In our increasingly plastic-filled world, the impact on wildlife is becoming more evident. Many animals, both on land and in the sea, are inadvertently consuming plastic and suffering the consequences. This issue has raised concerns among scientists, conservationists, and animal lovers alike, as it poses a significant threat to the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Marine animals, such as sea turtles, dolphins, and whales, are particularly vulnerable to plastic ingestion. These majestic creatures mistake floating plastic bags and other debris for food, leading to severe consequences. The ingestion of plastic can cause internal injuries, blockages in the digestive system, and even starvation. It is estimated that millions of marine animals suffer and die each year due to plastic consumption.
However, the problem is not limited to marine environments. Terrestrial animals, including birds, mammals, and reptiles, are also affected. Birds, for example, often mistake colorful plastic pieces for food and inadvertently feed them to their chicks. This can lead to malnutrition and even death. Additionally, land-dwelling animals may consume plastic particles indirectly through contaminated water or soil, further exacerbating the issue.
The consequences of animals consuming plastic go beyond the individual level. Plastic ingestion can disrupt entire ecosystems. For example, predators may consume smaller animals that have ingested plastic, leading to the bioaccumulation of toxins in their bodies. This can have long-term effects on the health and reproductive abilities of these predators, ultimately affecting the balance of the ecosystem.
Understanding the impact of plastic consumption on wildlife is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. Initiatives aimed at reducing plastic pollution, promoting recycling, and raising awareness about the issue are essential steps towards mitigating the harm caused to animals by human activities. By taking action now, we can help protect the diverse and fragile ecosystems that are home to countless species.
- The Problem of Plastic Pollution
- The Impact on Wildlife
- Animals that Accidentally Eat Plastic
- The Consequences for Marine Creatures
- 1. Ingestion
- 2. Suffocation and entanglement
- 3. Chemical exposure
- 4. Disrupted ecosystems
- Q&A:
- How does plastic consumption affect wildlife?
- Which animals are most affected by plastic consumption?
- Are land animals also at risk of consuming plastic?
- Is there any solution to reduce plastic consumption by animals?
The Problem of Plastic Pollution
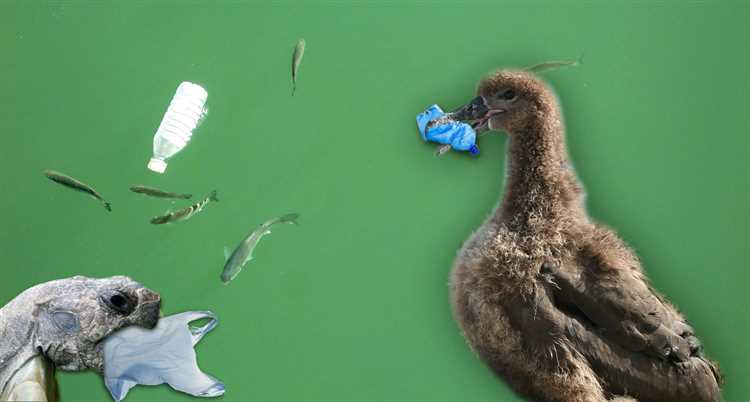

Plastic pollution has become a global environmental crisis, with devastating impacts on wildlife and ecosystems. The widespread use of plastic materials, combined with improper waste management and disposal practices, has led to an alarming increase in plastic pollution in our oceans, rivers, and other natural habitats.
Plastic is a durable and versatile material that is designed to last for hundreds of years. However, this durability also means that plastic does not biodegrade like natural materials. Instead, it breaks down into smaller pieces known as microplastics, which can persist in the environment for thousands of years.
Animals, both marine and terrestrial, are inadvertently consuming plastic in alarming quantities. This occurs when plastic debris is mistaken for food or ingested accidentally. Animals may ingest plastic directly from the environment, such as through contaminated water or prey, or indirectly through the consumption of other animals that have consumed plastic.
The ingestion of plastic can have severe consequences for wildlife. The physical presence of plastic in an animal’s digestive system can cause internal injuries, blockages, and impair the ability to eat and digest food. Additionally, the chemicals and toxins present in plastic can leach into an animal’s body, resulting in toxicity and even death.
Plastic pollution poses a significant threat to marine life, in particular. Sea turtles, seabirds, dolphins, and whales are among the most affected species. Many marine animals mistake plastic bags, straws, and other debris for jellyfish or other prey items. Ingesting these items can lead to starvation, entanglement, and ultimately death.
The problem of plastic pollution requires urgent attention and action. Efforts to reduce plastic consumption, improve waste management systems, and promote sustainable alternatives are necessary to mitigate the impacts on wildlife and ecosystems. It is crucial for individuals, communities, businesses, and governments to work together to address this pressing environmental issue and ensure a sustainable future for our planet.
The Impact on Wildlife
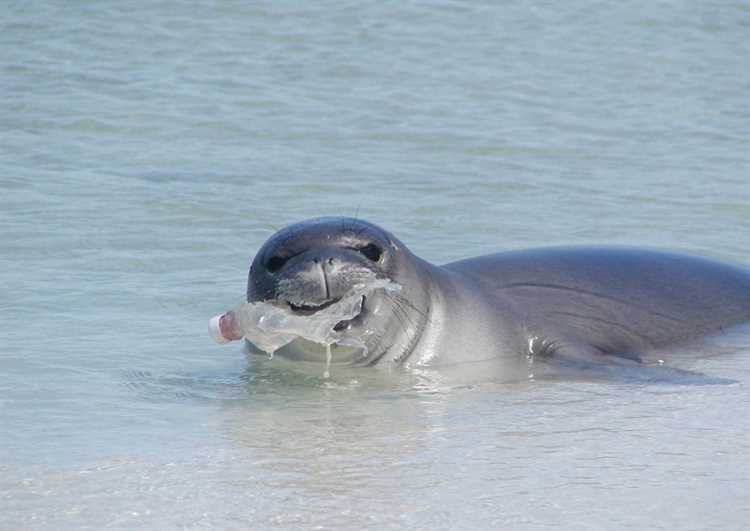

Plastic pollution has had a devastating impact on wildlife around the world. Marine animals, such as whales, dolphins, and sea turtles, often mistake plastic for food and end up consuming large quantities of it. This can lead to severe health issues, including starvation, dehydration, and organ damage.
Plastic ingestion can also cause blockages in an animal’s digestive system, preventing them from properly eating and digesting their food. This can eventually lead to malnutrition and even death. In addition, the chemicals present in plastic can leach into an animal’s body, causing further harm and disrupting their reproductive systems.
Not only does plastic consumption harm individual animals, but it also poses a threat to entire ecosystems. When an animal dies as a result of plastic ingestion, it can have a cascading effect on the food chain. Predators that rely on the abundance of prey can suffer from a decline in food availability, which can further impact other species and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem.
The impact of plastic pollution on wildlife is not limited to marine animals. Land animals, such as birds, can also be affected. Birds often mistake small plastic particles for food and feed them to their young, resulting in malnourished offspring. Plastic litter can also entangle animals, causing injuries and impairing their ability to hunt, fly, or escape from predators.
The long-term effects of plastic pollution on wildlife are still being researched, but it is clear that urgent action is needed to mitigate its impact. Efforts such as reducing plastic consumption, recycling, and clean-up campaigns are crucial in protecting and preserving our planet’s precious wildlife.
Animals that Accidentally Eat Plastic
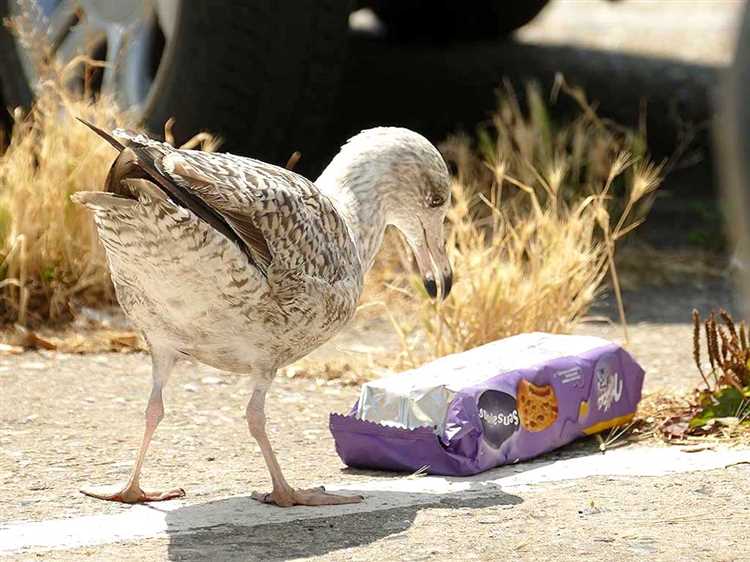

Plastic pollution is an alarming environmental issue that affects a wide range of animal species. Unfortunately, many animals inadvertently consume plastic, mistaking it for food or inadvertently consuming it along with their regular diet. This unintentional ingestion of plastic has detrimental effects on the health and well-being of these animals.
Marine animals, such as sea turtles, seabirds, and marine mammals, are particularly vulnerable to accidentally eating plastic. Sea turtles often mistake floating plastic bags for jellyfish, which is one of their primary food sources. The ingestion of plastic can lead to digestive blockages, malnutrition, and even death for these gentle creatures.
Seabirds also face significant consequences from accidentally ingesting plastic. They often feed on small fish or plankton near the water’s surface, where plastic debris is prevalent. Seabirds may swallow plastic particles or get entangled in plastic fishing nets, resulting in injuries or hindering their ability to find food.
In addition to marine animals, land animals are also at risk of inadvertently consuming plastic. For example, cows and sheep can mistakenly consume plastic wrappers or bags that contaminate their grazing areas. This can potentially lead to health issues, including gastrointestinal problems or blockages, affecting their overall well-being.
The impact of accidental plastic consumption on wildlife goes beyond individual animals. It can disrupt ecosystems and have cascading effects on entire food webs. Animals that accidentally eat plastic may suffer from reduced reproductive success or weakened immune systems, making them more susceptible to diseases. The presence of plastic in the environment also poses a threat to the health and survival of predators that rely on these affected animals as a food source.
Efforts to mitigate plastic pollution and its impact on wildlife are crucial. Awareness campaigns, waste management strategies, and the development of eco-friendly alternatives can help reduce the amount of plastic that enters the environment. By addressing this issue, we can protect not only animal species but also the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
The Consequences for Marine Creatures
Plastic pollution has become a major concern for marine creatures. With an estimated 8 million metric tons of plastic entering the oceans every year, many animals are unintentionally consuming this harmful material.
1. Ingestion
One of the primary consequences of plastic consumption for marine creatures is ingestion. Marine animals often mistake plastic debris for their natural prey and end up consuming them. This can lead to internal injuries, blockages in the digestive system, and even death.
2. Suffocation and entanglement
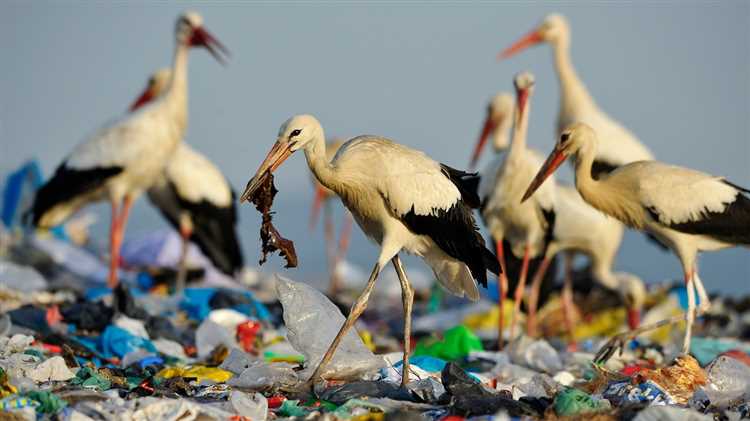

Marine creatures like turtles, seals, and dolphins can also become entangled in plastic waste, such as discarded fishing nets or plastic bags. This can restrict their movement, impair their ability to breathe, and cause drowning or suffocation.
3. Chemical exposure
Plastic debris in the oceans can release toxic chemicals such as bisphenol A (BPA) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). When marine creatures consume plastic, these chemicals can enter their bodies and accumulate over time. This can have detrimental effects on their reproductive systems, immune systems, and overall health.
4. Disrupted ecosystems
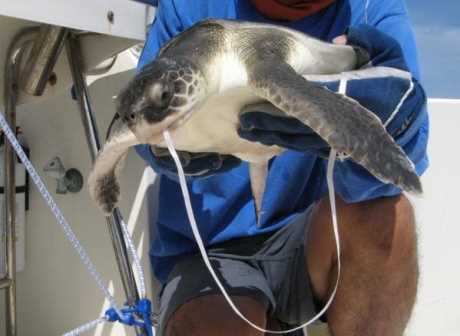
The impact of marine creatures inadvertently consuming plastic extends beyond individual animals. Plastic pollution can disrupt entire ecosystems. For example, when a predator consumes plastic-contaminated prey, the toxins can accumulate and move up the food chain, affecting other animals and potentially humans who rely on seafood as a source of sustenance.
In conclusion, the consequences of marine creatures inadvertently consuming plastic are far-reaching and pose significant threats to their well-being and the overall health of marine ecosystems. Urgent action is required to address the issue of plastic pollution and prevent further harm to these vulnerable creatures.
Q&A:
How does plastic consumption affect wildlife?
Plastic consumption has a detrimental impact on wildlife. When animals mistakenly ingest plastic, it can cause internal injuries, blockages, and even death. Additionally, plastics can release toxins when broken down, which can further harm the animal’s health.
Which animals are most affected by plastic consumption?
Many marine animals, such as sea turtles, dolphins, and seabirds, are greatly affected by plastic consumption. These animals often mistake floating plastic debris for food and consume it, leading to devastating consequences for their health and well-being.
Are land animals also at risk of consuming plastic?
Yes, land animals are also at risk of consuming plastic. For example, deer and other herbivores may accidentally eat plastic while foraging in areas where plastic waste is present. This can lead to digestive issues and other health problems.
Is there any solution to reduce plastic consumption by animals?
There are several solutions that can help reduce plastic consumption by animals. One approach is to reduce plastic waste by implementing effective recycling and waste management systems. Another solution is to raise awareness about the issue and promote responsible plastic disposal. Innovations in biodegradable plastics can also help minimize the impact of plastic on wildlife.