in the transportation of plastic pollution into the ocean. Cities and communities located near rivers often deposit their waste into these water bodies, and plastic litter can be carried downstream. Additionally, urban areas experience high levels of plastic waste, which can be transported through storm drains and sewage systems into rivers and ultimately into the ocean.
3. Coastal Activities
Coastal activities, such as fishing, boating, and tourism, also contribute to plastic pollution in the ocean. Discarded fishing gear, known as ghost gear, is a significant contributor to marine plastic pollution. Additionally, beach-goers may leave behind plastic items, such as food containers, straws, and cigarette butts, which can be swept into the ocean by tides and currents.
4. Offshore Activities
Offshore activities, including shipping and oil drilling, can also introduce plastic into the ocean. Dumping of plastic waste and litter from ships and offshore platforms can directly pollute the marine environment. Cargo ships may also lose cargo, which can include plastic pellets or containers, during transit, further contributing to marine plastic pollution.
Efforts to reduce plastic pollution in the ocean involve improving waste management systems, implementing stricter regulations, and promoting sustainable practices. By understanding the sources of plastic pollution, we can work towards addressing this issue and protecting our oceans for future generations.
Accumulation of Plastics in Fish
In recent years, there has been growing concern about the accumulation of plastics in the environment and its potential impact on various ecosystems. One area of particular concern is the accumulation of plastics in fish, which has been well-documented in numerous studies.
Plastics are non-biodegradable materials that can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. As a result, they are often found in bodies of water, where they can be ingested by fish and other aquatic organisms. Microplastics, which are tiny fragments of plastic less than 5mm in size, are of particular concern. These can be formed through the degradation of larger plastic items or can be released directly into the environment through products such as microbeads in personal care products.
When fish consume plastics, either directly or indirectly through their prey, the plastics can accumulate in their digestive systems. This accumulation can lead to a range of negative effects, including reduced feeding efficiency, impaired growth and reproduction, and increased susceptibility to disease. In addition, plastics can also contain chemicals such as plasticizers and flame retardants, which can leach into the tissues of the fish and potentially have further negative effects on their health.
Studies have shown that marine and freshwater fish from various regions around the world can contain significant amounts of plastics in their digestive systems. In some cases, the levels of plastics found in fish can be comparable to or even higher than those found in the surrounding water. This indicates that fish are actively ingesting and accumulating plastics from their environment.
It is important to note that the consumption of fish contaminated with plastics can potentially expose humans to these harmful substances. As fish is a common food source for many people, this raises concerns about the potential health risks associated with consuming fish that has accumulated plastics.
In conclusion, the accumulation of plastics in fish is a significant issue that highlights the broader problem of plastic pollution in our environment. Efforts to reduce the amount of plastic waste entering our oceans and waterways are crucial to protect both marine life and human health.
Q&A:
Is it true that humans consume plastic when they eat fish?
Yes, it is true. Recent studies have shown that humans consume plastic through fish consumption. This is mainly because fish are exposed to plastic pollution in the ocean and ingest microplastics, which are tiny particles of plastic. When humans eat these fish, they can ingest these microplastics as well.
How does plastic pollution in the ocean affect fish?
Plastic pollution in the ocean can have severe effects on fish. Fish can mistake plastic particles for food and consume them, which can lead to various health issues. Plastic can block their digestive systems, cause internal injuries, and disrupt hormone levels. Additionally, these ingested plastics can accumulate in the tissues of fish, which means that humans who consume these fish can also ingest plastic.
Are there any health risks associated with consuming plastic through fish consumption?
Yes, there are potential health risks associated with consuming plastic through fish consumption. When humans ingest microplastics, these particles can accumulate in their bodies and may have toxic effects. Some studies have suggested that microplastics can release harmful chemicals, such as additives used in the production of plastics, which can have negative impacts on human health. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of these risks.
What can be done to reduce plastic consumption through fish consumption?
Several measures can be taken to reduce plastic consumption through fish consumption. Firstly, reducing plastic pollution at its source is crucial. This can be achieved through proper waste management, recycling, and limiting the use of single-use plastics. Additionally, individuals can make informed choices about the fish they consume by opting for fish that are known to have lower levels of plastic contamination. It is also important to raise awareness about the issue and encourage sustainable fishing practices to mitigate plastic pollution in our oceans.